Ammonia Engine
US Senators Show Strong Interest in Ammonia-Fueled Shipping
The Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee, led by Chairman Lisa Murkowski (R-Alaska) and Ranking Member Joe Manchin (D-West Virginia), recently hosted a hearing on offshore energy technologies. I was invited to testify on technology and policy options for eliminating greenhouse gas emissions from the marine shipping sector, and I used the opportunity to spotlight ammonia's central role in that effort.
Picking bunker winners: the mono-fuel / dual-fuel duel
This week, DNV GL published its annual Maritime Forecast to 2050, concluding that “e-ammonia, blue ammonia and bio-methanol are the most promising carbon-neutral fuels in the long run.” DNV GL’s assumptions that determine this long run, however, suggest a significant mid-term reliance on fossil LNG. This risks locking the industry into a long-term emissions trajectory incompatible with the IMO’s 2050 GHG targets, in part because of significant fuel supply and infrastructure investments. These investments could become more ‘sticky’ than expected. A host of alternative opinions have been published in the days before and after DNV GL published its report. These suggest that, for ammonia, the long run could begin this decade. Among others, MAN ES has announced that its ammonia engine will be available for retrofits by 2025.
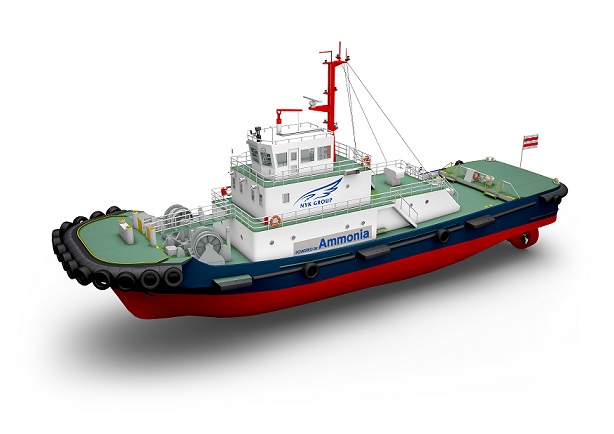
Japan's NYK and partners to develop ammonia fueled and fueling vessels
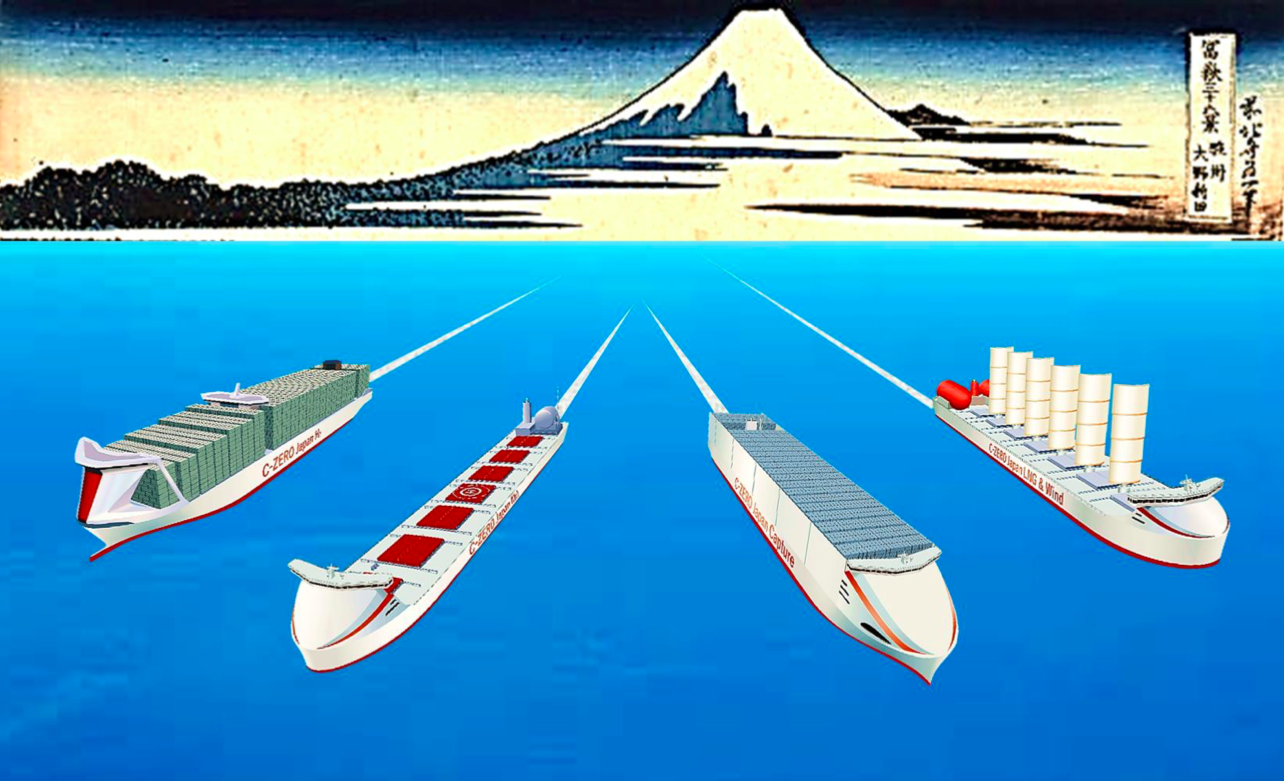
In recent weeks, the Japanese shipping company NYK Line has announced a series of high-profile research and development collaborations that aim to establish ammonia fueled vessels and fuel supply. Its partners in these projects include classification society Class NK, engine manufacturer IHI Power Systems, and shipbuilder Japan Marine United Corporation. Three vessel types have been announced, so far, including an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier, an ammonia barge for offshore bunkering, and an ammonia-fueled tugboat (for navigating the barge). Pushing beyond the initial research phase, these collaborations aim for commercialization and to put these vessels “into practical use.”
How to get approval of an ammonia fuelled vessel
Wärtsilä, Repsol, and Knutsen to test ammonia four-stroke engine
This week, engine manufacturer Wärtsilä announced “the world’s first long term, full-scale, testing of ammonia as a fuel in a marine four-stroke combustion engine.” The project will begin in the first quarter of 2021, at the Sustainable Energy Catapult Centre’s testing facilities at Stord, Norway. It is supported by a NOK 20 million (USD 2 million) grant from the Norwegian Research Council.
Maersk and partners launch Center for Zero Carbon Shipping
This morning, the Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping was announced. Launched with a “start-up donation” of DKK 400 million (USD 60 million) from the A.P. Møller Foundation, this new research institute intends “to develop new fuel types and technologies,” to decarbonize the maritime sector. Behind the Center for Zero Carbon Shipping is a significant industrial consortium with seven founding members (actively seeking additional partners): ABS, A.P. Moller – Maersk, Cargill, MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, NYK Lines, and Siemens Energy.
Maritime Ammonia: ready for demonstration
At least four major maritime ammonia projects have been announced in the last few weeks, each of which aims to demonstrate an ammonia-fueled vessel operating at sea. In Norway, Color Fantasy, the world's largest RORO cruise liner, will pilot ammonia fuel. Across the broader Nordic region, the Global Maritime Forum has launched NoGAPS, a major consortium that aims to deploy "the world's first ammonia powered deep sea vessel" by 2025. In Japan, a new industry consortium has launched that goes beyond on-board ship technology to include "owning and operating the ships, supplying ammonia fuel and developing ammonia supply facilities." And the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), which published its roadmap last month, aims to demonstrate ammonia fuel on "an actual ship from 2028" — specifically, a 80,000 dwt ammonia-fueled bulk carrier.
Wärtsilä Tests Internal Combustion of Ammonia
Last week Wärtsilä, the Finnish engine and energy equipment manufacturer, unveiled the latest stage in its engagement with ammonia as an energy vector. In a press release headlined “Wärtsilä advances future fuel capabilities with first ammonia tests,” the company described a test program aimed at exploring ammonia’s properties as an internal combustion fuel. Kaj Portin, General Manager of Fuel & Operational Flexibility in Wärtsilä’s Marine division, commented that “the first tests have yielded promising results.”