New IEA report: using low-carbon ammonia to decarbonise power
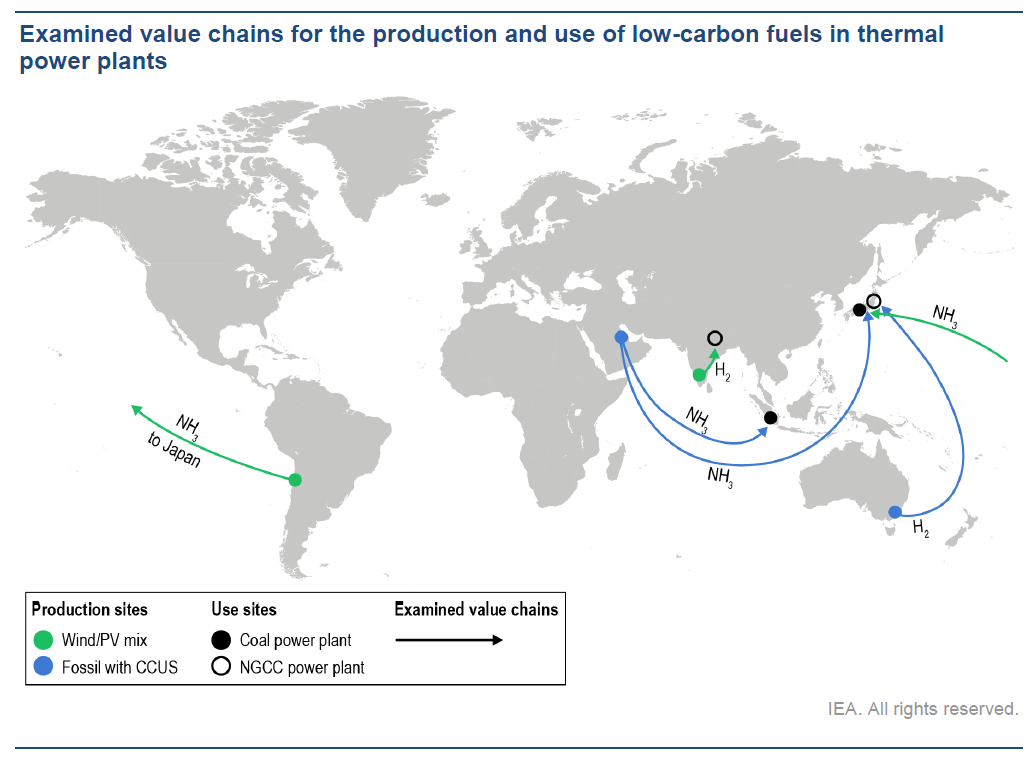
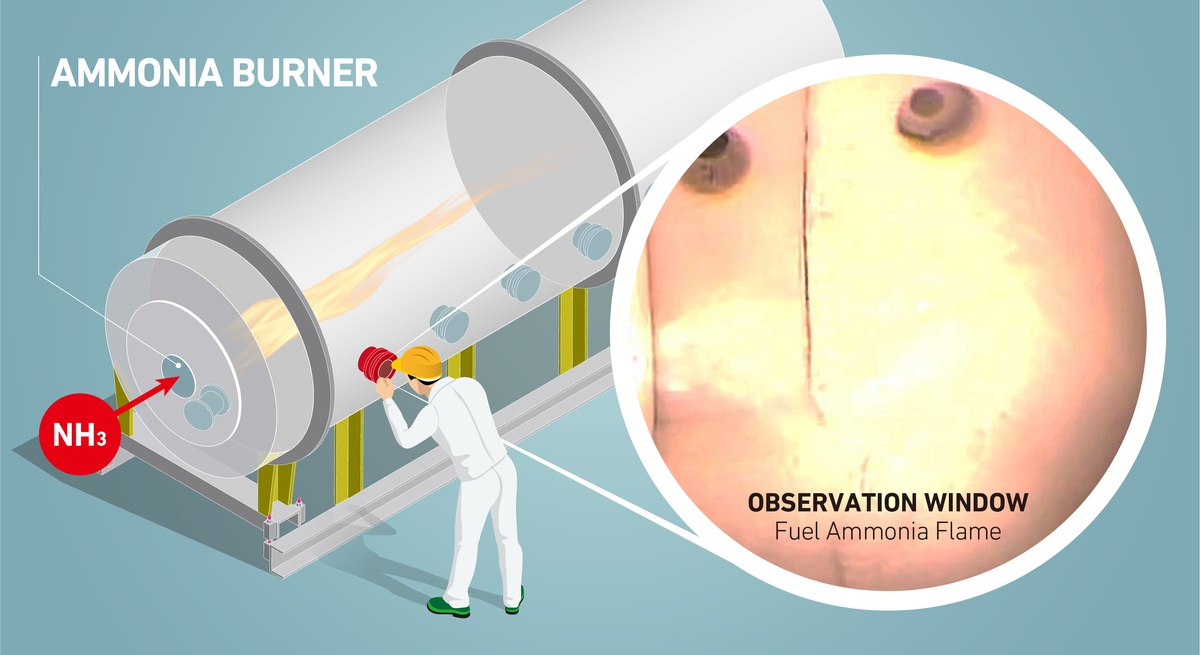
The Role of Low-Carbon Fuels in the Clean Energy Transitions of the Power Sector forecasts a significant role for low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia in decarbonising the power sector, and highlights the promising results of co-firing trials to date (both coal power plants and gas turbines). The report also outlines some key next steps to enable the widespread use of these low-carbon fuels.