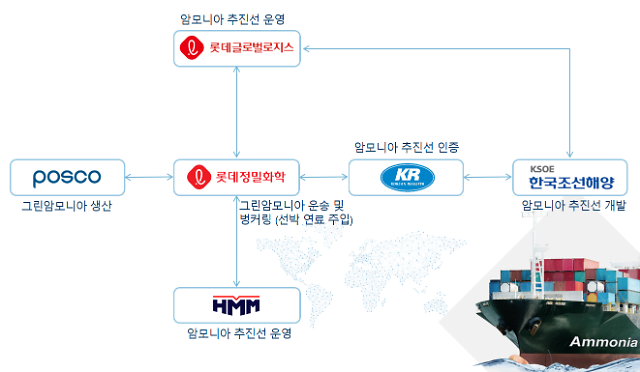
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE, RWE, BASF combine for 2 GW "Offshore-to-X" project, green ammonia exports from Tasmania, coal co-combustion trials in Japan, Japanese shipping industry chases decarbonisation, South Korean companies join together in local green ammonia consortium, new funding for ammonia-from-wastewater research and Horisont Energi and Equinor join forces for the Polaris project.