Electrochemical Ammonia
Nitrogenase Inspired Peptide-Functionalized Catalyst for Efficient, Emission-Free Ammonia Production
Future of Ammonia Production: Improvement of Haber-Bosch Process or Electrochemical Synthesis?
Comprehensive Evaluation of NH3 Production and Utilization Options for Clean Energy Applications
254th ACS Meeting, Energy and Fuels Symposium “The Ammonia Economy” — Synthesis, Utilization & Nitrogen Reduction
In late August, the day before the exciting solar eclipse, the Ammonia Economy symposium was held as part of the Energy and Fuels Division of the American Chemical Society (ACS) National Meeting in Washington DC. This marks the third gathering of Ammonia related research since 2015 at the national level ACS conference. This year, in addition to the important focus on chemistries for the utilization of ammonia, the rapidly developing field of homogeneous catalysts and biological processes for nitrogen fixation was included as a major theme.
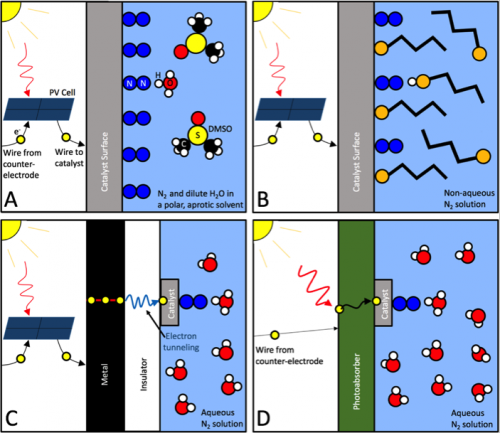
Overcoming the Selectivity Challenge in Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis
In the last 12 months ... The research community has made great progress toward solving the "selectivity challenge" in electrochemical ammonia synthesis. Although, rather than an actual solution, mostly what we have is a range of sophisticated work-arounds that succeed in making this problem moot.
High Efficiency Electrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia from Nitrogen at Ambient Temperature and Pressure
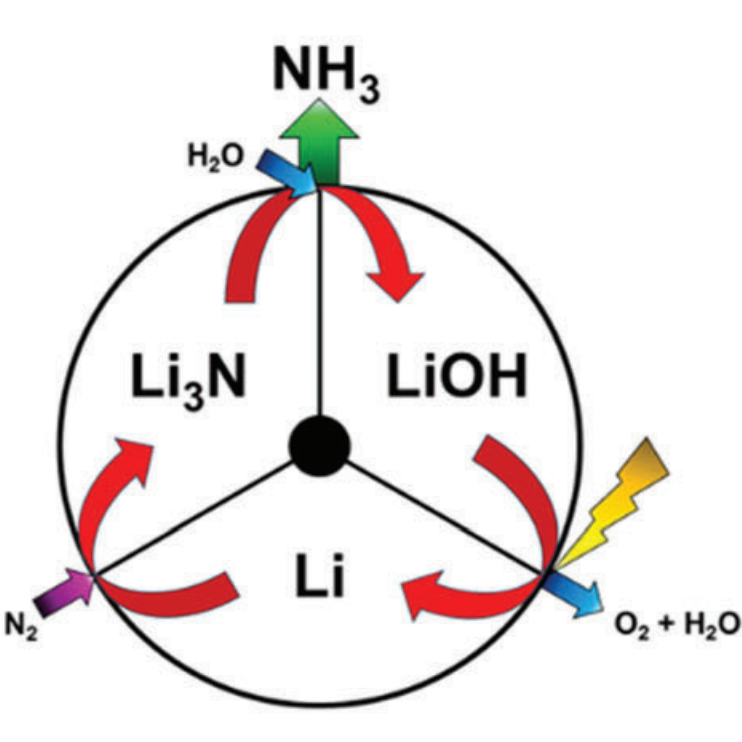
Sustainable ammonia synthesis: SUNCAT's lithium-cycling strategy
New research coming out of Stanford University suggests a fascinating new direction for electrochemical ammonia synthesis technology development. The US-Danish team of scientists at SUNCAT, tasked with finding new catalysts for electrochemical ammonia production, saw that 'selectivity' posed a tremendous challenge - in other words, most of the energy used by renewable ammonia production systems went into making hydrogen instead of making ammonia. The new SUNCAT solution does not overcome this selectivity challenge. It doesn't even try. Instead, these researchers have avoided the problem completely.
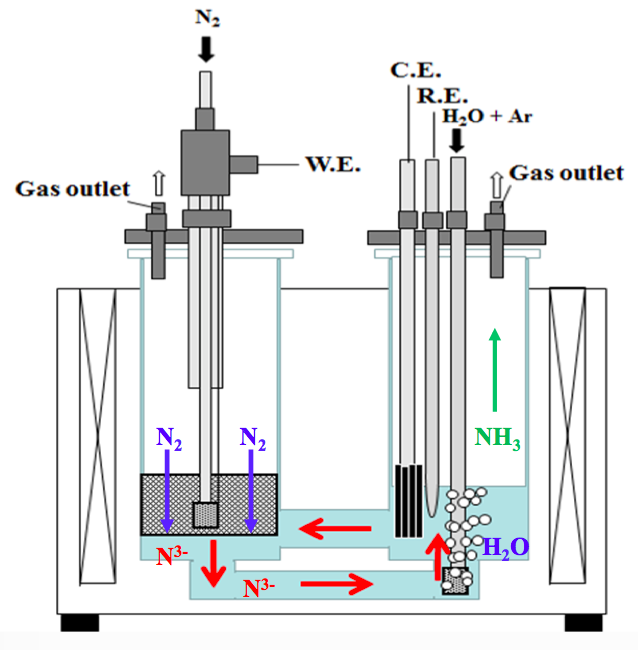
Electrochemical ammonia synthesis in South Korea
One of the many encouraging announcements at the recent Power-to-Ammonia conference in Rotterdam was the news that the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has extended funding for its electrochemical ammonia synthesis research program by another three years, pushing the project forward through 2019. KIER's research target for 2019 is significant: to demonstrate an ammonia production rate of 1x10-7 mol/s·cm2. If the KIER team can hit this target, not only would it be ten thousand times better than their 2012 results but, according to the numbers I'll provide below, it would be the closest an electrochemical ammonia synthesis technology has come to being commercially competitive.
On the Ground in Germany
Yet another national laboratory is developing technology for renewable ammonia, this time in Germany at the DLR, the German Aerospace Center. At the Institute of Thermodynamic Engineering, the DLR is developing a method for electrochemical ammonia synthesis at ambient conditions.