In a national address, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced that the new National Hydrogen Mission would be a key pillar of his government's plan for India to achieve energy independence within 25 years. The plan would mean would mean India produces around 1.3 million tonnes of green ammonia by the end of the decade, requiring several GW of dedicated electrolysers to supply the necessary green hydrogen.
Electrolysis
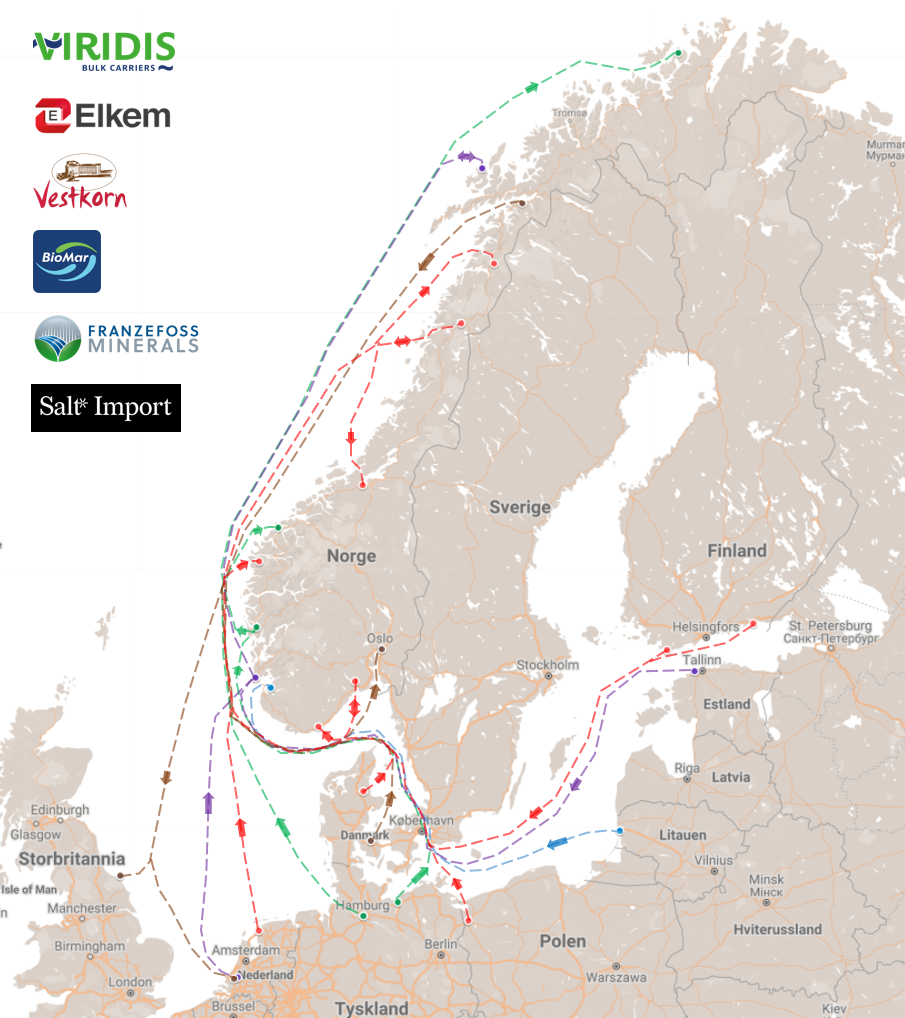
The Ammonia Wrap: an ammonia-powered shipping network in northern Europe and more
This week: an ammonia-powered shipping network in northern Europe, Sluiskil update, green projects in Uruguay, green ammonia in Ireland: a new update!, Euronav to develop ammonia-powered tankers, ammonia part of Equinor's net-zero by 2050 strategy, H2Site to install first on-site crackers in France and updates from Australia.
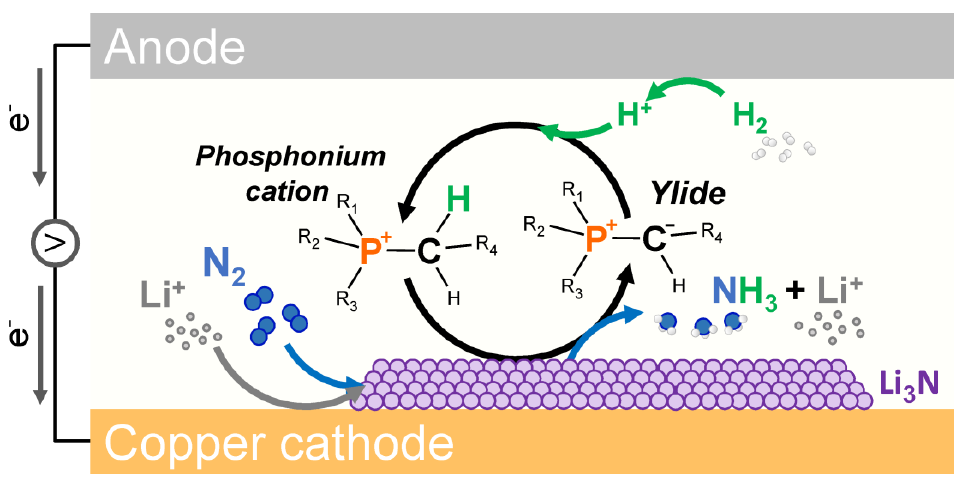
The Ammonia Academic Wrap: a new breakthrough for eNRR research and more
This week: a new breakthrough for eNRR research, ammonia production from food waste and brown-water, the huge potential of green ammonia production from hybrid solar-wind across the globe, predicted cost dynamics of electrolyser technology, and hydrogen production using selective ion membranes.
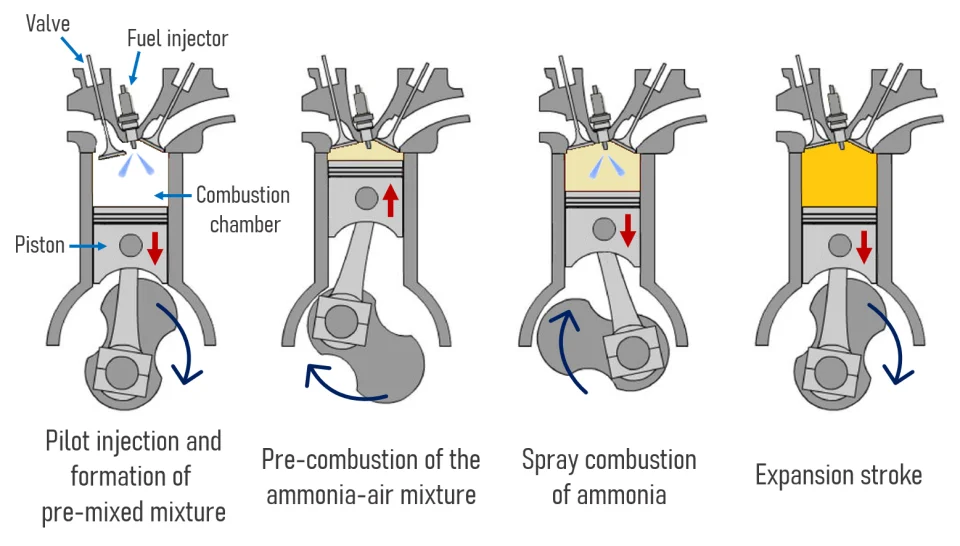
The Ammonia Wrap: green bunker fuel hub planned for the Baltic Sea
News this week: future green bunker fuel hub planned for Bornholm, more Haldor Topsoe news, Australia partners up, 23 key players kick-off ammonia maritime fuel study, $100 billion hydro-hydrogen and ammonia in the DR Congo, Egypt planning $4 billion green hydrogen project, AP Ventures leads investment in Amogy, full steam ahead for MS Green Ammonia, new blue ammonia plant in Canada and new engineering contracts signed for key blue ammonia projects.
The Ammonia Wrap: 30 GW Power-to-X project in Mauritania and more
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: a 30 GW Power-to-X project in Mauritania, green hydrogen and ammonia in Egypt, €8 billion for 62 hydrogen projects in Germany, Cummins' electrolyser gigafactory in Spain, Ammonia engine development in Portugal and Shchekinoazot gets a new decarbonisation partner.
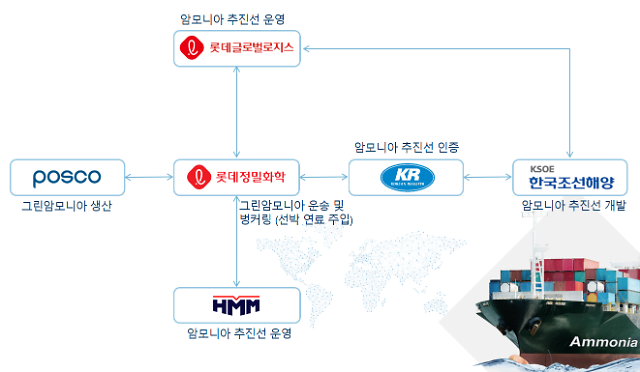
The Ammonia Wrap: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE and more
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE, RWE, BASF combine for 2 GW "Offshore-to-X" project, green ammonia exports from Tasmania, coal co-combustion trials in Japan, Japanese shipping industry chases decarbonisation, South Korean companies join together in local green ammonia consortium, new funding for ammonia-from-wastewater research and Horisont Energi and Equinor join forces for the Polaris project.
The Ammonia Wrap: ICE announces its new green ammonia "SuperGiant", Cummins and KBR team up on integrated solutions, a new green ammonia pilot in Minnesota and decarbonisation of existing plants in Russia
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. There's so much news this edition that we're bringing you two, special Wrap articles. Our first focuses on ammonia production - both existing and new build plants. This week: InterContinental Energy to build 25 GW of green ammonia production in Oman, Cummins and KBR to collaborate on integrated green ammonia solutions, New green ammonia pilot plant for Minnesota, Stamicarbon launches new technology for sustainable fertilizer production in Kenya, Haldor Topsoe and Shchekinoazot to explore ammonia plant decarbonisation in Russia, 1 million tonne blue ammonia per year in Norway and Trammo announces off-take MoU for 2GW AustriaEnergy plant in Chile.
The Ammonia Academic Wrap: "seamless" cracking, improving Haber Bosch, a novel green power-to-ammonia-to-power solution and a review into the use of ammonia as a fuel
Welcome to the Ammonia Academic Wrap: a summary of all the latest papers, developments and emerging trends in the world of ammonia energy R&D. This week: "seamless" ammonia cracking tech from Northwestern, a new electrolysis catalyst, successful integration of ammonia synthesis and separation for improved efficiency, more research needed into transition metal catalysts for Haber Bosch, a novel, green power-to-ammonia to power system and a review on ammonia as a potential fuel.
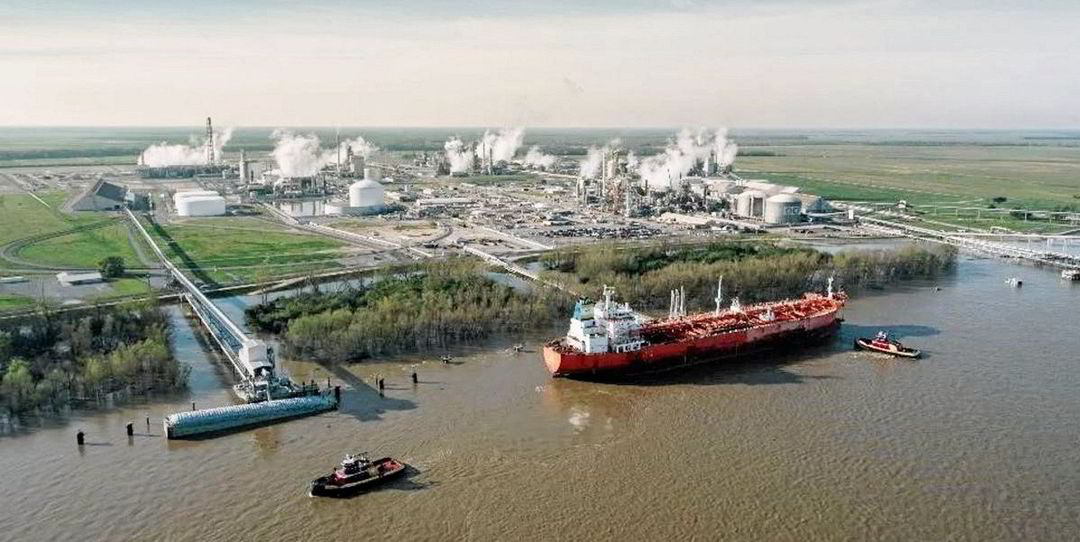
The Ammonia Wrap: world's largest ammonia manufacturing complex begins decarbonising, and a welcome boost for EU fertiliser producers
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: the world's largest ammonia manufacturing complex begins decarbonising, a call for green hydrogen projects in Chile, new maritime decarbonisation forecast from MAN ES, decarbonised shipping at the Biden climate summit and Fertilizers Europe welcomes the new Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism.