The Ammonia Wrap: Ørsted's P2X vision for the North Sea, Gunvor's new sustainability commitments, the finance world backs green hydrogen and Hydrofuel-Ontario Tech's new partnership
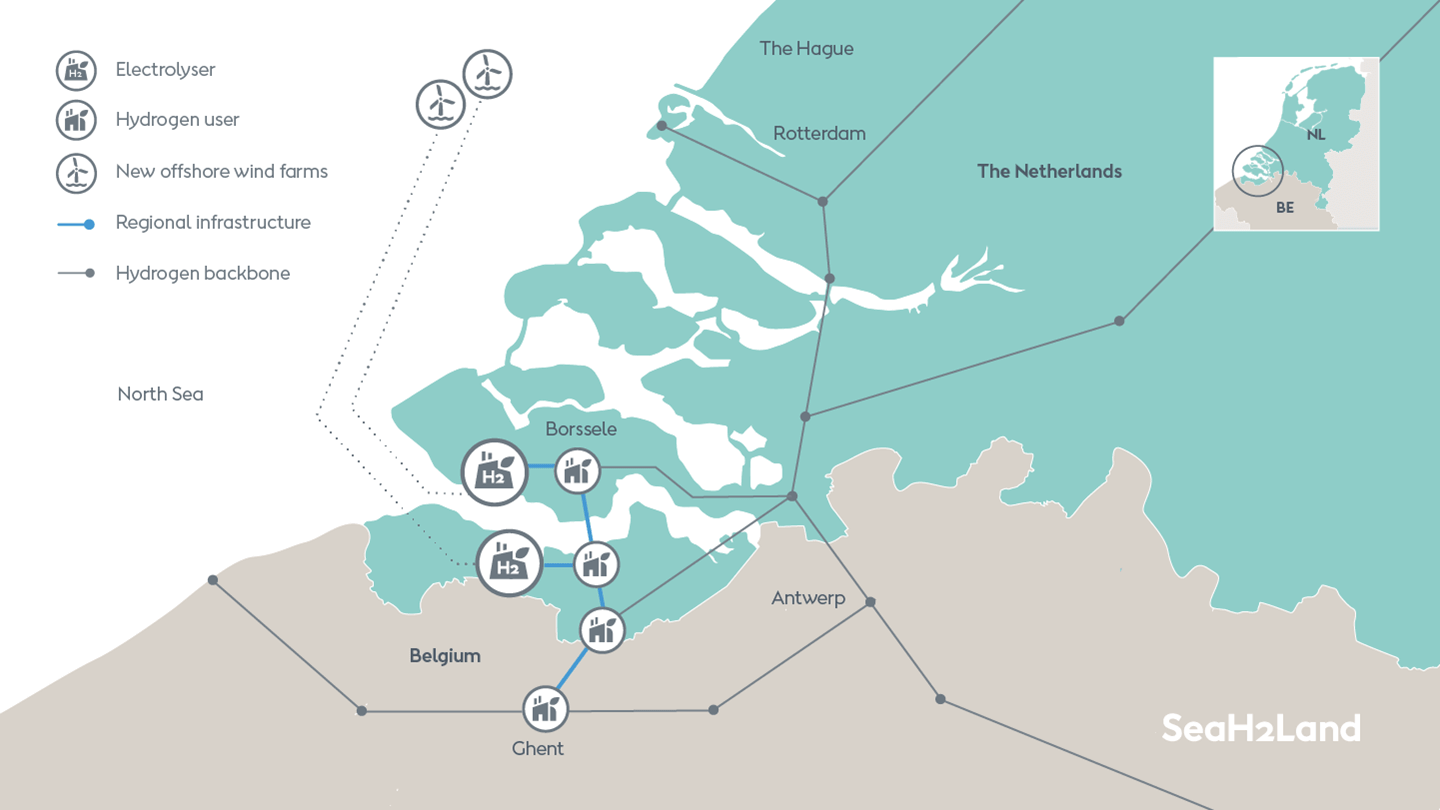
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: Ørsted unveils its P2X vision for the North Sea, energy trader Gunvor commits $500 million to sustainability, emissions reductions, finance world backs green hydrogen, Hydrofuel and Ontario Tech join forces and a new blue hydrogen/ammonia collaboration.