Emissions Testing
Everllence B&W ME-LGIA: Powering the future with our two-stroke ammonia engine
WinGD Dual-fuel Ammonia Engine
Foshan Xianhu Laboratory & partners: new ammonia-fueled, zero-carbon aluminium furnace unveiled in China
Foshan Xianhu Laboratory and its collaborators have unveiled a new ammonia-fueled aluminium rod furnace, replacing a conventional, gas-powered multi-bar furnace in the production process.
J-ENG: testing complete, 2-stroke ammonia engine ready to roll out
Japan Engine Corporation has announced commercial readiness for its new 2-stroke, dual-fuel engine. The first engine unit will be installed on an ammonia-fueled medium gas carrier next month, with the vessel scheduled to enter service in 2026.
Global Maritime Forum: alternative fuels rapidly progressing to commercial deployment
GMF’s new report finds that both ammonia and methanol fuels are now “ready” for commercial deployment, but a concerted push is required to enable scale-up beyond 2030. The report highlights the increased familiarity (and confidence) from key maritime stakeholders with ammonia fuel, and a recommendation to independently verify emissions from the first ammonia-fueled vessels.
Ammonia bunkering: moving from demonstrations to operations
In our recent episode of Project Features, we explored the outcomes from a recent ammonia bunkering demonstration at the Port of Rotterdam. With twelve ammonia transfer and bunkering demonstrations occurring in nine global locations since 2024, where does the Port Readiness Level for ammonia bunkering stand in Rotterdam and elsewhere, what are the key technical learnings, and what gaps remain?
Ammonigy, Heraeus: successful four-stroke engine demonstration
Ammonigy, Heraeus Precious Metals and the Technical University of Darmstadt have partnered to demonstrate operations using cracked ammonia fuel in a four-stroke MAN test engine. The performance and efficiency of the test engine when running on ammonia-hydrogen fuel was comparable to natural gas operations, and use of an exhaust aftertreatment system reduced potentially harmful nitrogen-based emissions to near-zero levels.
Azane and Ofiniti: digitalisation of ammonia bunkering
Azane Fuel Solutions and Ofiniti will partner to build a digital delivery service for Azane’s planned network of ammonia bunkering facilities across Scandinavia.
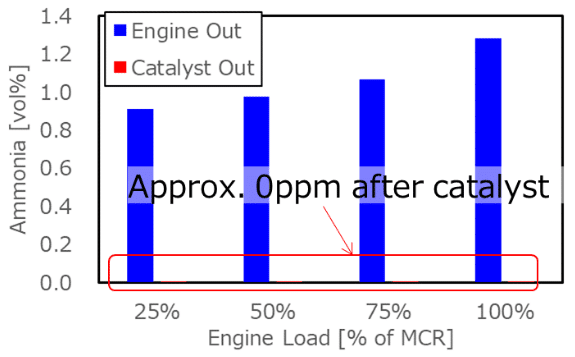
Emission performance of ammonia-fueled, four-stroke marine engines
We explore recent, full-scale, four-stroke engine testing results from IHI and Wärtsilä. Testing indicates N2O emissions can be almost fully eliminated with catalytic treatment, and significantly lower NOX emissions for engines running in ammonia mode, compared to running on diesel. While ammonia slip remains a key consideration due to the design of a four-stroke engine, catalytic treatment of the exhaust can eliminate even high concentrations, and release mitigation systems have already been designed and deployed to ensure safe operations.