N-Fuels vs. C-Fuels: Nitrogen “superior” to carbon as a hydrogen carrier
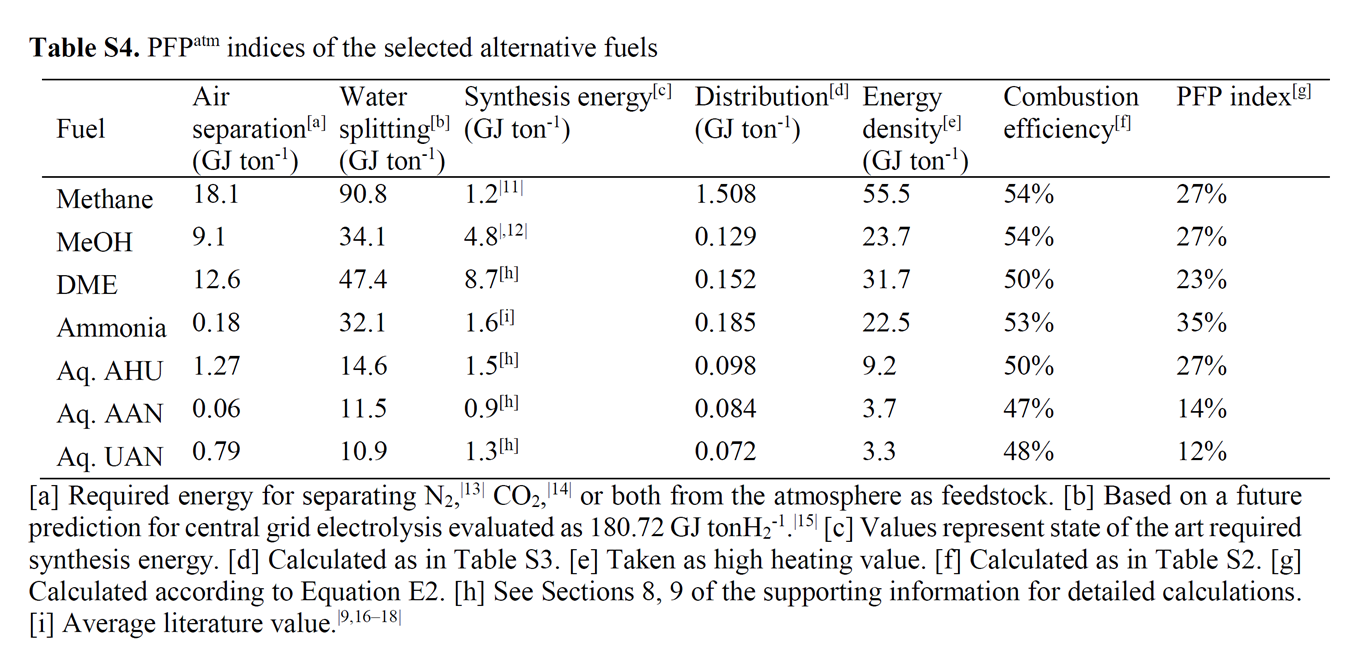
Gideon Grader, a Faculty Dean at Technion Israel Institute of Technology, and Bar Mosevitzky, one of the members of his laboratory, spoke in separate talks at the NH3 Energy + Topical Conference about one of the Grader Research Group’s key focuses: nitrogen-based energy carriers. Grader and his team champion the idea that ammonia can be the starting rather than ending point for nitrogen-containing fuels for heat engines. The focuses of their research include ammonium hydroxide ammonium nitrate (AAN), ammonium hydroxide urea (AHU), and urea ammonium nitrate (UAN). As described below, this work is an indispensable addition to the C-fuel vs. N-fuel debate well known to proponents of ammonia energy. And the Grader team stakes out a position: per the abstract of Grader’s talk, “using nitrogen as a hydrogen carrier can potentially offer a superior option.”