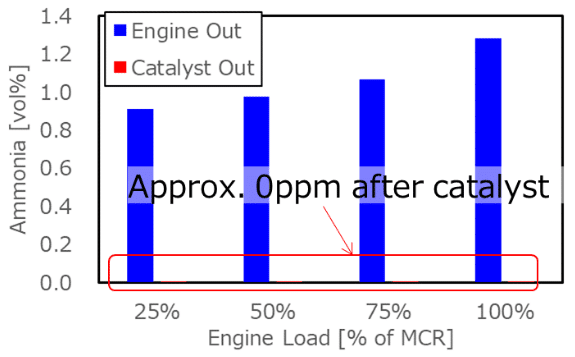
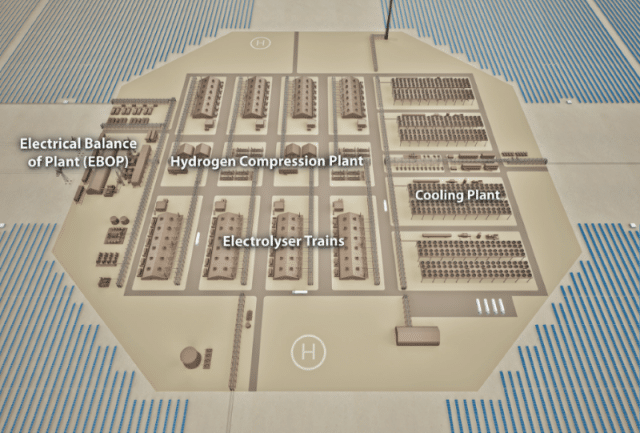
Envision & KBR: AI optimized ammonia production
Envision Energy has released further details about its AI architecture, with two “foundation models” working in tandem to optimize renewable energy inputs for ammonia production, potentially unlocking millions of tons of production potential in China. Meanwhile, KBR and UK-based Applied Computing will combine AI capabilities with an existing digital control platform, allowing users to optimize operations.