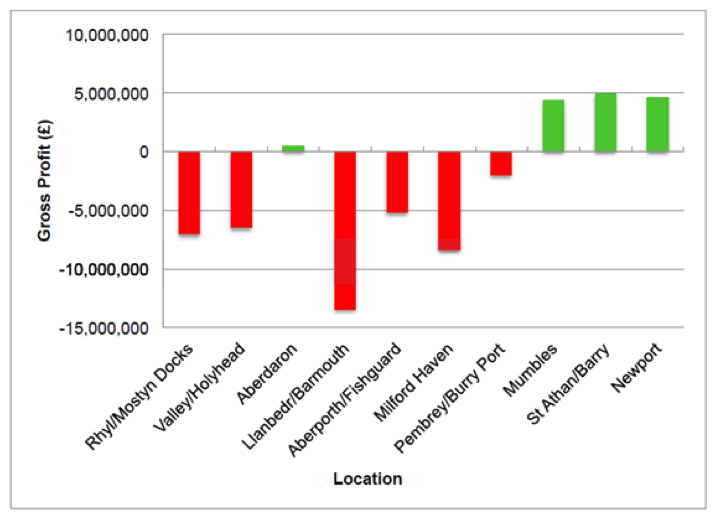
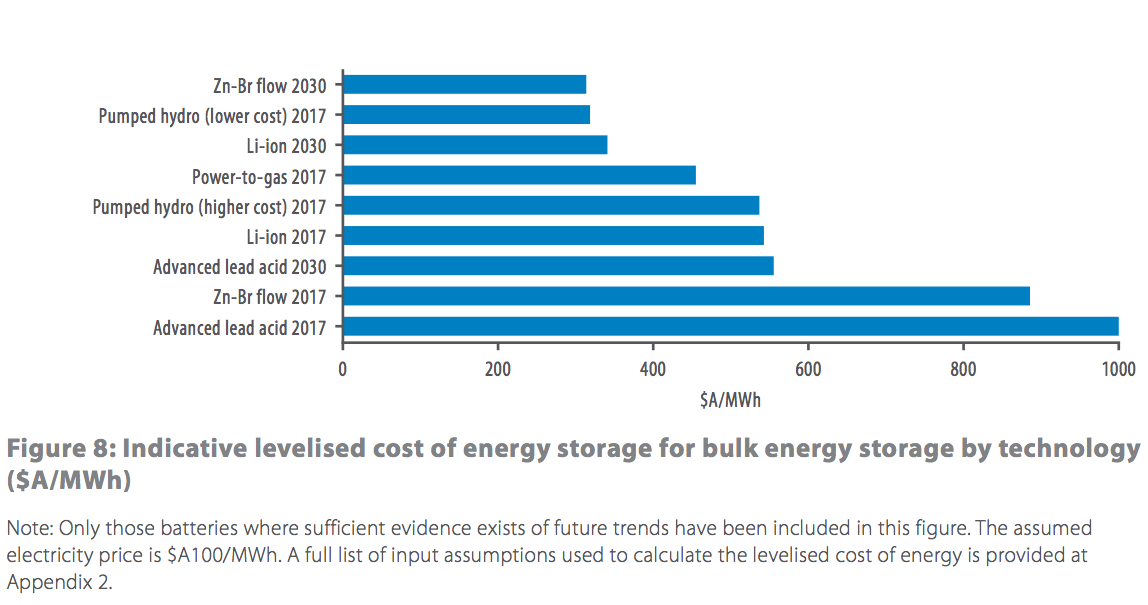
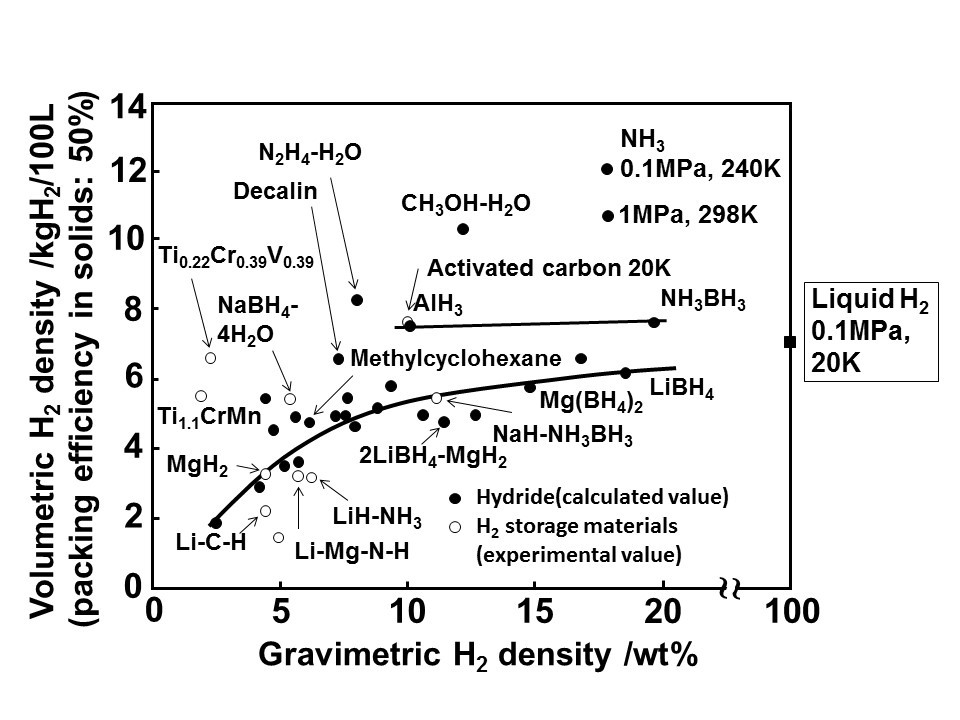
A new report from Australia identifies ammonia as a key part of a hydrogen-based high-volume energy storage system. On November 20, Australia’s Council of Learned Academies (ACOLA) and its Chief Scientist released “The Role of Energy Storage in Australia’s Future Energy Supply Mix.” In addition to hydrogen, the report covers pumped hydro, batteries, compressed air, and thermal systems. Its rationale for including ammonia is starkly simple: “Hydrogen gas is difficult to transport due to its low density; instead, it is proposed that hydrogen is converted to ammonia for transport, and then converted back to hydrogen for use.” Although an ultimate ranking of energy storage options is not provided, the hydrogen-ammonia combination arguably emerges as the best option in terms of economics, environmental and social impact, and deployability.