Fuel Cells
The Ammonia Academic Wrap: a new breakthrough for eNRR research and more
This week: a new breakthrough for eNRR research, ammonia production from food waste and brown-water, the huge potential of green ammonia production from hybrid solar-wind across the globe, predicted cost dynamics of electrolyser technology, and hydrogen production using selective ion membranes.
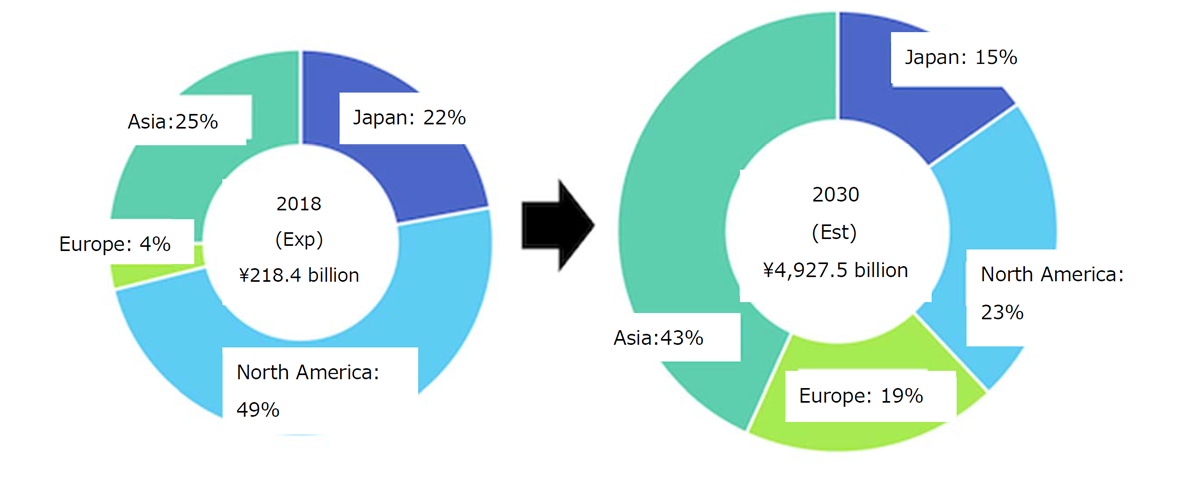
Rapid Long-Term Growth Projected for Fuel Cells
Last month the Fuji-Keizai Group released its latest biennial review of the global market for fuel cells, “Future Outlook for Fuel Cell-Related Technology and Market in 2018.” This is at least the third iteration of the report, and comparison across the different editions shows how expectations have evolved. The report features both polymer electrolyte and solid oxide fuel cells. Although not mentioned in the report, a number of groups are working on direct ammonia versions of both technologies.
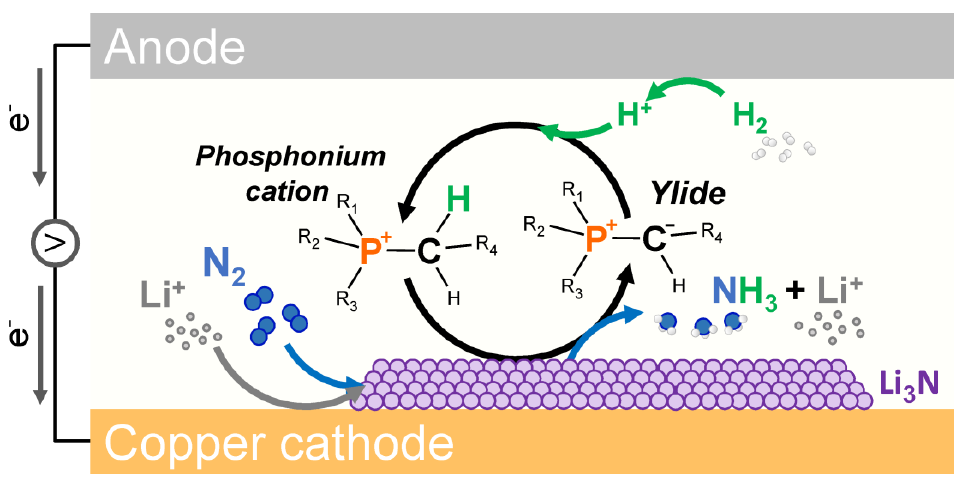
Catalytic Membrane Reactors for Efficient Delivery of High Purity Hydrogen from Ammonia Decomposition
Ammonia as a Renewable Fuel for the Maritime Industry
Last week, I wrote about a crucial new report that discusses four fuel technologies: batteries, hydrogen, ammonia, and nuclear. These could reduce the shipping sector's emissions in line with targets set in the IMO's Initial GHG Strategy. The report, Reducing CO2 Emissions to Zero, concludes that "all industry stakeholders ... need to get on with the job of developing zero CO2 fuels." This call to action should be consequential: it comes from the International Chamber of Shipping, an influential industry group that represents "more than 80% of the world merchant fleet." This week, I provide an example of the kind of research required, with an update on a project that aims to demonstrate "the technical feasibility and cost effectiveness of an ammonia tanker fueled by its own cargo." Although this project is still in its early days, I want to highlight three aspects that I believe will be crucial to its success. First, the work is being done by a consortium, bringing together many industry stakeholders, each with its own expertise and commercial interests. Second, the scope of research extends beyond conventional engine configurations to include not just new fuels but also new technology combinations; in other words, rather than assess new fuels in old engines, it aims to develop optimized propulsion designs for zero-emission fuels. And, third, its consideration of ammonia as a fuel begins with a comprehensive safety analysis.
The new generation of fuel cells: fast, furious, and flexible
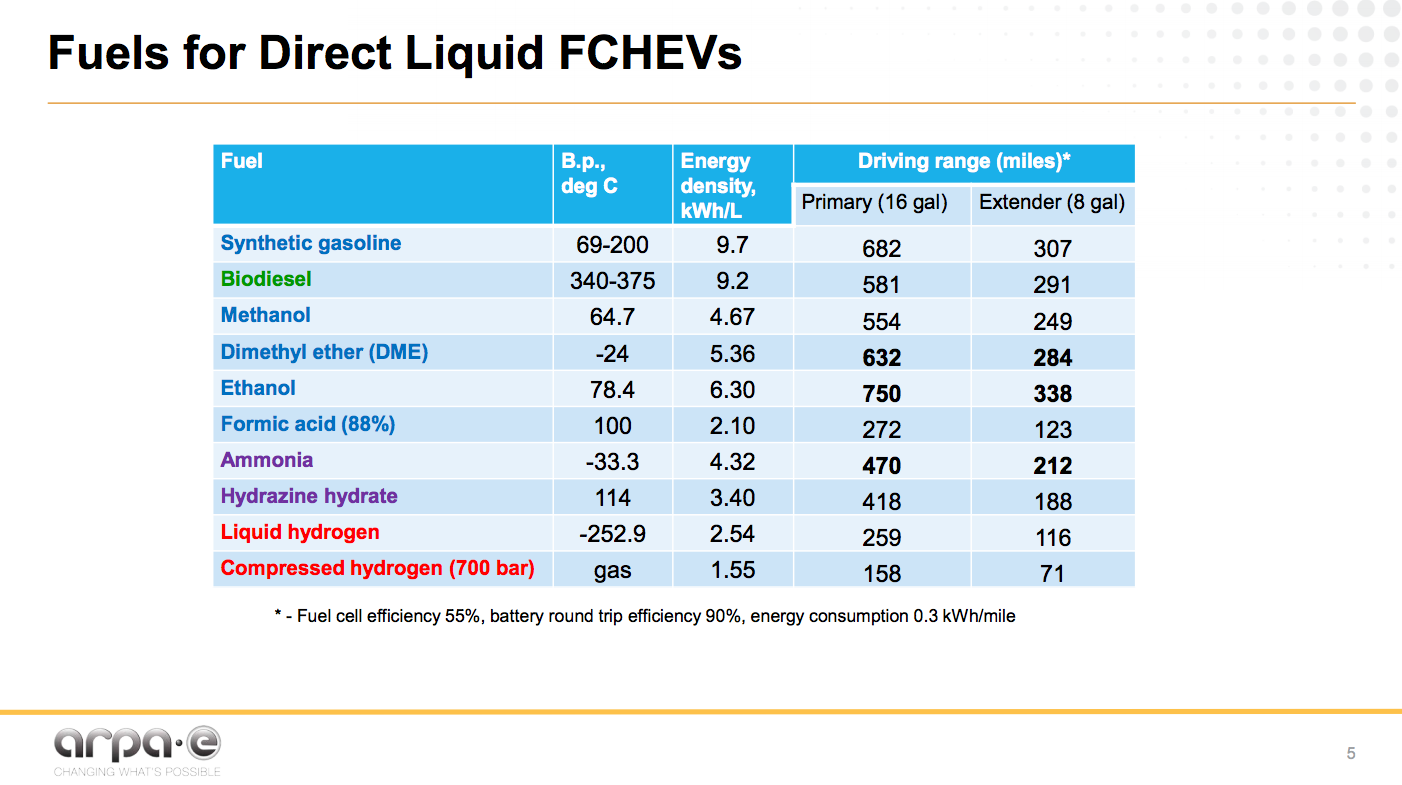
At ARPA-E's recent Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, DC, Program Director Grigorii Soloveichik presented his vision for the future of transportation: hybrid electric vehicles that combine the advantages of both plug-in battery and fuel cell technologies. This "optimal solution" will require a new generation of fuel cell that is "fast, furious, and flexible." Fast, in terms of start-up / shut-down time. Furious, in terms of energy density. And flexible, in terms of fuel choice - specifically sustainable liquid fuels, like ammonia.