Low-carbon Fertilizers
Low and zero-carbon fertilizers in Europe
Meet Yara and Fertilizers Europe, two organisations currently exploring the potential for renewable fertilizer in Europe.
Brazil’s first electrolysis-based ammonia plant takes shape
Brazil’s largest fertiliser producer Unigel has launched the country’s first industrial-scale electrolytic hydrogen & ammonia project. 60 MW of grid-connected, thyssenkrupp nucera electrolysers will feed the production 60,000 tonnes per year of ammonia. An existing ammonia production plant in Camaçari, Bahia province will provide the foundation for the project, which seeks to leverage the high share of renewable electricity in Brazil’s national grid. In other South American news, Uruguay’s officially-released Green Hydrogen Roadmap sets out ambitious decarbonisation goals. Green ammonia has a role both as an export commodity and for domestic use.
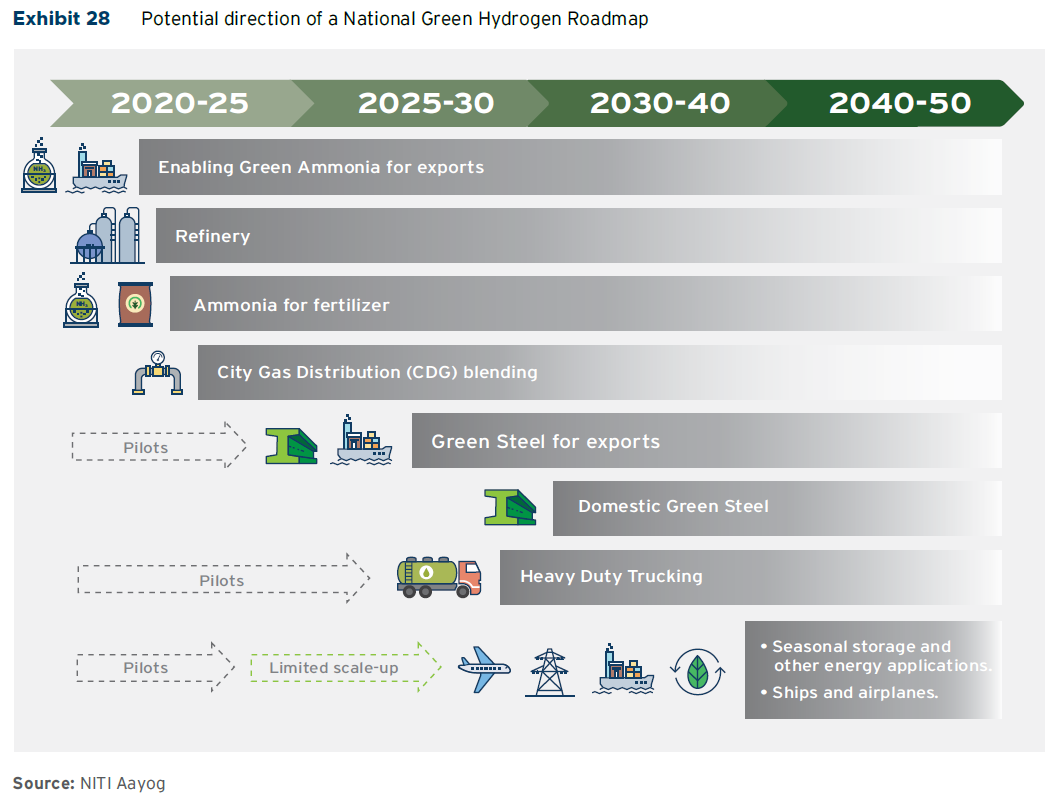
Harnessing opportunities for deep decarbonisation in India: new report
A new report from Indian government think-tank NITI Aayog and the Rocky Mountain Institute has outlined the enormous opportunity for India to produce renewable hydrogen & ammonia. Ammonia establishes itself early as a key part of this transition: both via the use of renewable hydrogen for fertiliser production, and as a near-term export vector. The report envisions 160 GW of installed electrolysers by 2030, of which nearly 100 GW could be dedicated to producing ammonia. This would make India one of the world’s largest producers of renewable ammonia for export by the end of the decade.
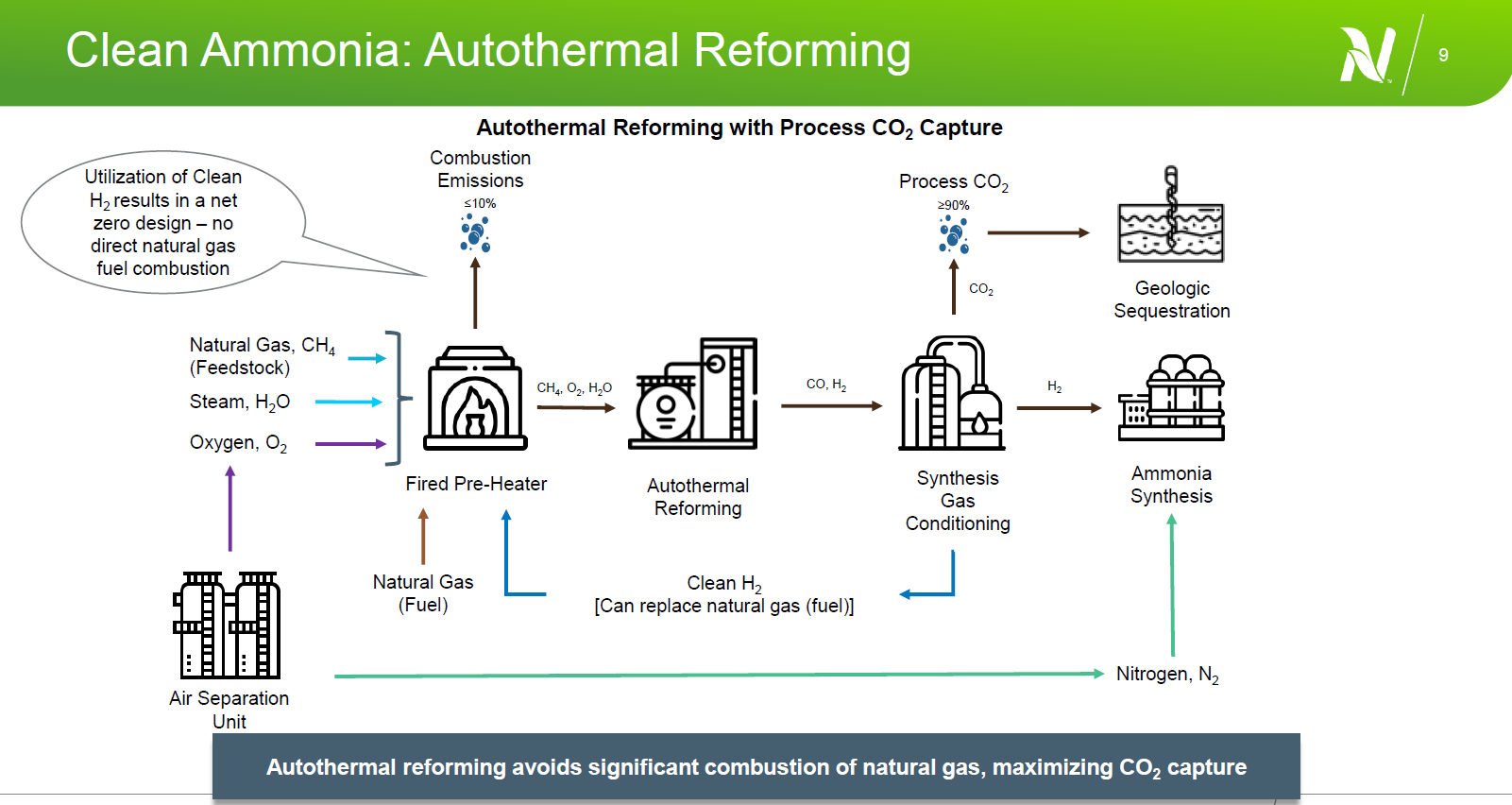
Decarbonizing fossil-based ammonia production in North America
Our latest Ammonia Project Features webinar focused on various pathways for decarbonizing fossil-based ammonia production in North America. Blake Adair from Nutrien took us on a tour of some of his organisation’s existing low-carbon ammonia production facilities. He also explained how the technology solutions already exist to drive down emissions from hydrogen production, and improve rates of carbon capture. Dr. Amgad Elgowainy from Argonne National Laboratories then presented his team’s analysis of carbon dioxide mitigation costs for ammonia production, noting that current federal incentives for CCS projects already have a material impact on project costs. With incentives in place and mature technology available, we will soon see more low-carbon ammonia production projects emerge in North America.
TotalEnergies and Adani join forces on renewable hydrogen in India
TotalEnergies will acquire a 25% stake in Adani New Industries Limited (ANIL), with ANIL to act as the “exclusive platform” for Total and Adani to produce and commercialise renewable hydrogen in India. Together the pair have set ambitious targets: 1 million tonnes renewable hydrogen production per year and 30 GW of new renewable generating capacity by 2030. The first project in focus will be a 1.3 million tonne per year urea plant to displace current fertiliser imports.
New ammonia partnerships in Japan, Indonesia
JGC Corporation has entered into a series of new ammonia partnerships. As part of a wider agreement to license KBR’s patented ammonia production technology, a new renewable ammonia pilot plant will be developed near Fukushima. JGC will team up in an “alliance agreement” with TOYO Corporation to develop fuel ammonia production projects and import terminals in Japan. And in Indonesia - where TOYO is currently assessing the feasibility of retrofitting an existing ammonia plant to run entirely on renewable energy - JGC and Indonesia’s national energy organisation Pertamina will collaborate on key decarbonisation projects.
Low-carbon ammonia in North America
Join Nutrien and Argonne National Laboratory to explore the landscape of low-carbon ammonia in North America. Our speakers explore projects under-development, LCA considerations and the technologies on offer to bring low-carbon ammonia to life.
DECHEMA and Fertilizers Europe: decarbonizing ammonia production up to 2030
DECHEMA and Fertilizers Europe recently released a new report detailing how & where the European fertilizer industry can decarbonize leading up to 2030. Technology options for CO2-emission reduction of hydrogen feedstock in ammonia production explores decarbonization pathways including energy efficiency improvements, carbon capture & sequestration, renewable hydrogen feedstock and grid-based electrolysis. It proposes a detailed roadmap towards 19% emissions reduction from the EU fertilizer industry by 2030, and – looking ahead to 2050 – forecasts the almost complete decarbonization of the industry, via zero-carbon electricity generation in the EU and the growth of renewable hydrogen production. With the right policy & regulatory levers in place, Fertilizers Europe believes there is no reason the transition cannot happen faster.