Maritime Fuel
Maritime actors push on with overcoming ammonia fuel safety concerns
Two recent reports (one from Bureau Veritas & Total, the other from the Together in Safety consortium) illustrate just how seriously the maritime industry is pursuing low carbon ammonia fuel. While progress in the maritime ammonia space is impressive, safety risks are widely-acknowledged and work remains to be done.
Both reports identify key hazards facing adoption of ammonia as a maritime fuel, and echo points heard before in the development of methanol & LNG as maritime fuels: high-risk hazards currently exist that must be eliminated, mitigated or controlled. But Together in Safety concludes the way forward will be via collaboration & shared responsibility - something we’re already seeing in the multiple high-profile safety studies and consortia working around the globe. Thankfully, the willingness of significant maritime players to engage on ammonia and the momentum for change are both high.
AmmoniaDrive
The University of Amsterdam and TU Delft will lead an academic-industry consortium that will determine the feasibility of combining ammonia-fed solid-oxide fuel cells with internal combustion engines for maritime propulsion. The AmmoniaDrive project just received over €2 million in support from the Dutch government, and is the latest in a series of hybrid and fuel cell-based propulsion projects using ammonia as an onboard fuel.
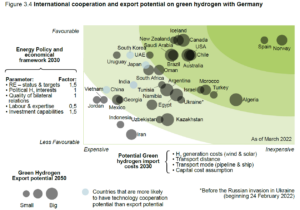
New roadmap for ammonia imports into Germany
A Fortescue-led Australian-German business coalition has released a roadmap and ten-point action plan to meet ambitious ammonia import targets for Germany. Policy recommendations on the EU and Australian side of the emerging supply chain include financial support to address the first-mover disadvantage. Guidehouse have laid out recommendations of their own in a new report, which finds maritime shipping of ammonia over long distance is the best import option, and that - ideally - hydrogen derivatives should be shipped into Germany in the form required by end users, saving on reconversion costs.
Meanwhile in Copenhagen, EU Commission Executive Vice-President Frans Timmermans has backed the shipping industry to make the transition faster than expected, with ammonia to be the “future fuel”.
First Approval in Principle for Project Sabre in Singapore
ABS has granted Approval in Principle to Keppel Offshore & Marine for an ammonia-fueled, ammonia bunkering vessel. The new vessel is a key component of Project Sabre: a high-profile consortium of maritime organisations aiming to commence ammonia bunkering in Singapore by 2030.
ExxonMobil’s Slagen terminal to become a low-emissions hub
ExxonMobil, Grieg Edge, North Ammonia, and GreenH will explore options to transform Exxon’s existing Slagen terminal into a production & distribution hub for renewable ammonia and hydrogen maritime fuels. The group has identified the potential to produce 200,000 tonnes of electrolytic hydrogen production per year at the site, as well as distributing 100,000 tonnes per year of renewable ammonia. Exxon’s wider plans for low-carbon ammonia also include two large-scale production hubs (one each in the US and the UK).
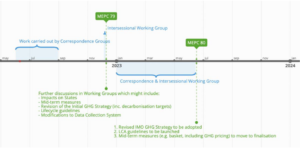
Reflections on the last meeting of the Marine Environment Protection Committee: the time is ripe for maritime ammonia
To develop sufficient ammonia supply to meet future maritime fuel demands, we face a herculean task. The recent meeting of the IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 78) gives us an insight into the key next steps to address financial & regulatory challenges. For the first time, MEPC 78 introduced the idea of a “Zero by 2050” goal for global shipping: a steep change in ambition. The use of funds from mechanisms like carbon pricing to ensure a fair, just and equitable transition, the necessity of high-impact investment to drive the fuel transition, and the adoption of new LCA guidelines in the next twelve months were also discussed. The drive & ambition shown at MEPC 78 indicates that the time is ripe for maritime ammonia to position itself as the fuel of choice for the global shipping industry.
Ammonia-powered vessels & maritime engines: development updates
This week we explore four announcements in the maritime ammonia space:
- Færder Tankers Norway will receive $20 million in Enova funding to develop two ammonia-powered vessel designs: a tanker and a car carrier.
- Mitsubishi Shipbuilding has completed a conceptual design for an LPG-ammonia dual-fuel VLGC, with Approval in Principle granted by ClassNK.
- Delivery dates have been set for the first eight of Höegh Autoliners’ Aurora-class, ammonia-powered car carriers, with China Merchants Heavy Industry to deliver vessels from late 2024.
- WinGD and Hyundai Heavy Industries will collaborate to deliver the first WinGD two-stroke engine capable of running on ammonia by 2025.
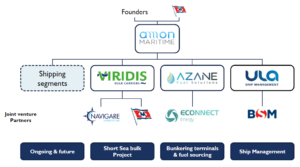
AMON Maritime: Ammonia-fueled ships and networks
In our most recent episode of Maritime Ammonia Insights we introduced the Amon Maritime consortium. Amon is unique, as it builds from the ground up and shares risk to remove the chicken-and-egg dilemma faced by new maritime ammonia players. Acknowledging that external funding has been essential to reach the point where they are at today, Amon Maritime has progressed as a shipping company and ammonia bunkering network at remarkable speed. With their novel approach and impressive progress to date, there are many takeaways for the wider maritime stakeholder environment to consider. Amon’s CEO André Risholm and CCO Karl Arthur Bræin joined Conor Fürstenberg Stott to discuss the opportunities ahead.