At least four major maritime ammonia projects have been announced in the last few weeks, each of which aims to demonstrate an ammonia-fueled vessel operating at sea. In Norway, Color Fantasy, the world's largest RORO cruise liner, will pilot ammonia fuel. Across the broader Nordic region, the Global Maritime Forum has launched NoGAPS, a major consortium that aims to deploy "the world's first ammonia powered deep sea vessel" by 2025. In Japan, a new industry consortium has launched that goes beyond on-board ship technology to include "owning and operating the ships, supplying ammonia fuel and developing ammonia supply facilities." And the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), which published its roadmap last month, aims to demonstrate ammonia fuel on "an actual ship from 2028" — specifically, a 80,000 dwt ammonia-fueled bulk carrier.
Maritime Fuel
Ammonia Included in Japan's International Resource Strategy
Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has singled out ammonia for the role it can play in the country’s creation of a "carbon-free society." The news was embedded in METI’s New International Resource Strategy which was released on March 30. In the report's framing, ammonia is cited for its association with “the concept of importing renewable energy produced in other countries.” In a departure from the practice found in most reports on the energy transition, the ammonia discussion stands alone and not as one item on a roster of potential renewable energy vectors.
Wärtsilä Tests Internal Combustion of Ammonia
Last week Wärtsilä, the Finnish engine and energy equipment manufacturer, unveiled the latest stage in its engagement with ammonia as an energy vector. In a press release headlined “Wärtsilä advances future fuel capabilities with first ammonia tests,” the company described a test program aimed at exploring ammonia’s properties as an internal combustion fuel. Kaj Portin, General Manager of Fuel & Operational Flexibility in Wärtsilä’s Marine division, commented that “the first tests have yielded promising results.”
Lloyd’s Register: how ammonia can be the ideal renewable marine fuel
We've recently reported a series of ammonia-fueled vessel development and demonstration projects led by industry consortia. One of these, in which Lloyd's Register is joined by Samsung Heavy Industries, MISC, and MAN Energy Solutions, is developing "an ammonia-fuelled tanker." In an interview with Ship Technology magazine this month, Lloyd's Register provided some new details about this project and added context for their ammonia-fueled vessel development plans.
Environmental and Economic Assessment of Ammonia as a Fuel for Ships
This month, the Korean Register published a comparative assessment of the environmental and economic merits of using ammonia as a maritime fuel. The work, written in collaboration with researchers at Pusan National University, is published in the open-access Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. It concludes that "ammonia can be a carbon-free fuel for ships," and presents "a meaningful approach toward solving GHG problems in the maritime industry."
Maritime decarbonization is a trillion dollar opportunity
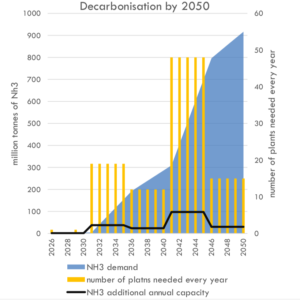
In January 2020, the Global Maritime Forum published new analysis that calculates "the capital investment needed to achieve decarbonization" in line with the International Maritime Organization's Initial GHG Strategy. The result of this analysis, which assumes that ammonia will be "the primary zero carbon fuel choice adopted by the shipping industry," is an aggregate investment of between $1 trillion and $1.4 trillion dollars, from 2030 to 2050, or roughly $50 to $70 billion per year across two decades. Ship-side costs are only 13% of this number. The bulk of the investment will be directed towards green ammonia plants for maritime fuel synthesis. By 2050, this global fuel demand is estimated to be more than 900 million tons per year of green ammonia, more than five time today's total global output of conventional ammonia.
Korean Register Sees Ammonia as Preferred Alternative Maritime Fuel
Last week the classification society Korean Register of Shipping (KR) released Forecasting the Alternative Marine Fuel: Ammonia, a “technical document on the characteristics and the current status of ammonia as ship fuel.” One hesitates to take the title too literally, but the report really does forecast that ammonia will be the alternative marine fuel. Over the last year, a number of maritime transport stakeholders – engine producers, government agencies, other classification societies – have identified ammonia as a promising means of industry decarbonization. But in joining the group, KR makes a notably explicit and complete case in ammonia’s favor.
MAN ammonia engine update
In November 2019, MAN ES published a technical paper describing the design and performance of its two-stroke green-ammonia engine. The paper also quietly announces the intentions of MAN ES to exploit ammonia energy technologies in a new business case, Power-to-X (PtX, "the carbon-neutral energy storage and sector coupling technology of the future"). In other words, MAN is moving into green ammonia fuel production.
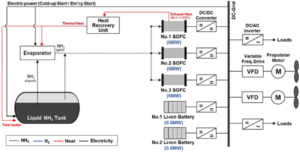
Viking Energy to be retrofit for ammonia fuel in 2024
This morning, it was announced that the "Viking Energy," a supply vessel for Equinor's offshore operations, will be modified to run on a 2 MW direct ammonia fuel cell. This will be a five year project: the technology will be scaled-up on land before being installed on the vessel, which will begin a year of GHG emission-free operations in 2024. The Norwegian partners leading this "world's first" project include shipowner Eidesvik, contractor Equinor, and ammonia producer Yara, as well as Wärtsilä (Wärtsilä Norway), responsible for power technology and ammonia storage and distribution systems, and Prototech, delivering the fuel cell system.