The maritime industry has been engaged in a frenzy of research since April 2018, when the International Maritime Organization (IMO) announced its Initial GHG Strategy mandating a 50% reduction in shipping's emissions by 2050. Three recent announcements illustrate the speed and depth of progress across a range of maritime stakeholders. In the government sector, the UK has launched its Clean Maritime Plan, which identifies ammonia as one of its strategic "clean growth opportunities." In finance, a coalition of 11 banks representing a shipping portfolio of around $100 billion has launched the Poseidon Principles to "redefine the role of banks in the maritime shipping sector." And class society ABS launched its Global Sustainability Center in Singapore to analyse, certify, and validate alternative fuels and new technologies; its Director of Global Sustainability will speak at the inaugural conference of the Ammonia Energy Association--Australia, held in Clayton, VIC, on August 22-23. His subject will be "Green ammonia as marine bunker fuel."
Maritime Fuel
Safe and Effective? New Study Evaluates Ammonia as a Marine Fuel
In mid-June the Dutch naval architecture firm C-Job released "Safe and effective application of ammonia as a marine fuel," a thesis written by the firm’s Lead Naval Architect Niels de Vries for the Marine Technology Master of Science program at the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. While the thesis delivers an extensive assessment of ammonia's potential effectiveness as a marine fuel, it breaks new ground in its consideration of ammonia's safety in this context.
New Coalition Plans to Build Offshore Green Fueling Hubs
Last week Wärtsilä, the Finnish engine and energy equipment manufacturer, unveiled a concept for producing and distributing low-carbon maritime fuels from purpose-built facilities in the waters off northern Europe. Dubbed Zero Emission Energy Distribution at Sea (ZEEDS), the initiative is intended to help meet the International Maritime Organization’s target of halving the shipping sector's carbon dioxide emissions by 2050. And although Wärtsilä’s press release on June 3 mentions only “clean fuels,” the headline used by logistics-sector publisher Freight Week for their June 5 story is “Offshore fuel hubs to supply green ammonia for zero-emission future.”
Sailing on Solar: EDF report identifies ammonia as "one of the most promising" maritime fuels
In May, the Environmental Defense Fund published Sailing on Solar, a significant new report that assesses the potential for green ammonia to be used as a maritime fuel, reducing the global shipping industry's carbon emissions. Its 60-page techno-economic analysis concludes that "green ammonia can – indeed should – be adopted as a greenhouse gas-free fuel more easily, quickly and safely than people may assume." Indeed, Sailing on Solar estimates that, to meet decarbonization targets, ammonia will need to start being adopted in ships "during the 2020s."
Fuels Without Carbon: Prospects and the Pathway Forward for Zero-Carbon Hydrogen and Ammonia Fuels
A new report from CATF, Fuels Without Carbon: Prospects and the Pathway Forward for Zero-Carbon Hydrogen and Ammonia Fuels, explores how a massive scale-up in the production and use of zero-carbon hydrogen and ammonia might help decarbonize segments of the power sector, the industrial sector, and the transportation sector (both marine and ground). Fuels Without Carbon looks at how the availability of zero-carbon hydrogen and ammonia fuels could help address several vexing climate-energy challenges, and it examines the steps that need to be taken to fully understand and address the safety and environmental risks associated with the two chemicals. Fuels Without Carbon also identifies several public and private sectors initiatives — including a few being pursued by CATF — for analyzing the opportunities and challenges associated with hydrogen and ammonia fuel, educating stakeholders about the potential benefits and risks, designing and advocating for appropriately supportive policies, and engaging with key power and mobility companies.
UK Department of Transport recommends launch of ammonia / hydrogen powered vessels within 5-15 years
In January 2019, the UK Department for Transport published a policy paper outlining its vision for the maritime sector over the coming decades. Among the many recommendations contained in Maritime 2050: navigating the future, is a medium-term objective to place "a group of hydrogen or ammonia powered domestic vessels in operation." The "strategic ambition" driving this recommendation is the expectation that "the UK will ... lead the way in taking action on clean maritime growth enjoying economic benefits from being an early adopter or fast mover." Moving forward, these recommendations will be developed into policy in the government's forthcoming Clean Maritime Plan, scheduled to be published in Spring 2019.
MAN Energy Solutions: an ammonia engine for the maritime sector
In June 2018, MAN Diesel & Turbo rebranded itself MAN Energy Solutions, reflecting the maritime engine market leader's "strategic and technological transformation" towards sustainability. The company was "taking a stand for the Paris Climate Agreement and the global pursuit of a carbon-neutral economy." According to Uwe Lauber, Chairman of the Board, "our activities have a significant impact on the global economy. In shipping, for example, we move more than half of the global stream of goods ... [and] the path to decarbonising the maritime economy starts with fuel decarbonisation, especially in container shipping." This week, the company took a significant step towards realizing its vision, disclosing that it is "pressing ahead with developing ... an ammonia-fuelled engine." This builds on the technology development pathway that MAN ES presented at the NH3 Energy+ Topical Conference at Pittsburgh in October 2018. The budget and timeline are set: the €5 million (USD$5.7 million) project will last two to three years and, if the shipowners decide to deploy the finished product, "the first ammonia engine could then be in operation by early 2022."
The most efficient way to decarbonise the shipping sector
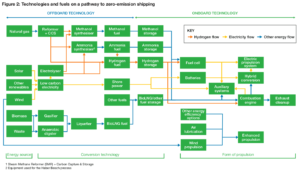
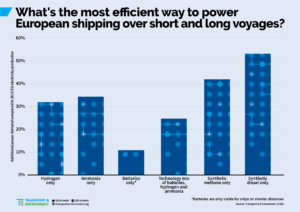
A new report, Roadmap to Decarbonising European Shipping, identifies a mix of three technologies - batteries, hydrogen, and ammonia - as being "by far the most efficient way to decarbonise the sector." Even so, to satisfy demand from EU's carbon-free shipping sector in 2050, this technology mix will require the installation of huge amounts of additional renewable power generation, equivalent to 25% of the EU's total electricity production.
Ammonia as a Marine Fuel