JERA’s new growth strategy: significant role for ammonia
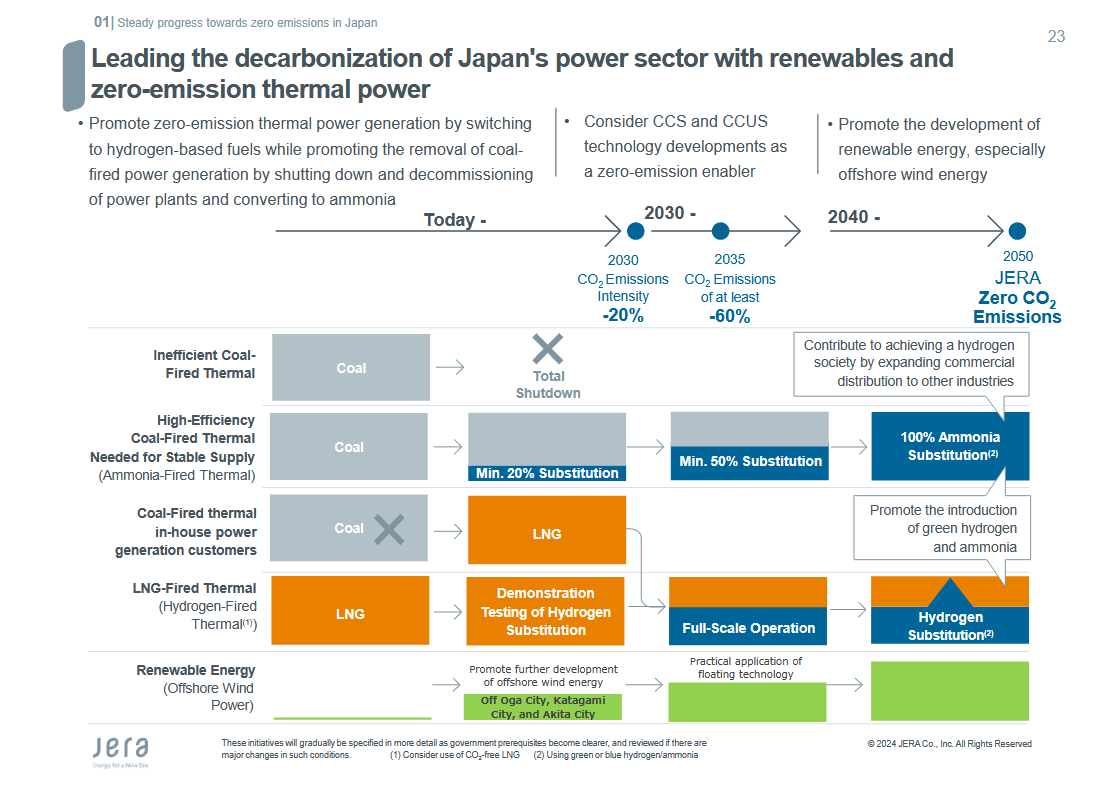
From near-zero volumes today, JERA has set its sights on being a “pioneer player” in the emerging global value chain for ammonia, handling 7 million tons every year by 2035. JERA is also aiming for 100% substitution of ammonia fuel in ultra-supercritical power stations in the 2040s, and to maintain currently low levels of NOX and SOX emissions from its power generating fleet.