On the Ground in Japan: Residential Fuel Cells
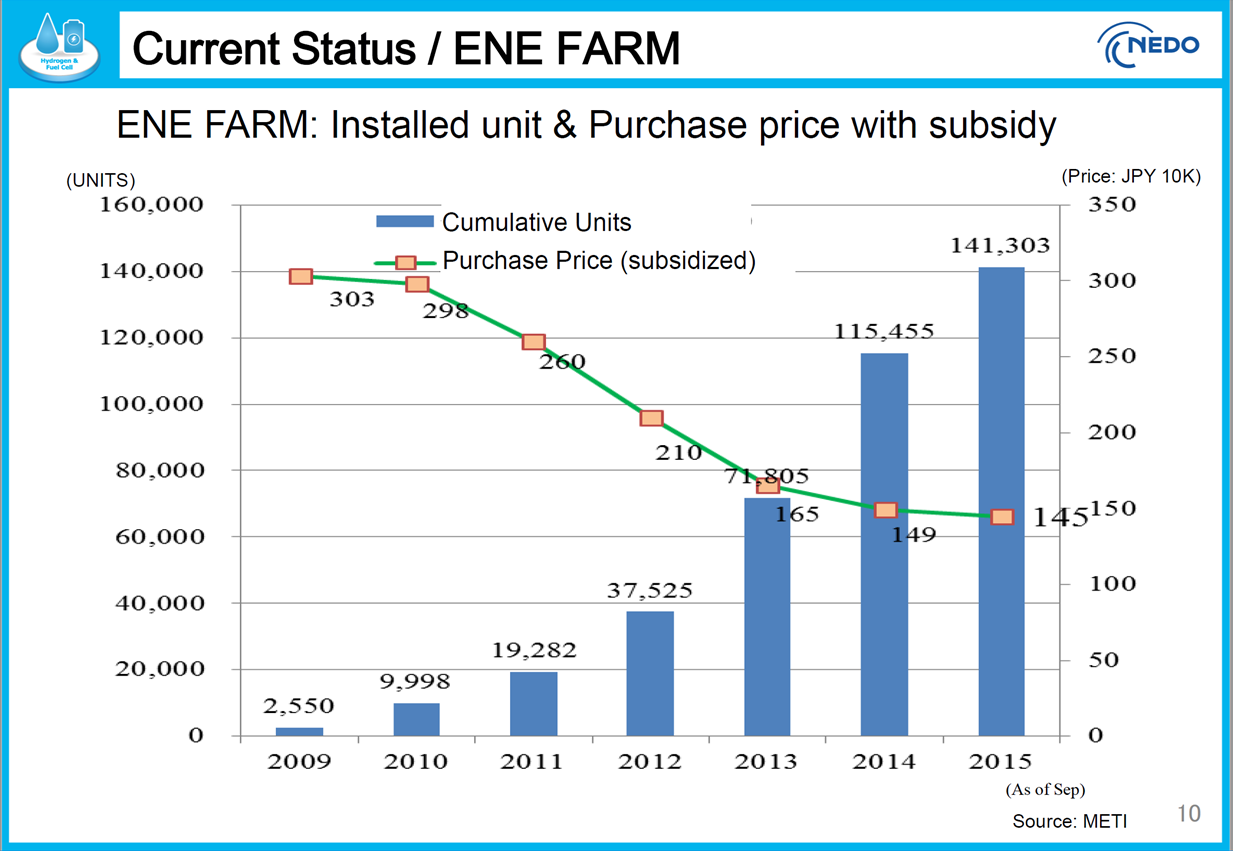
Last week Kaden Watch, a Japanese Web site for appliance news, reported that Tokyo Gas had delivered its 80,000th Ene Farm residential fuel cell system. This small news item, delivered by a niche media outlet, lifts a critical corner of the decidedly “big-tent” story of Japan’s strategy to develop a hydrogen-based energy economy. How the Ene Farm topic develops is likely to be a major factor in Japan’s ability to sustain its hydrogen vision -- and possibly a determinant of the role ammonia could play within it.