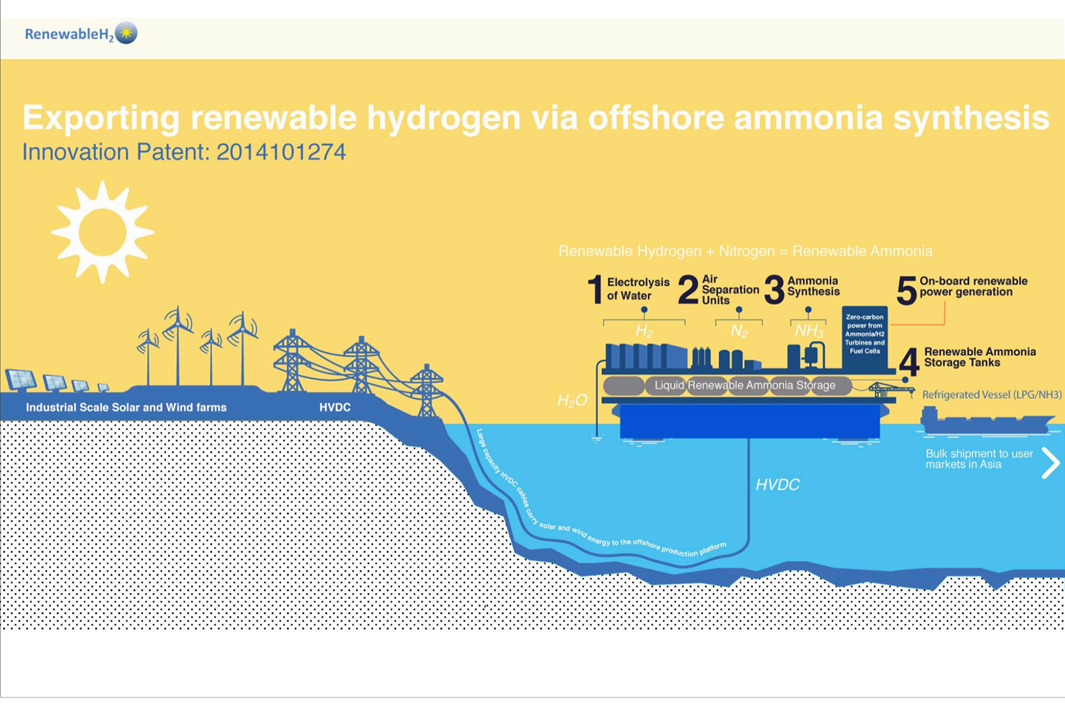
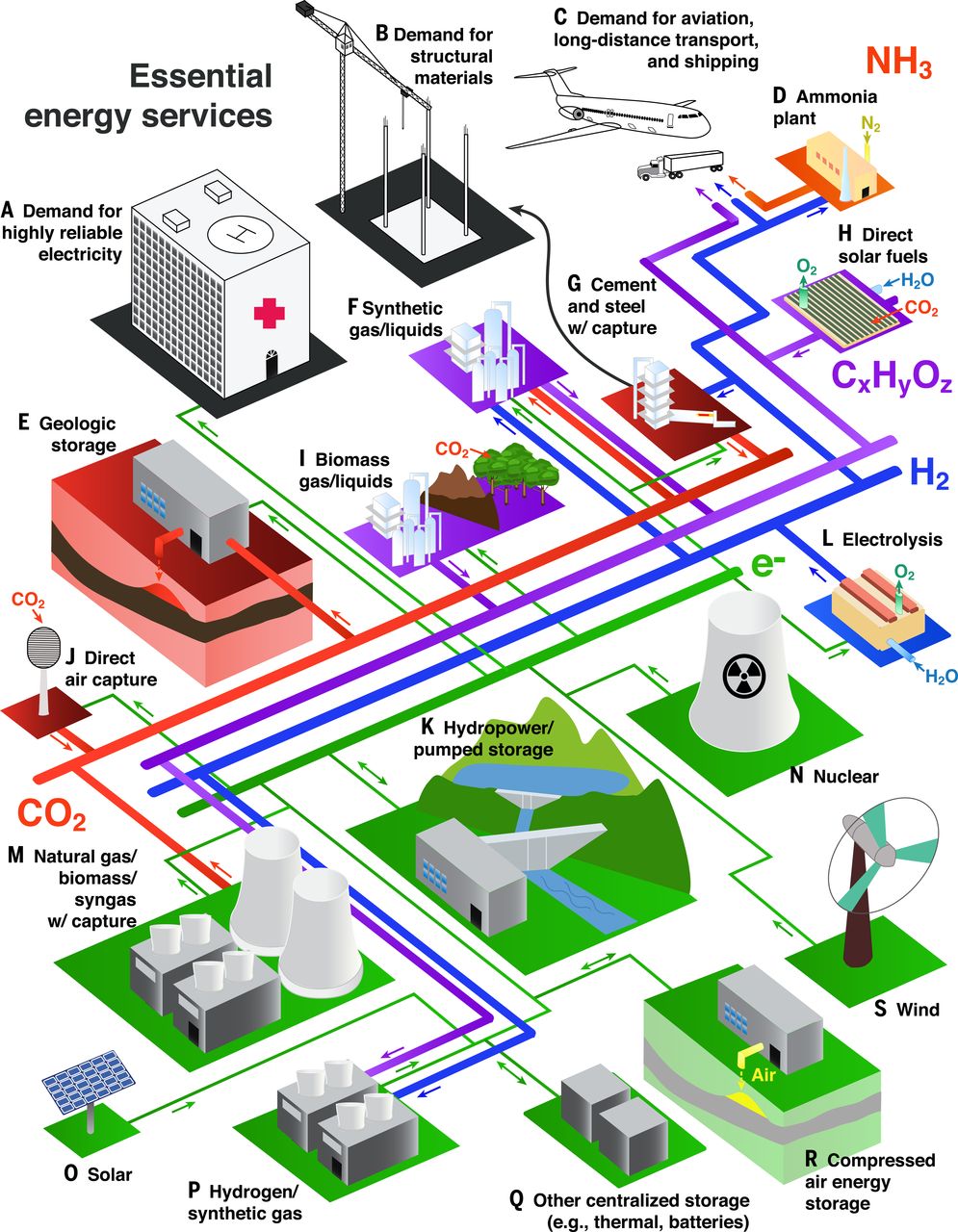
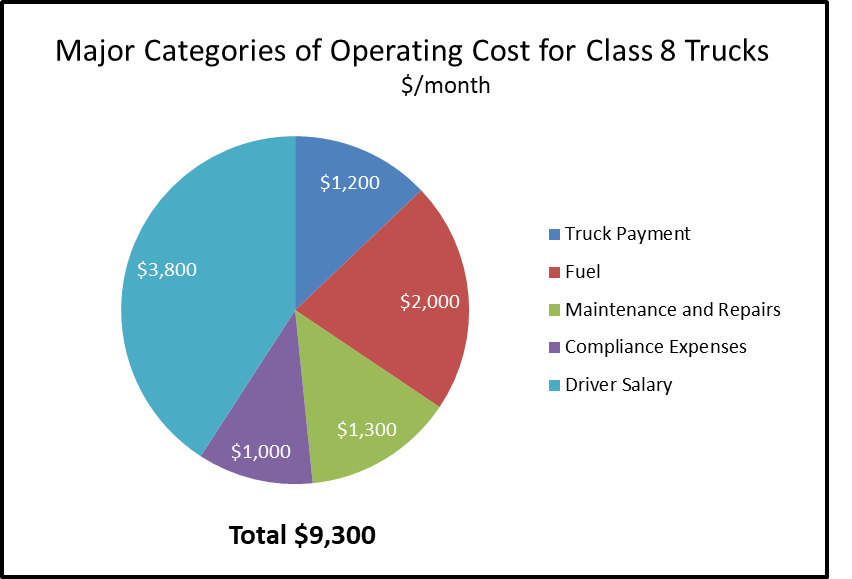
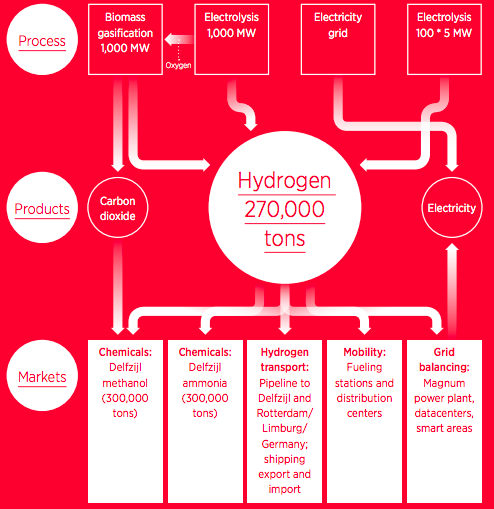
EPRI Releases Ammonia Energy Report
Last month the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) released Renewable Ammonia Generation, Transport, and Utilization in the Transportation Sector, the organization’s first public treatment of ammonia energy. The report is positioned as a communique from the cutting edge – a “Technology Insights Brief” from EPRI’s “Innovation Scouts” – and, bracingly, manages to be both brief and comprehensive. Within its format, it does an excellent job of conveying the positive case for ammonia energy and the R&D that will allow it to reach its potential.