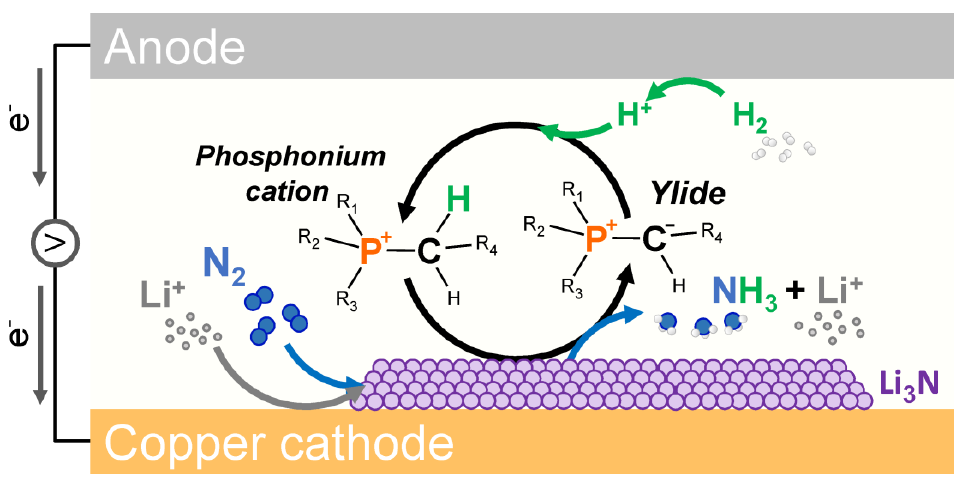
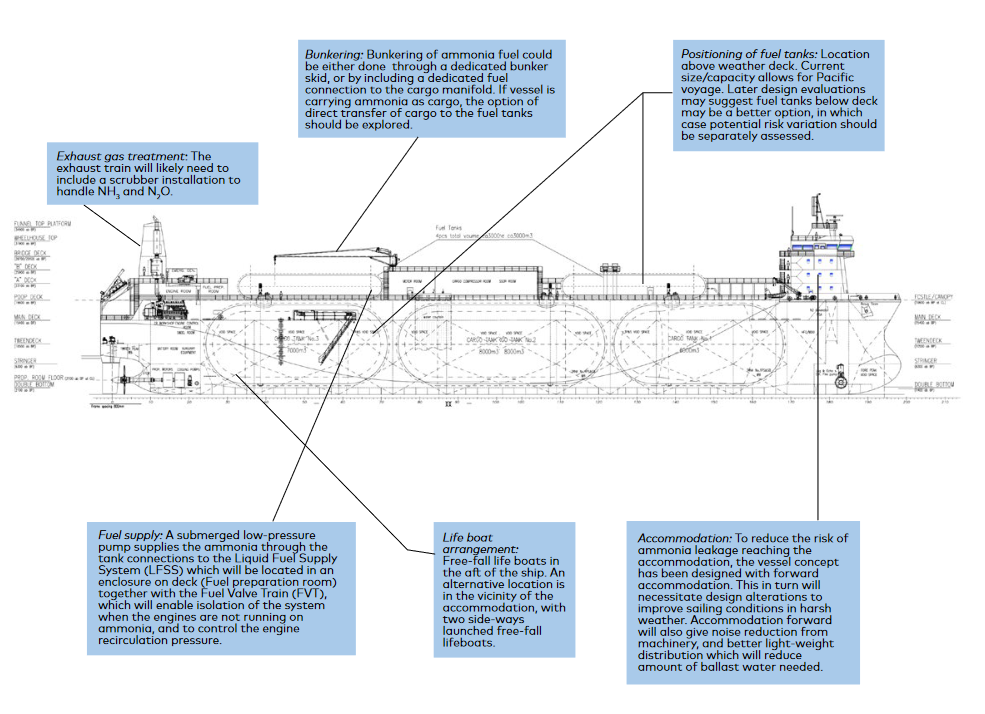
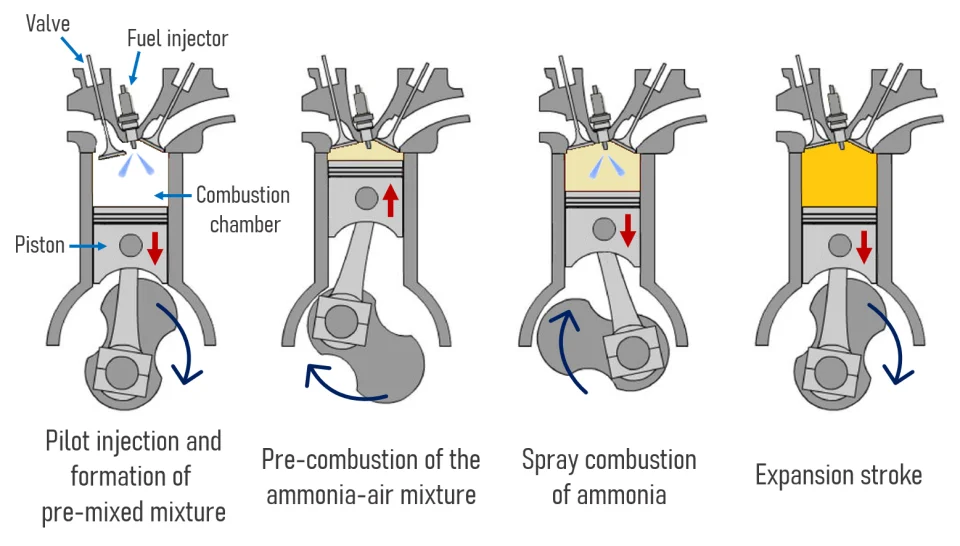
The Ammonia Wrap: 45 GW mega-project in Kazakhstan and more
This week: 45 GW mega-project in Kazakhstan, world-first industrial "dynamic" green ammonia plant, Japan's Idemitsu to use Tokuyama facility for ammonia imports, co-combustion test, more successful funding rounds, green ammonia in Ireland, South Africa's potential to fuel green shipping: new report, Obsky LNG becomes Obsky hydrogen/ammonia and more developments in the Middle East.