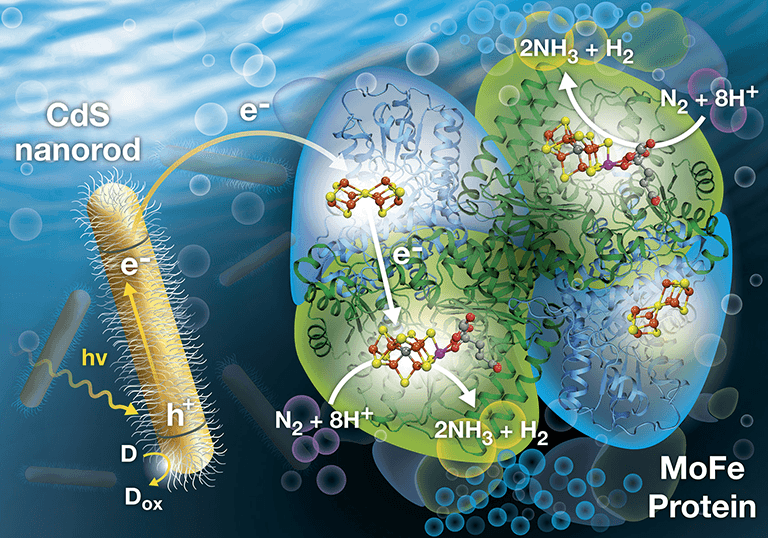Next-generation ammonia tech: biohybrid nanoparticles
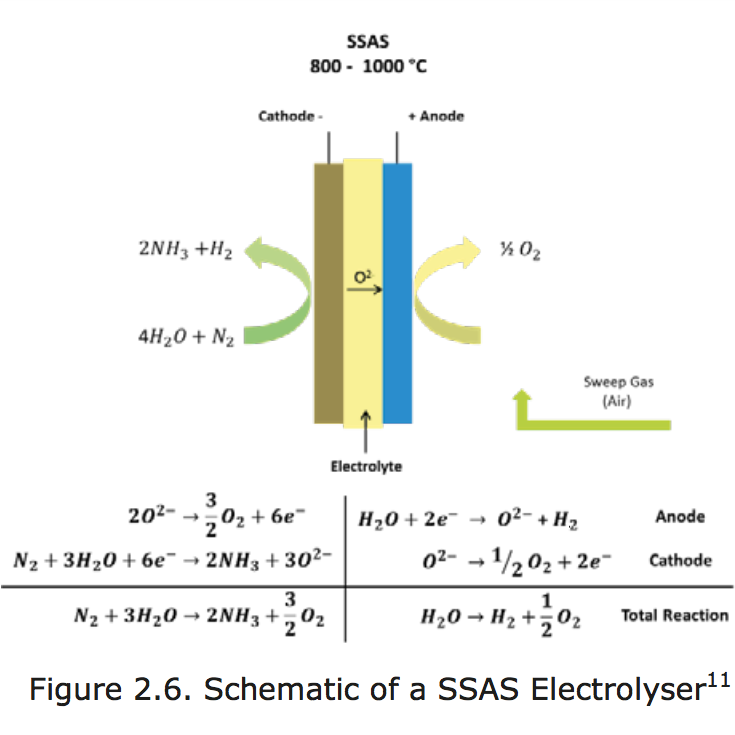
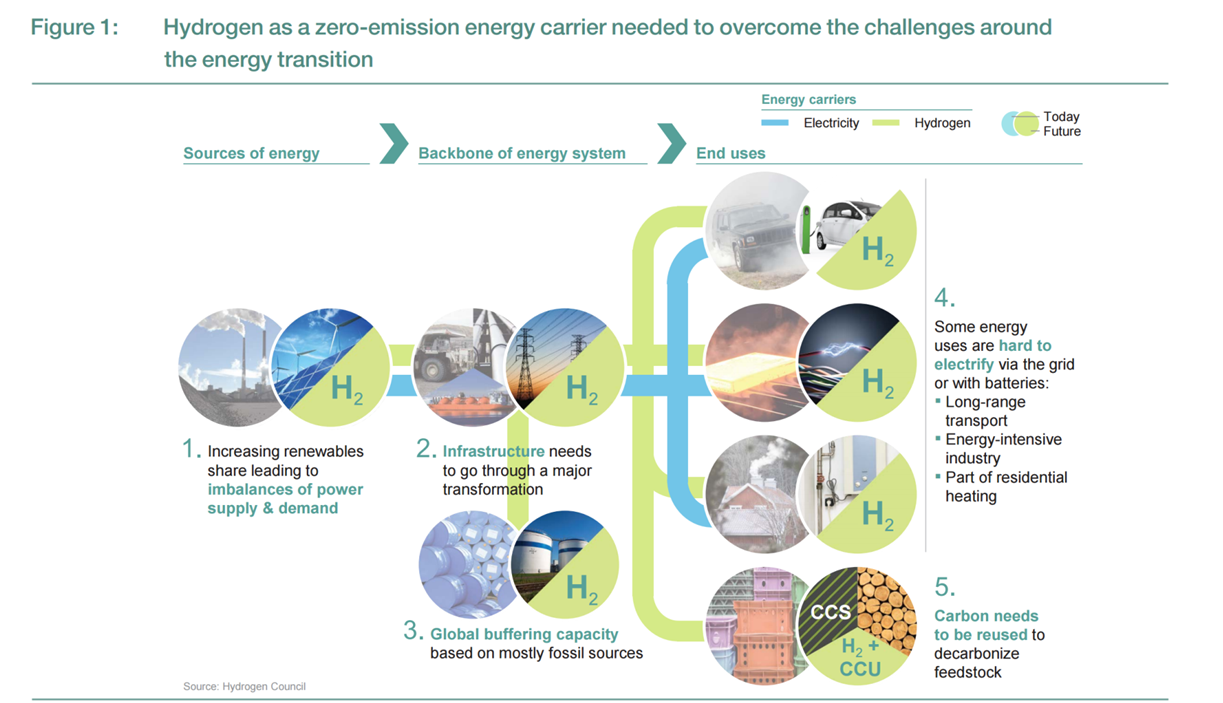
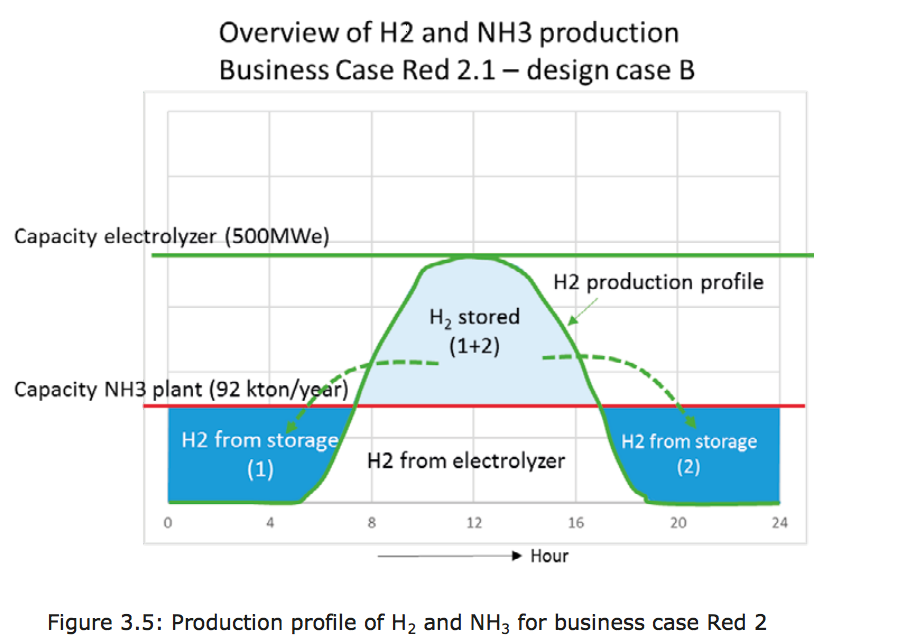
Sustainable ammonia can be produced today: doing so would use electrolyzers to make hydrogen to feed the traditional Haber-Bosch process. In a very few years, new technologies will skip this hydrogen production phase altogether and make ammonia directly from renewable power in an electrochemical cell. Further down the pipeline, next generation technologies will mimic nature, specifically the nitrogenase enzyme, which produces ammonia naturally. One of these next generation technologies is currently producing impressive results at the US Department of Energy's (DOE) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).