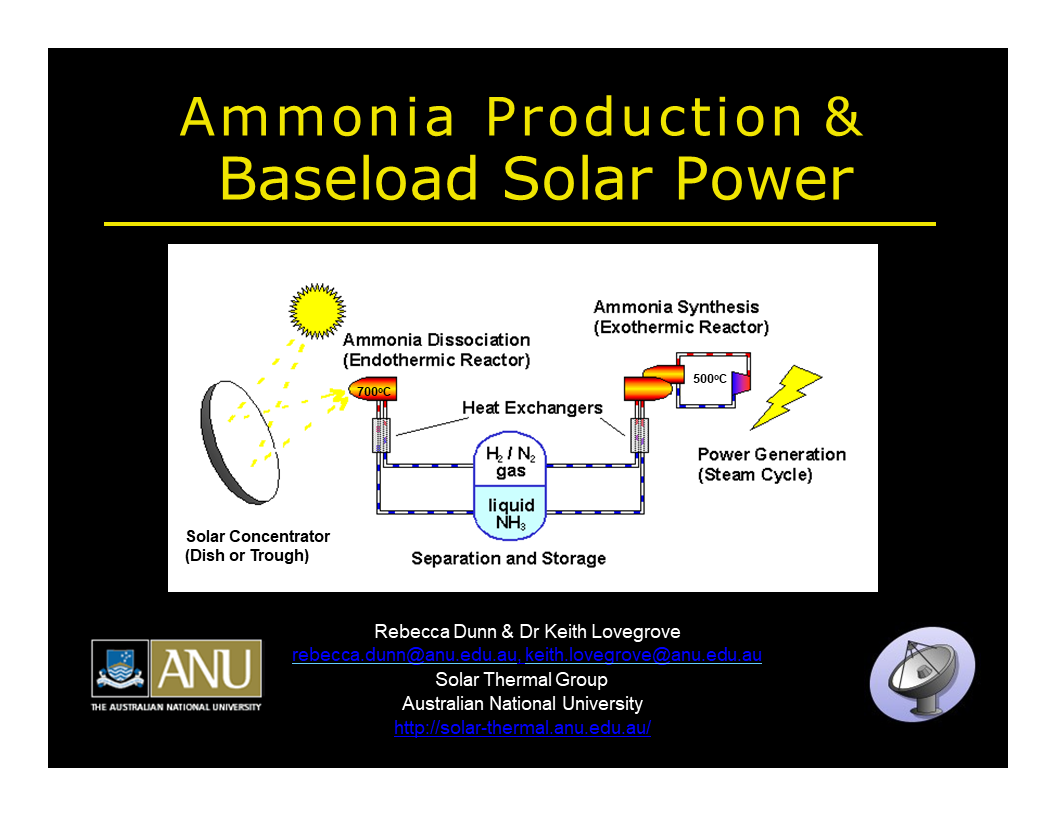
Nuon's Power-to-Ammonia update, and the first European ammonia fuel conference in 2017
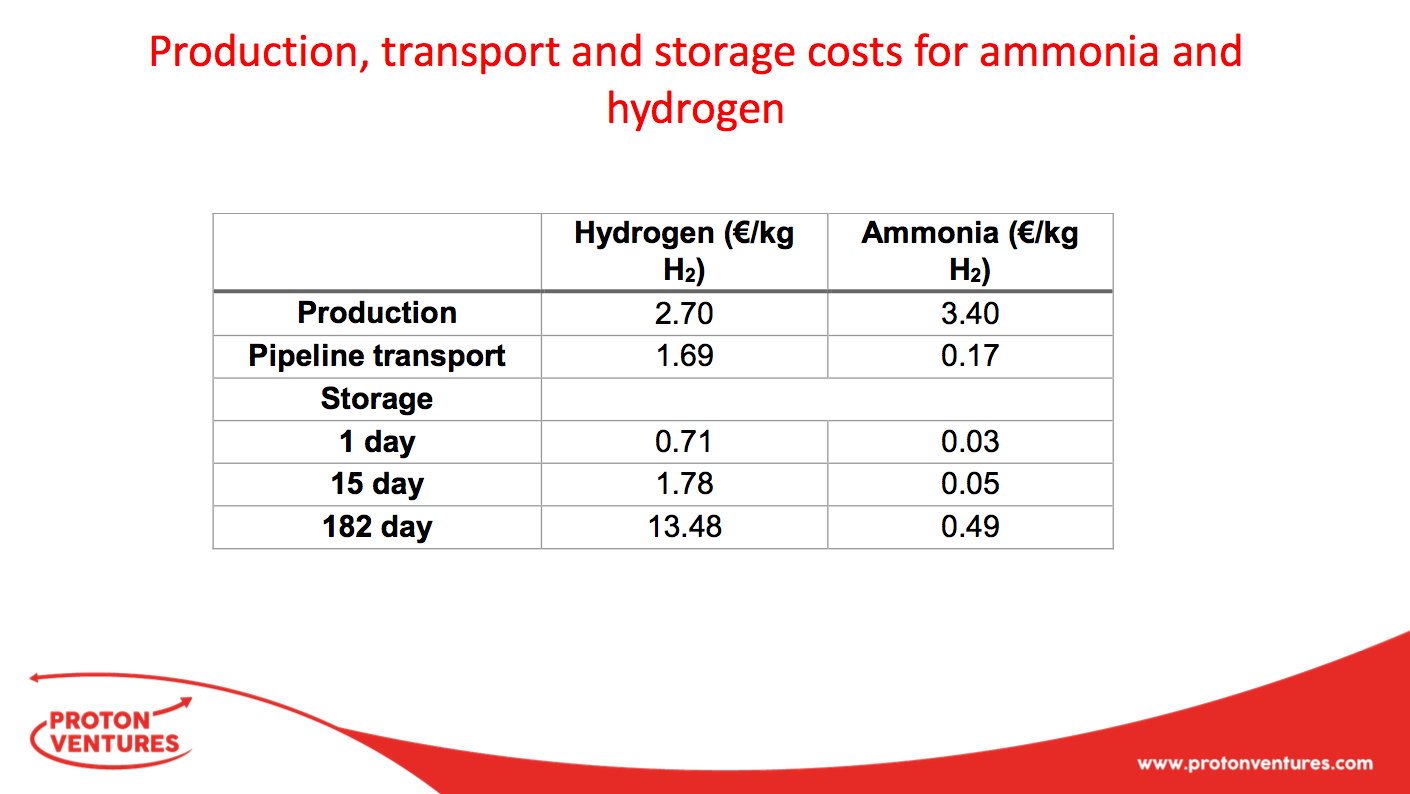
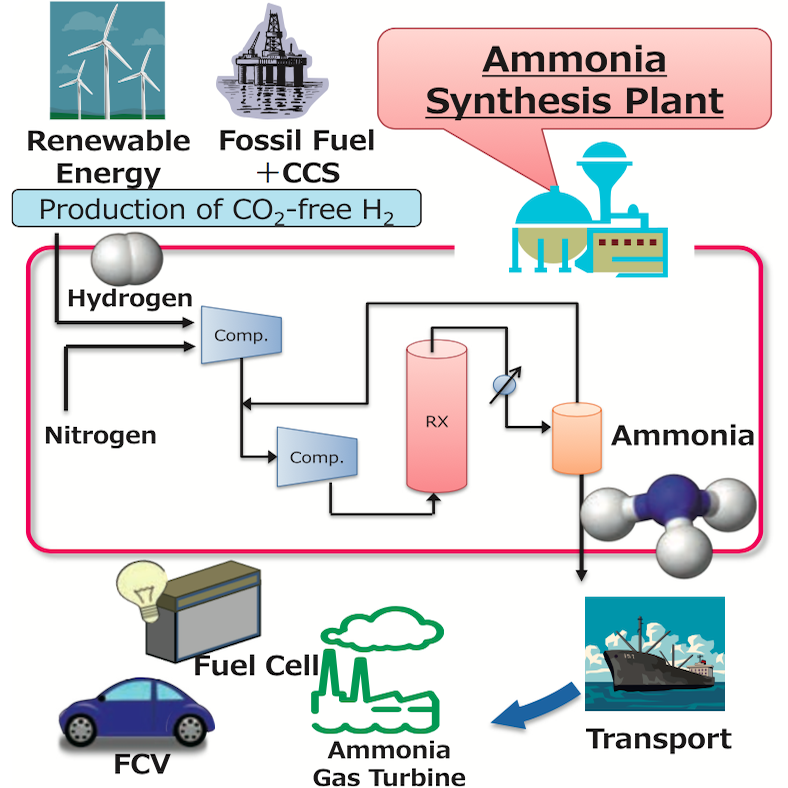
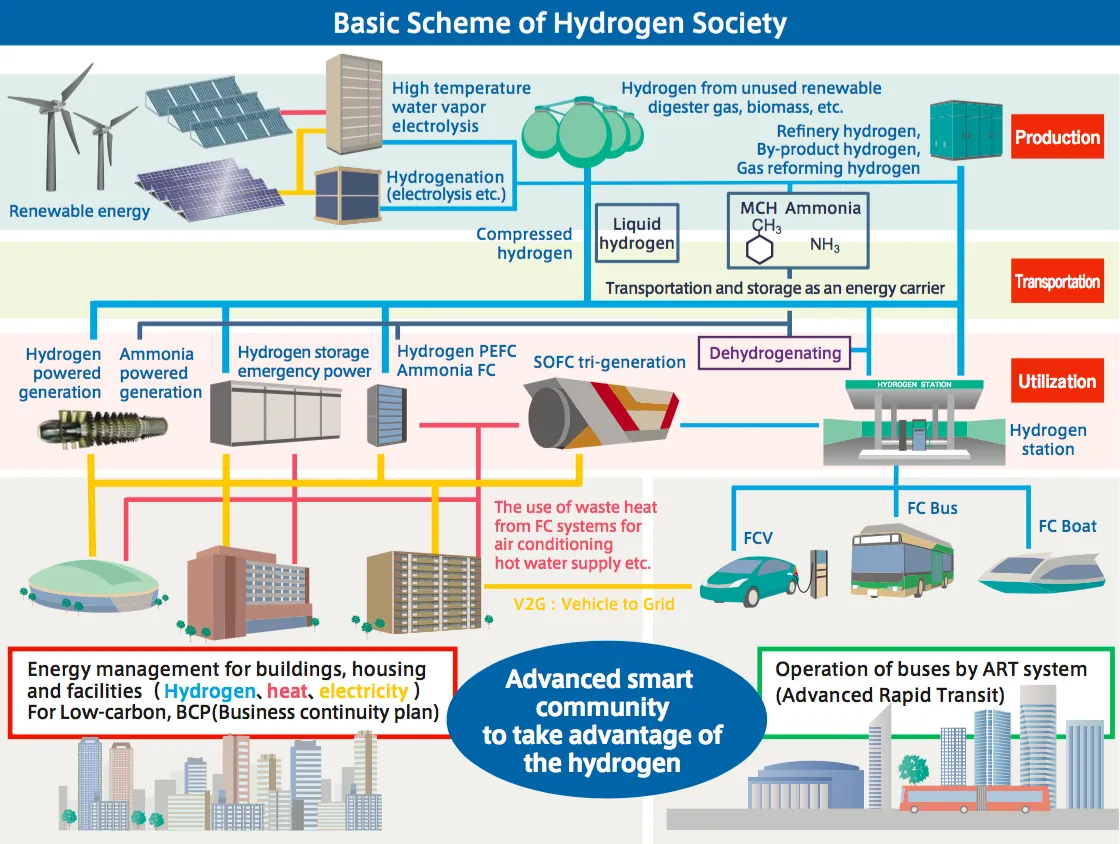
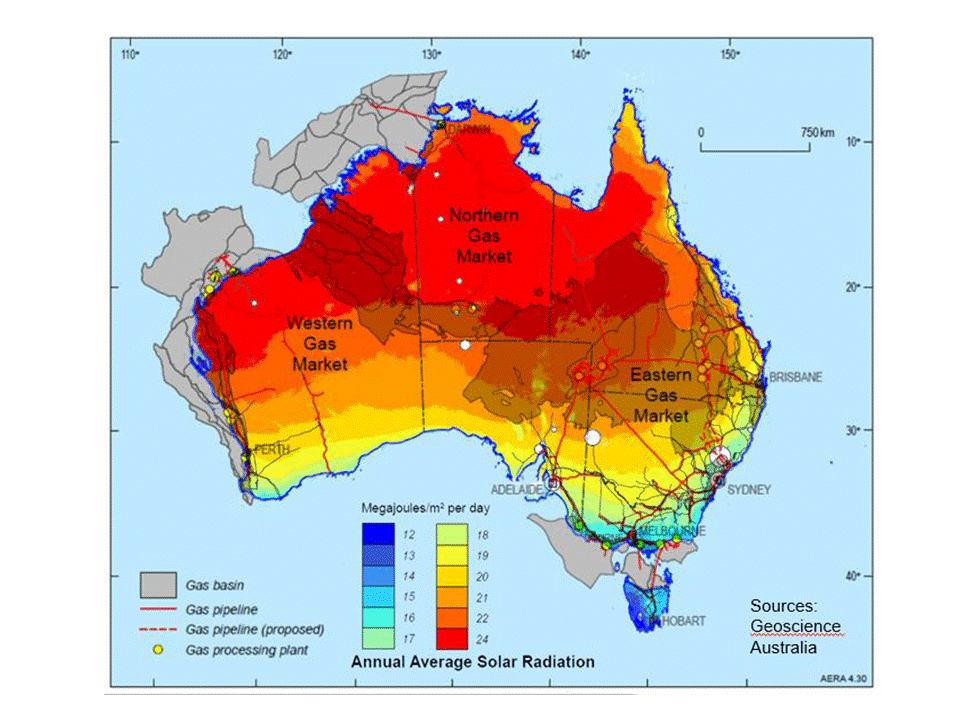
An article in the latest issue of Dutch-language magazine NPT Proces Technologie provides a detailed update on the Nuon project, about which we wrote a few months ago. Nuon's Power-to-Ammonia project looks at grid-scale storage of "seasonal surplus" electricity from wind and solar in the form of ammonia. Proton Ventures, the originators of the Power-to-Ammonia concept in The Netherlands, have also been sharing details of the project in recent conference presentations - and announced that they will be hosting the first European ammonia fuel conference, in Rotterdam, in May 2017.