A human factors approach to safety on ammonia-fueled vessels
By Julian Atchison on July 03, 2023
New analysis from Maersk McKinney Moller Center, Lloyd’s Register
A joint study into ammonia safety onboard three different vessel types has found that safety risks of ammonia fuel can be mitigated, but only if “effective technical and operational safeguards are implemented whilst addressing human factors considerations”. Recommendations for Design and Operation of Ammonia-Fuelled Vessels based on Multi-disciplinary Risk Analysis details a series of recommendations for vessel developers, including training & competency standards for seafarers working with or near ammonia fuel.
To enable sustainable and scalable new energy pathways such as ammonia as a marine fuel, we must advance technological developments. However, in the eagerness to transform, we must do so without compromising safety and reliability, by employing a strong risk-based change management approach. Care of our seafarers and strong safety management are imperative. This study has given us deep insights into risk and will provide critical understanding and intelligence to help guide the industry towards safe application of ammonia as a marine fuel.
Claus Winter Graugaard, Chief Technology Officer, Onboard Vessel Solutions, Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping in his organisation’s official press release, 27 June 2023
The study utilised the data-driven Quantitative Risk Assessment method to assess whether the individual risk of fatality per annum (or IRPA) for members of a ship’s crew was within acceptable levels when ammonia fuel was used on-board. Analysis of key identified risks produced total IRPA values well within tolerable limits, and comparable to real-world values for current seafarers in the British and European fleets (see below). The authors note that alternative fuels like ammonia face a unique challenge in QRA analysis, as their IRPA values will be intrinsically higher – new fuel risks have to be added on top of existing safety risks.
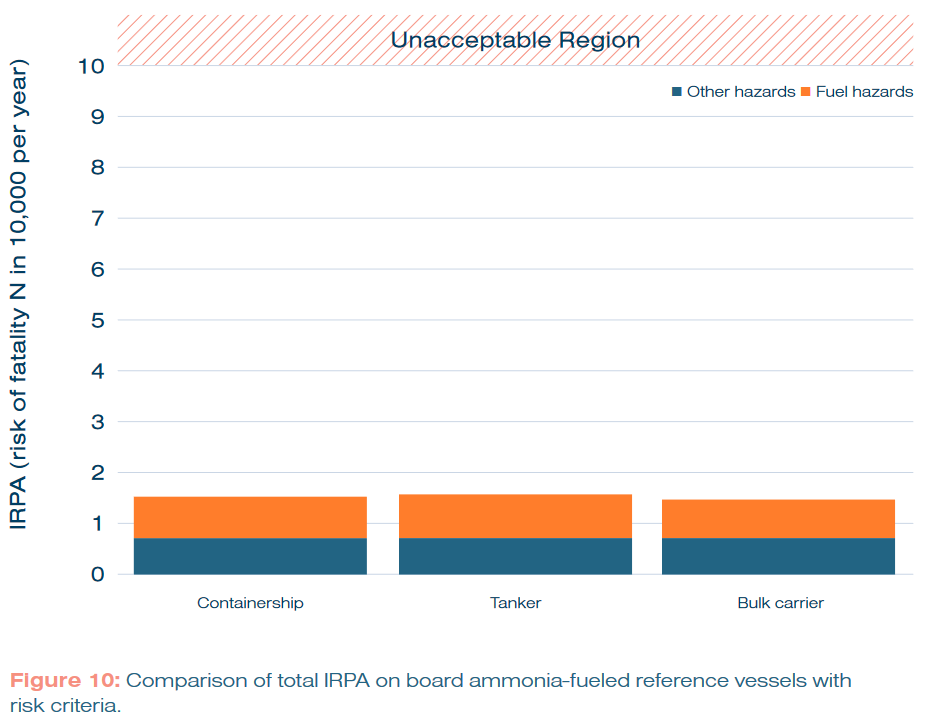
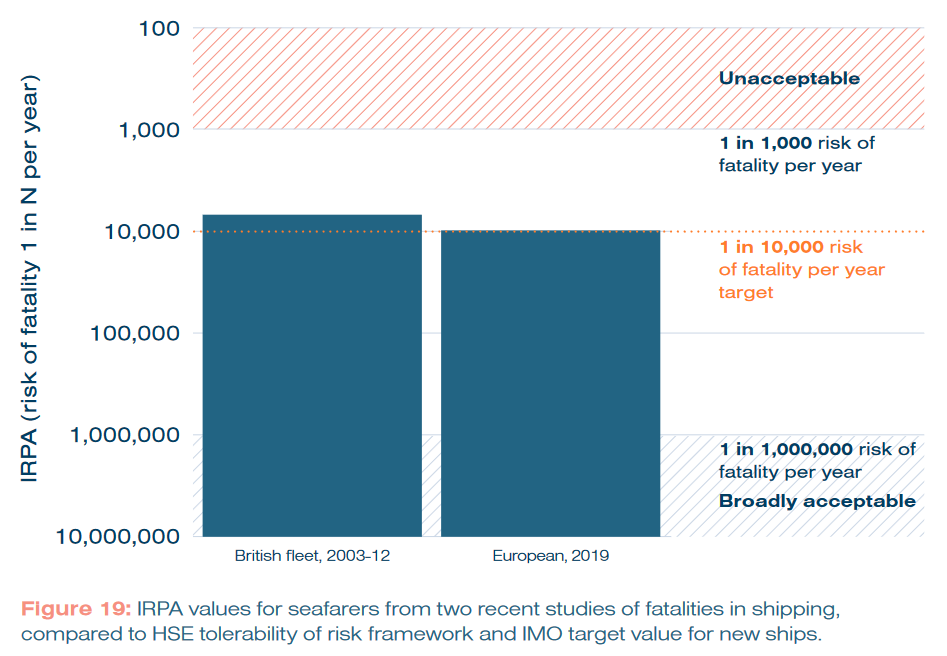
Recommendations to address human factors
The report authors conducted a series of collaborative workshops to identify relevant human factors and rate their impact (low, medium, or high). High impact factors included:
• Competence and training: specific training and upskilling will be needed to prepare crew for operation and maintenance on ammonia-fueled vessels.
• Process and procedures: safe work practices and standard procedures need to be updated and should be implemented through systematic change management programs.
• Occupational health hazards: effective occupational health safeguards, such as personal protective equipment (PPE), need to be developed and implemented.
• Process safety hazards: appropriate safety management procedures for emergency response and other events need to be developed.
Executive Summary from Recommendations for Design and Operation of Ammonia-Fuelled Vessels based on Multi-disciplinary Risk Analysis, MMMCZCS & LR Maritime Decarbonisation Hub (June 2023)
Vessel owners & operators must ensure that “suitable and sufficient” technical barriers and administrative controls are implemented to protect & separate the crew from various ammonia risks. Prior experience with gaseous fuels and cargoes within the industry will be valuable, as will the considerable experience in safely handling, transferring, and storing ammonia. A committed, whole-of-industry approach will be required to define the necessary guidelines, standards, regulations and best-practices.
Recommendations to address technical factors
High-priority recommendations include:
• Lower storage temperature reduces the safety risk from ammonia fuel.
• Divide the fuel preparation room into two or more separate spaces containing different groups of equipment that could leak ammonia.
• Access to and length of time spent in spaces containing ammonia equipment should be minimized, monitored, and controlled.
• Ventilation outlets from spaces containing ammonia equipment should be placed in a safe location adequately separated from areas accessed by crew, in order to avoid accidental release of toxic concentrations of ammonia affecting personnel.
• Multiple sensors of different types to detect ammonia leaks should be installed.
Executive Summary from Recommendations for Design and Operation of Ammonia-Fuelled Vessels based on Multi-disciplinary Risk Analysis, MMMCZCS & LR Maritime Decarbonisation Hub (June 2023)
The authors also note that the use of secondary containment systems like double-walled piping (especially outside of restricted areas) is a proven method for reducing ammonia risks in other sectors, and should be a standard feature on-board.
