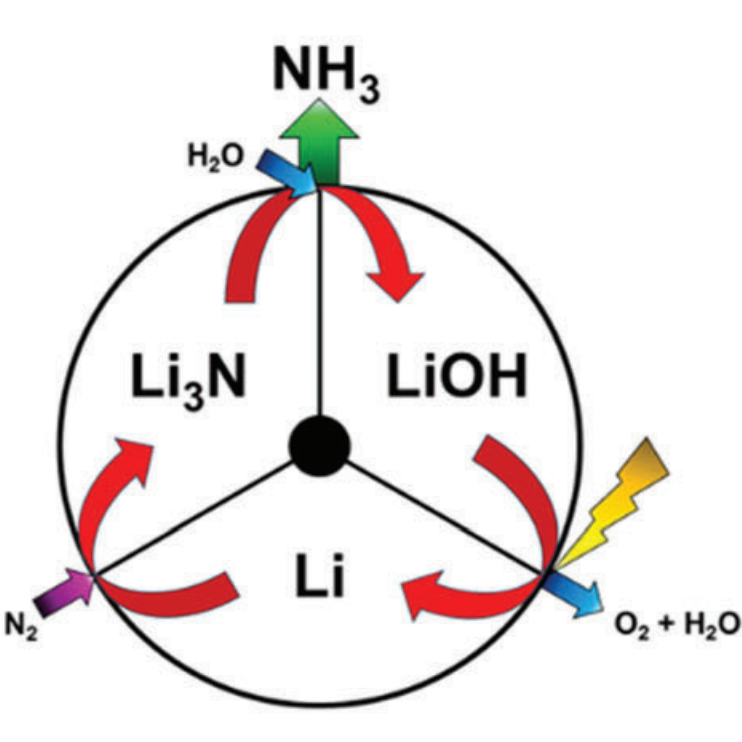
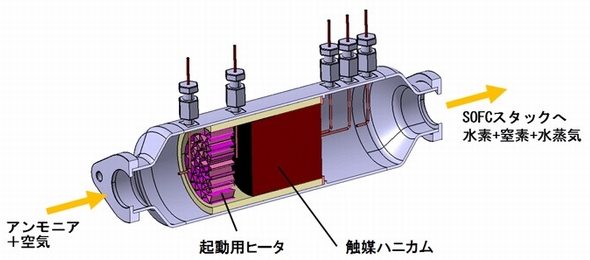
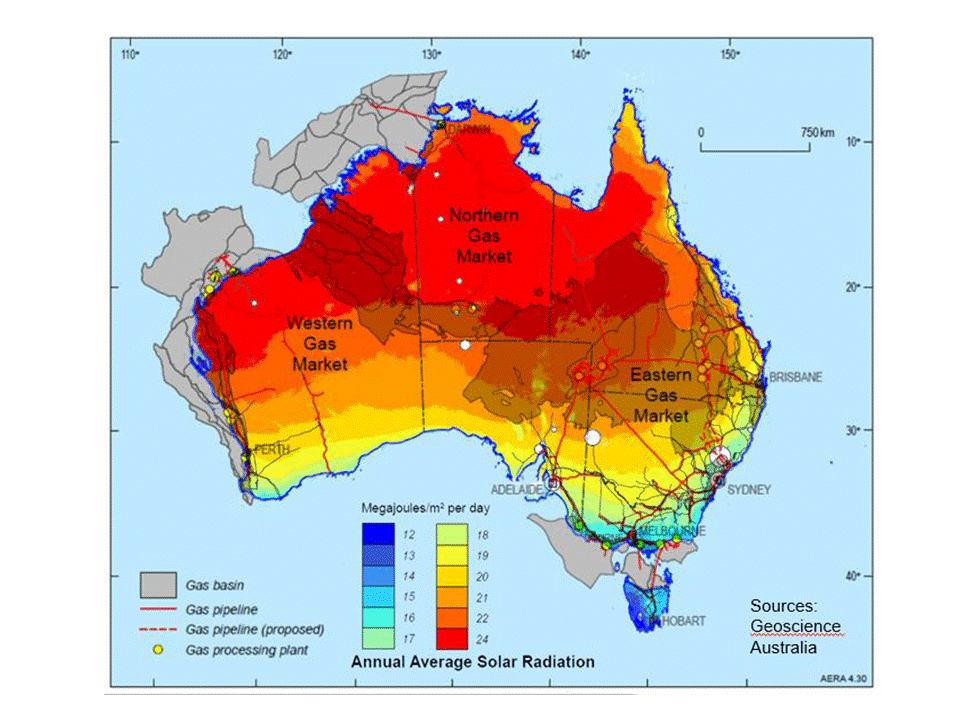
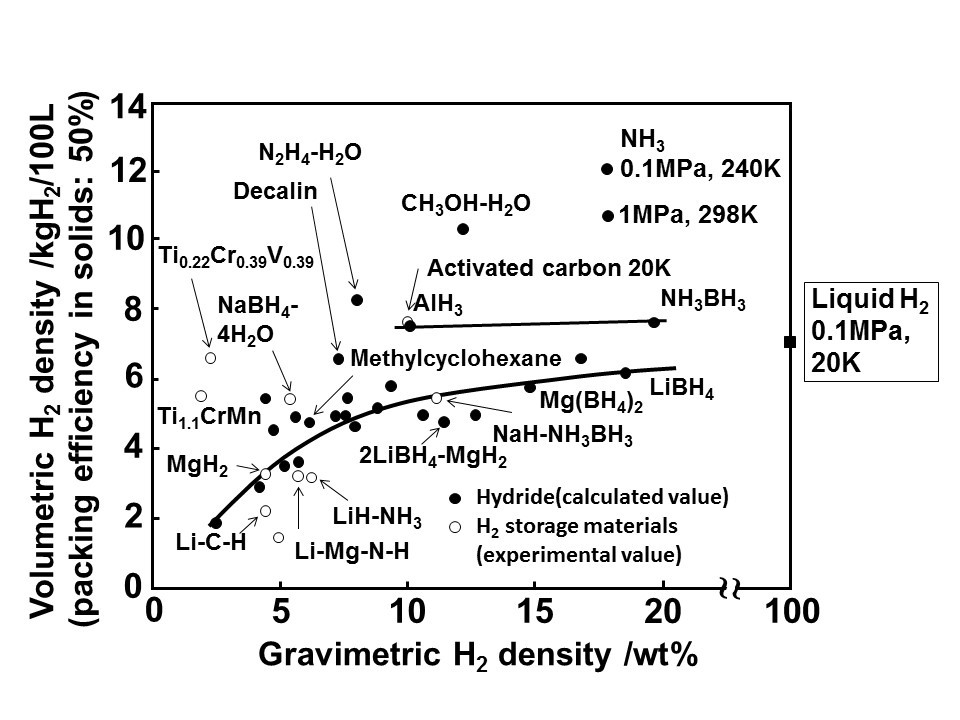
Major Development for Ammonia Energy in Japan
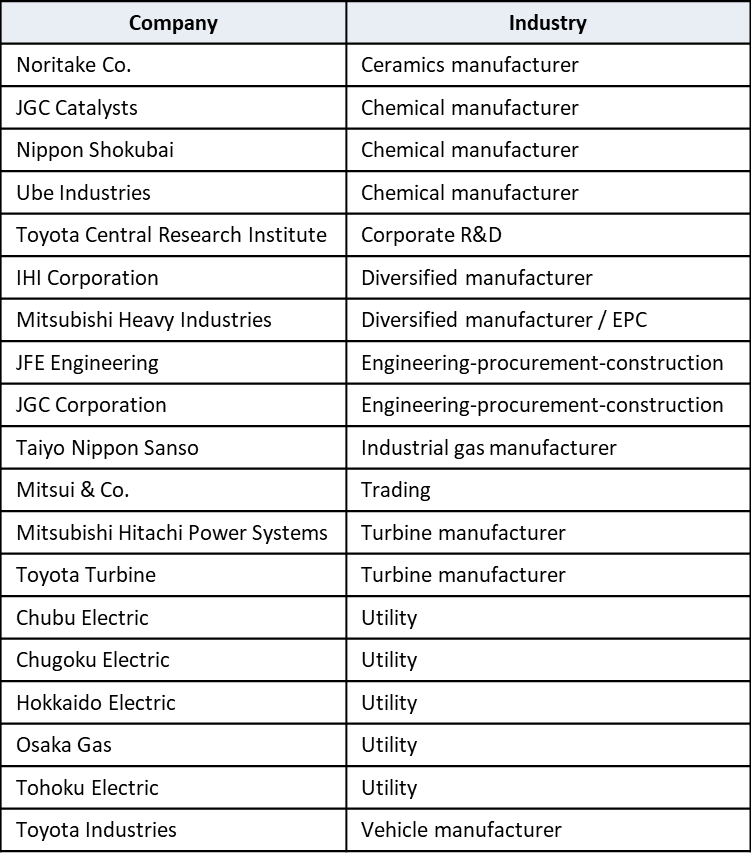
On July 25, the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) announced that a collection of companies and research institutions had come together to form a Green Ammonia Consortium. The 22-member group will take over responsibility for the ammonia aspect of the Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Program (SIP) Energy Carriers agenda when the SIP is discontinued at the end of fiscal 2018. A JST press release states that the Consortium intends to develop a strategy for “forming [an] ammonia value chain,” promote demonstration projects that can further commercialization, and enable “Japanese industry to lead the world market.”