Literature Review: Ammonia as a Fuel for Compression Ignition Engines
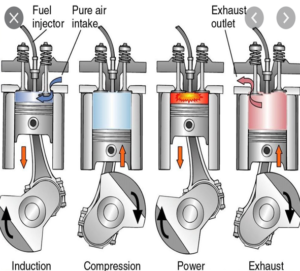
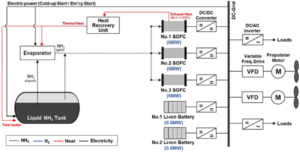
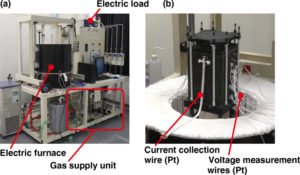
The diesel engine, also known as the compression ignition (CI) engine, has been a workhorse of the modern energy economy for more than a hundred years. Its role in the coming sustainable energy economy will be determined by its ability to co-evolve with climate-friendly fuels. Two researchers from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology in Japan have now examined the fit between ammonia and the CI engine. Pavlos Dimitriou and Rahat Javaid arrive at a two-part conclusion in their paper, “A review of ammonia as a compression ignition engine fuel,” published in January in the International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. Part one is good news: “Ammonia as a compression ignition fuel can be currently seen as a feasible solution.” Part two is a dose of qualifying reality: to manage emissions of N2O, NOx, and unburnt NH3, “aftertreatment systems are mandatory for the adaptation of this technology,” which means that ammonia-fueled CI engines are likely to be feasible “only for marine, power generation and possibly heavy-duty applications where no significant space constraints exist.”