KBR will integrate SolydEra’s solid oxide electrolysis technology into its proprietary K-GreeN® ammonia synthesis process thanks to a new MoU. K-GreeN® is the technology of choice for several significant ammonia mega-projects, including Avina Clean Hydrogen (Texas), and ACME Group (Oman).
Global
Certification with blockchain: H2Global makes the case
In a new policy brief, H2Global sets out the case for the use of blockchain in hydrogen certification. The use of a decentralised, digital, public ledger for key certification data could support the development of radically transparent and secure schemes, though H2Global acknowledges blockchain’s key limitations. To illustrate its potential, H2Global points to the success of two currently operating schemes based on blockchain: “GreenToken” and “Clean Energy Certification as a service” (CEC).
IEA: ammonia key to decarbonising shipping by 2050
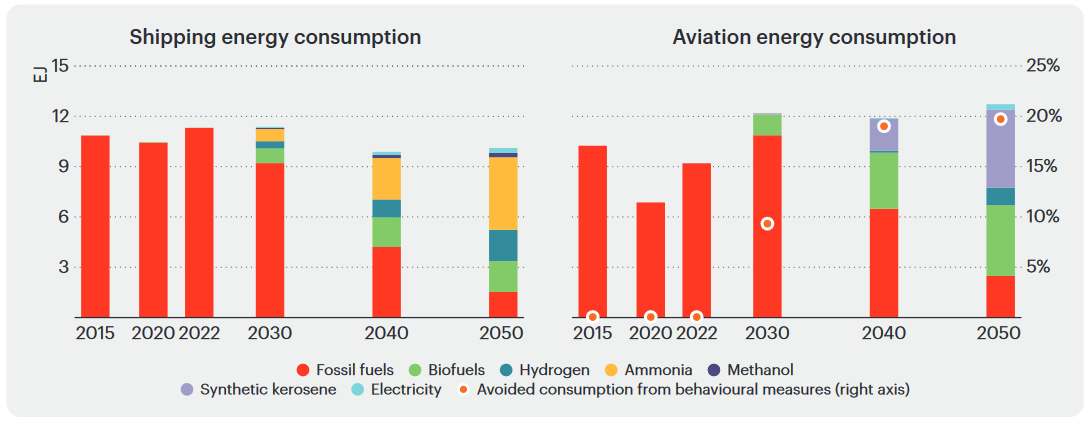
With international shipping activity to more than double by 2050, the IEA forecasts that ammonia’s share of final energy consumption in the industry will rise to 44% in 2050, with a suite of other low-carbon fuels to play smaller roles. Lloyd’s Register & OCI HyFuels have also forecast that ammonia (and particularly electrolytic ammonia) will become the most significant fuel in the maritime sector by 2050.
Technology Status: Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) Electrolysis
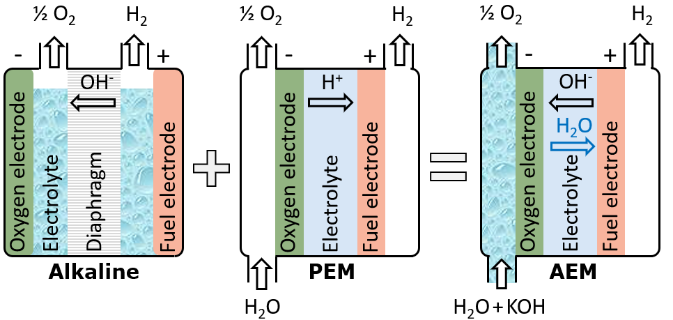
Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) electrolysis combines concepts from alkaline and PEM. Although AEM can potentially offer the best of both worlds compared to conventional technology, challenges such as oxygen sensitivity, stack scale-up and current density still need to be addressed. Germany-based Enapter is leading the commercialization of AEM systems, with other electrolyzer manufacturers now developing their own products.