Ammonia Gas Turbine
Hanwha Power Systems: deploying ammonia gas turbines onboard vessels
Hanwha Power Systems and GasLog will develop a comprehensive demonstration plan for the retrofit of existing large LNG carriers to be powered by ammonia gas turbines.
Finalists revealed for ammonia bunkering, power generation pilot on Jurong Island
Two potential consortia have been selected to develop and operate an ammonia power generation and bunkering pilot on Jurong Island, Singapore. Either Keppel Infrastructure or Sembcorp-SLNG will be selected to lead the project, which will feature a 60 MW, direct ammonia-fed gas turbine, linked to a 100,000 ton ammonia bunkering facility.
The 3rd Symposium on Ammonia Energy: Shanghai, Sept 22-26
Learn more about the 3rd Symposium on Ammonia Energy, to be held in Shanghai from 22-26 September this year. The AEA is a proud supporter of the event, which will showcase the latest R&D in ammonia energy. Hear from a program of global researchers, take part in industry collaboration workshops, and get the chance to explore local R&D in a series of site visits.
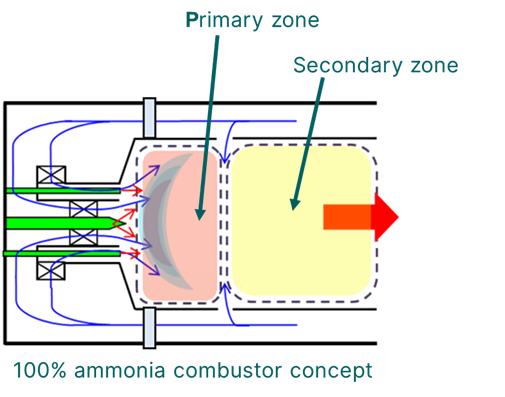
GE, IHI progress ammonia gas turbine technology roadmap
GE Vernova and IHI Corporation will proceed to the engineering and testing phase for their ammonia gas turbine roadmap for Asia. Based on their efforts in 2022 to demonstrate a low-N2O combustor for a 2 MW, 100% ammonia-fired turbine, IHI will lead development of a two-stage combustor for larger-scale gas turbine models.
PTT & MHI: ammonia energy in Thailand
In a 4-year partnership, PTT Global Chemical will collaborate with MHI to explore the feasibility of a large scale carbon neutral petrochemical complex in Thailand, powered by low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia-fueled gas turbines.
Ammonia-fired gas turbines in Ireland
Centrica Energy, Bord Gáis Energy and Mitsubishi Power will explore the development of Europe's first ammonia-fired power generation facility, based on the existing Whitegate power plant in Cork.