Ammonia Markets
Industry report sees multi-billion ton market for green ammonia
This week, Argus Media published a white paper on green ammonia. This includes an overview of potential new markets and market volumes, a round-up of green ammonia projects around the world, and an assessment of production technologies and their impact on the ammonia cost curve. Argus estimates that, by 2040, green ammonia could cost just $250 per ton. Argus is an industrial analysis and consulting firm with long experience in the ammonia market, which, traditionally, centers on the fertilizer sector. This white paper therefore provides a welcome commercial perspective on the outlook for ammonia energy.
South Korea Launches Hydrogen Cities Initiative
In October 2019 South Korea’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism announced a “hydrogen-powered cities” initiative that the World Economic Forum characterized as a bid to “win the race to create the first hydrogen-powered society.”
Maritime decarbonization is a trillion dollar opportunity
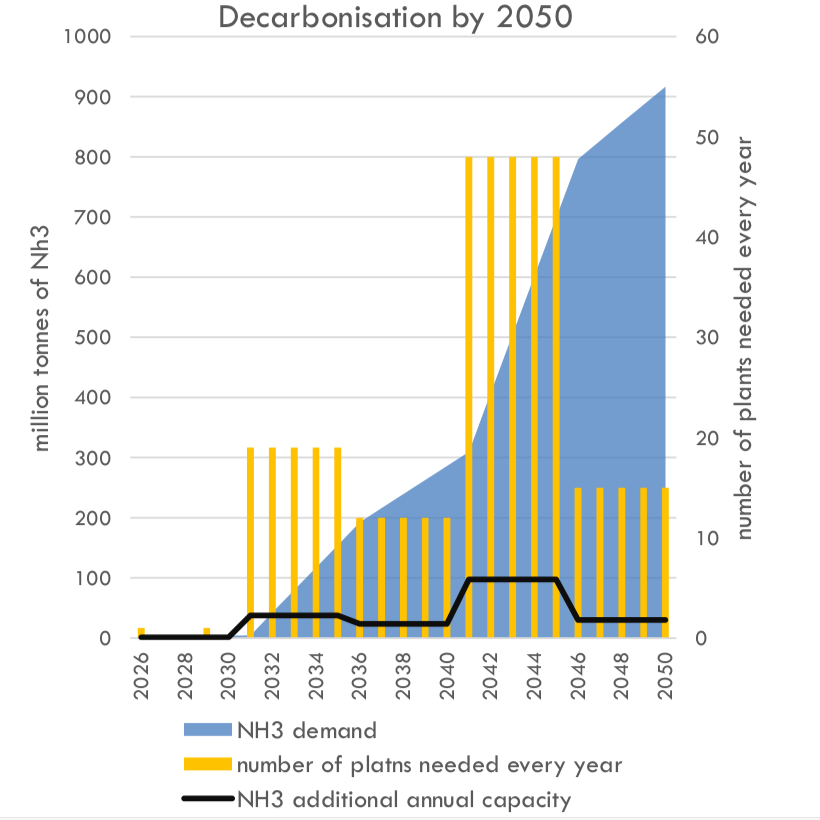
In January 2020, the Global Maritime Forum published new analysis that calculates "the capital investment needed to achieve decarbonization" in line with the International Maritime Organization's Initial GHG Strategy. The result of this analysis, which assumes that ammonia will be "the primary zero carbon fuel choice adopted by the shipping industry," is an aggregate investment of between $1 trillion and $1.4 trillion dollars, from 2030 to 2050, or roughly $50 to $70 billion per year across two decades. Ship-side costs are only 13% of this number. The bulk of the investment will be directed towards green ammonia plants for maritime fuel synthesis. By 2050, this global fuel demand is estimated to be more than 900 million tons per year of green ammonia, more than five time today's total global output of conventional ammonia.
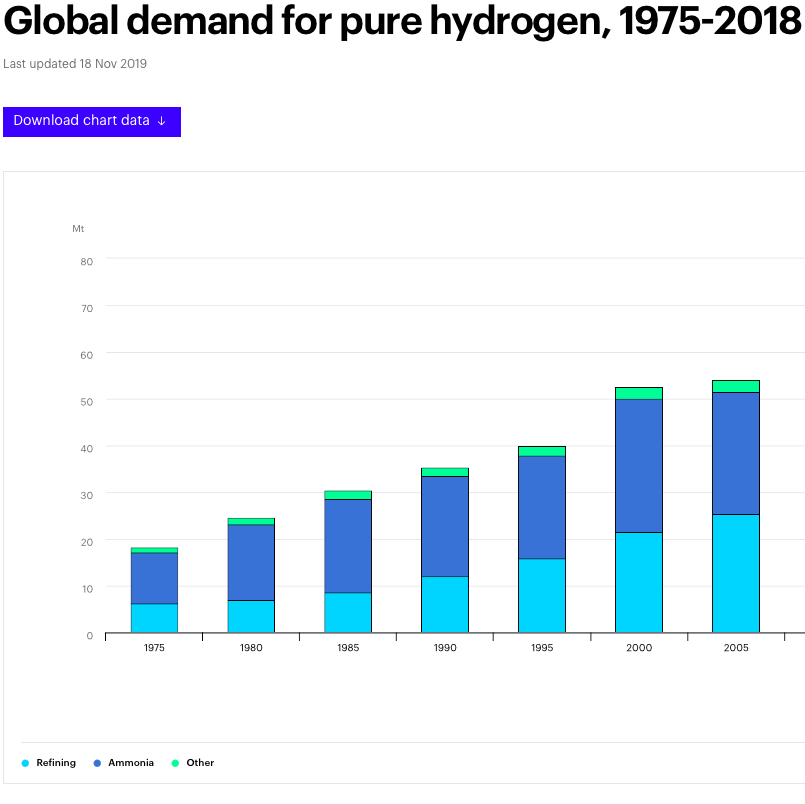
Updating the literature: Ammonia consumes 43% of global hydrogen
For years, many people — myself included — have been saying that ammonia consumes 55% of the hydrogen produced around the world. Although there are many authoritative sources for this figure, I knew that it was likely out of date. Until now, I had overlooked the International Energy Agency (IEA) 2019 report, The Future of Hydrogen, which provides up-to-date (and publicly downloadable) data for global hydrogen demand since 1975. According to the IEA, ammonia represented almost 43% of global hydrogen demand in 2018; refining represented almost 52%, and "other" demands accounted for 6%.
Keynote Speech: Implementation of Ammonia Energy Value Chain
Biomass Based Sustainable Ammonia Production
Ammonia Production Can be Practically Free
IEA Analysis: Green Chinese P2A Could Compete with Brown NH3
The IEA has developed a rigorous economic model to examine the proposition that resource intermittency can be managed by siting hydrogen facilities where variable renewable energy (VRE) resources have complementary daily and seasonal production profiles. Last month, IEA Senior Analyst Cédric Philibert shared modeling results from selected sites in China with an audience at the Energy Research Institute in Beijing. The exercise offers a first quantitative look at two important questions. First, what is the economic impact of "VRE stacking"? And second, what is the relative cost position of ammonia produced via a stacking approach?