Improved Haber-Bosch
Demonstrating CCS-based ammonia technologies in Japan
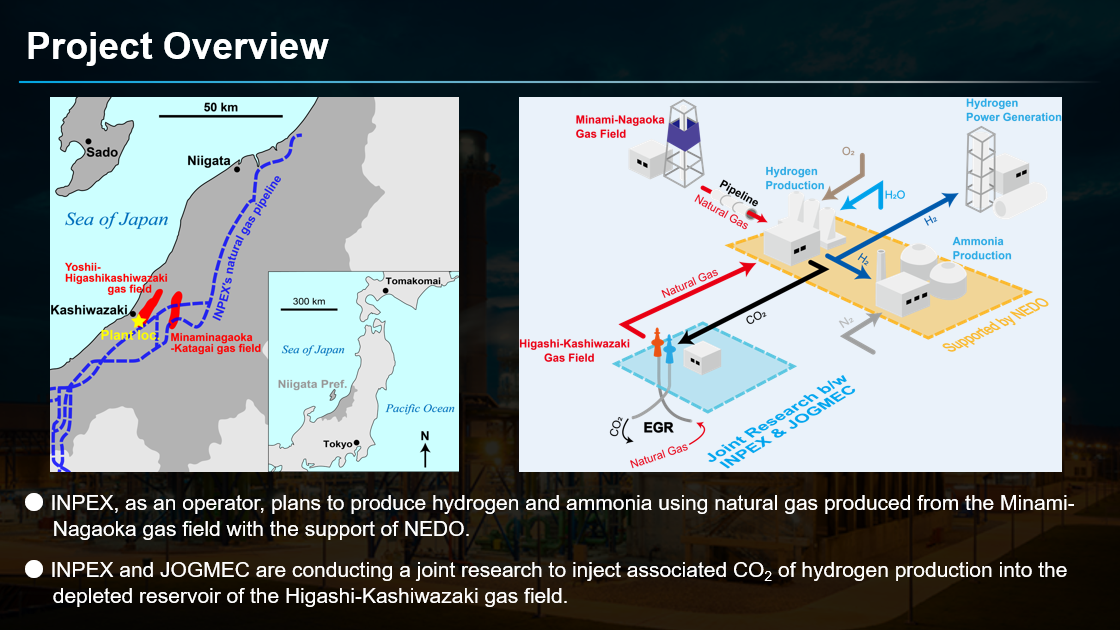
Our June episode of Ammonia Project Features focused on a new project in Niigata prefecture, which will demonstrate low-carbon, fossil-based ammonia production with a capacity of 500 tonnes per year. As part of the project, Japanese government organization JOGMEC will work with INPEX to develop enhanced gas recovery & CO2 sequestration monitoring technologies. Tsubame BHB will deploy its low-temperature, low-pressure ammonia synthesis technology based on an electride-supported catalyst developed at the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
Alternative synthesis start-ups: exploring the growing ecosystem in Australia and New Zealand
A fast-growing ecosystem of startups is progressing various technology pathways in Australia and New Zealand. Melbourne-based Jupiter Ionics is developing an electrolytic cell that will directly reduce nitrogen to ammonia under mild temperature and pressure conditions. In New Zealand, Liquium is embarking on a pilot-scale deployment of its miniaturised Haber Bosch technology. The University of Newcastle and Element One are progressing validation and pilot-phase deployments of AMMONIAC - a novel, “chemical-looping” ammonia production system. And in Sydney, PlasmaLeap is developing a plasma-based system, with on-farm trials already planned.
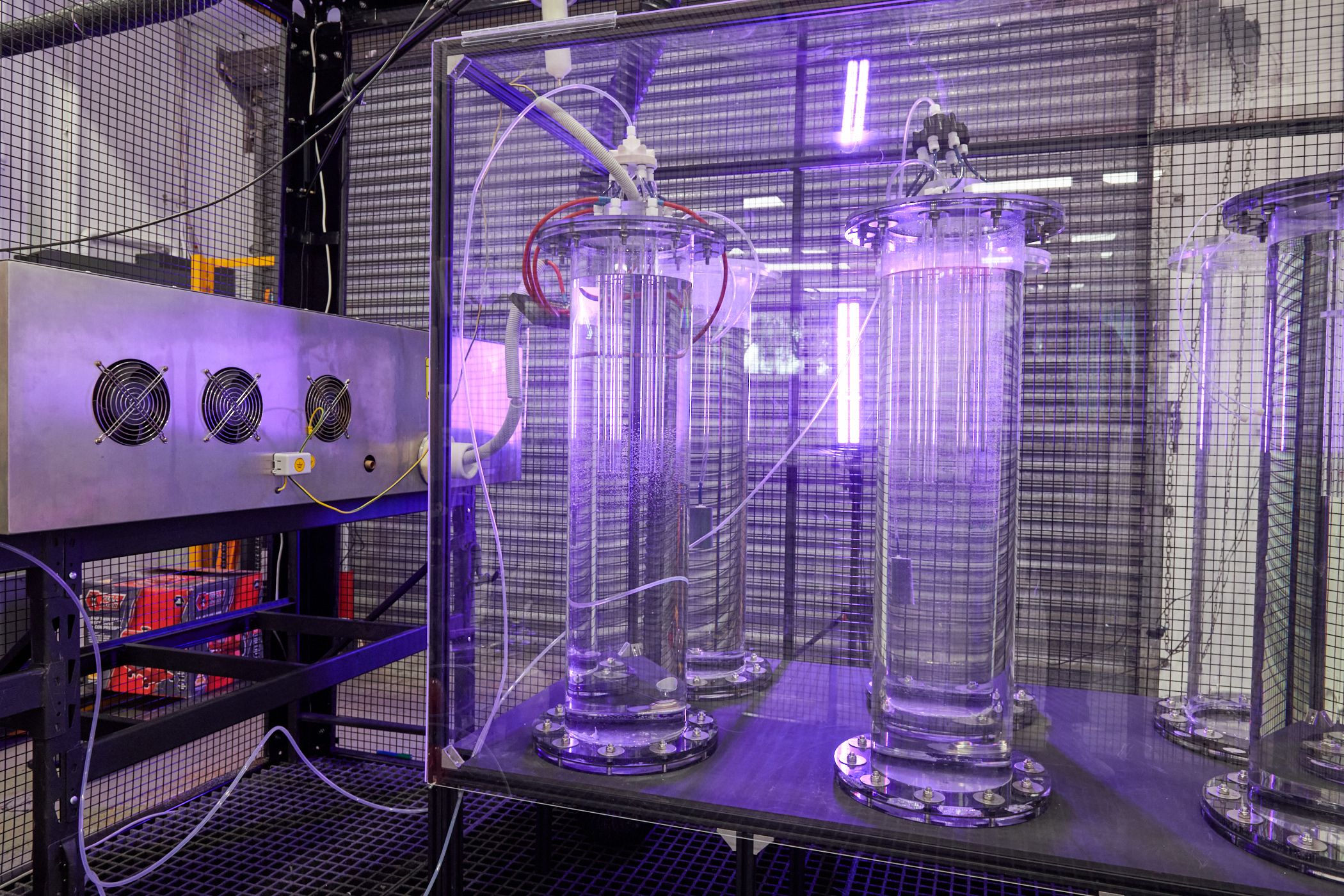
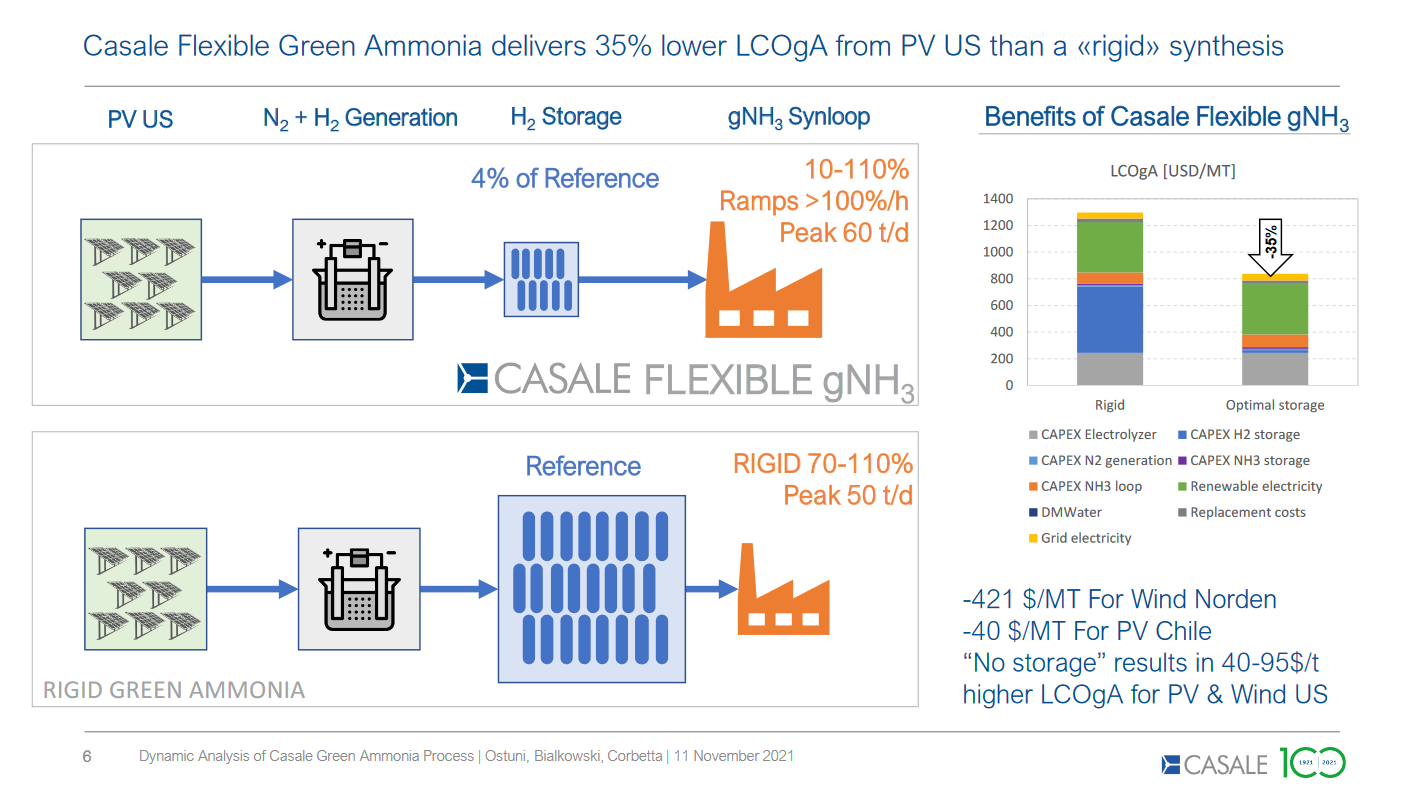
Flexible ammonia synthesis: shifting the narrative around hydrogen storage
Flexible ammonia production technology is currently scaling up to meet the challenges of fluctuating electricity feedstock. The ability to ramp down plants to 5 - 10% of their nominal load will minimize the requirement for hydrogen storage buffers and reduce the overall cost of renewable ammonia production. The first demonstration-sized flexible ammonia plants are due to begin operations later this year.
3rd generation ammonia synthesis: new catalysts & production pathways
We look at four new developments this week:
1. A team from DTU Energy and the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics have uncovered a new class of alternative catalysts for mild condition ammonia synthesis. The ternary ruthenium complex hydrides Li4RuH6 and Ba2RuH6 avoid the energy-intensive pathway of nitrogen dissociation in a "synergistic" manner.
2. A team from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials reported a highly selective (95%) plasma ammonia synthesis method.
3. A team from Delft University of Technology has presented an present an "unconventional electrochemical design" that physically separates hydrogen and dinitrogen activation sites.
4. A team at the Max Planck Institute for Coal Research has demonstrated a new mechanochemical ammonia synthesis system that operates at room temperature and pressures as low as 1 bar.