Improved Haber-Bosch
Microwave Catalysis for Ammonia Synthesis Under Mild Reaction Conditions
Advanced Catalysts Development for Small, Distributed, Clean Haber-Bosch Reactors
Vanadium As a Potential Catalytic Membrane Reactor Material for NH3 Production
Advances in Making High Purity Nitrogen for Small Scale Ammonia Generation
Scale up and Scale Down Issues of Renewable Ammonia Plants: Towards Modular Design
Ammonia Absorption and Desorption in Ammines
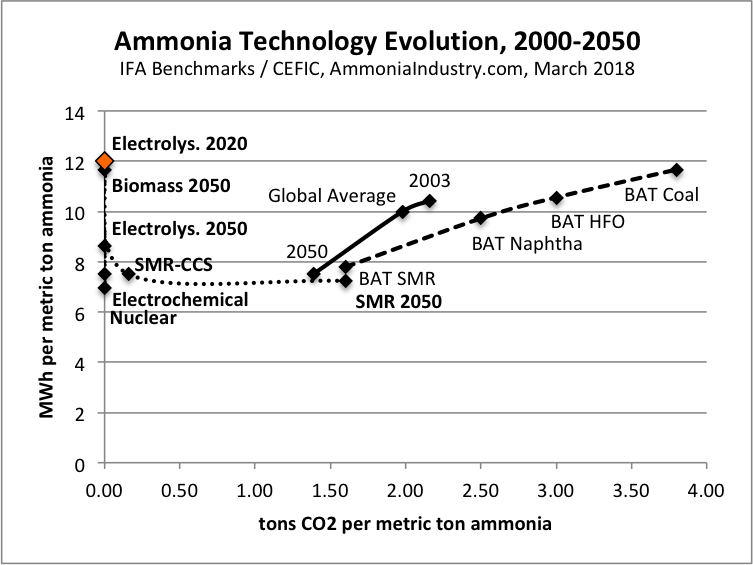
Ammonia technology portfolio: optimize for energy efficiency and carbon efficiency
Earlier this month, I had the pleasure of speaking at the International Fertilizer Association's (IFA) conference on the subject of Innovations in Ammonia. A key point was the benefit of technology diversification: as with any portfolio, whether an investment account or a global industry's range of available technologies, concentration in any area represents risk, and diversification represents resiliency. Unfortunately, the ammonia industry has grown highly concentrated, and its dependency upon one technology and one feedstock represents significant risk in tomorrow's markets. This article features five charts that aim to demonstrate why energy efficiency is insufficient as the only measure of technology improvement, why it is better to optimize instead of maximize, and why market evolution is necessary to support investment decisions in sustainable ammonia synthesis technologies.
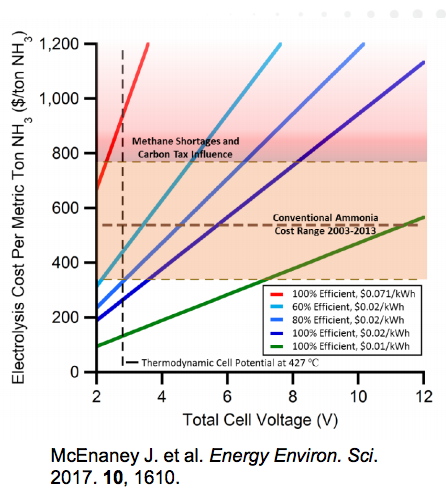
The Future of Ammonia: Improvement of Haber-Bosch ... or Electrochemical Synthesis?
During our NH3 Energy+ Topical Conference, hosted within AIChE's Annual Meeting earlier this month, an entire day of presentations was devoted to new technologies to make industrial ammonia production more sustainable. One speaker perfectly articulated the broad investment drivers, technology trends, and recent R&D achievements in this area: the US Department of Energy's ARPA-E Program Director, Grigorii Soloveichik, who posed this question regarding the future of ammonia production: "Improvement of Haber-Bosch Process or Electrochemical Synthesis?"