Ammonia technology portfolio: optimize for energy efficiency and carbon efficiency
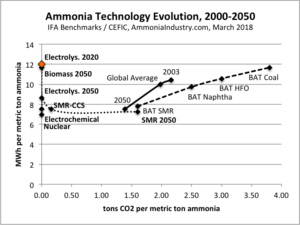
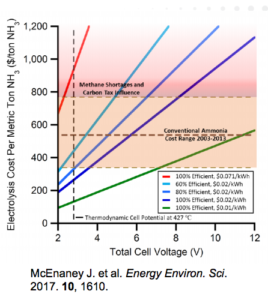
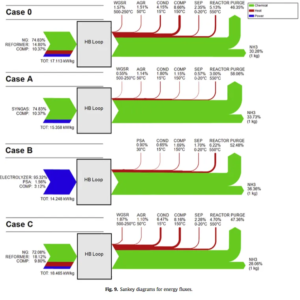
Earlier this month, I had the pleasure of speaking at the International Fertilizer Association's (IFA) conference on the subject of Innovations in Ammonia. A key point was the benefit of technology diversification: as with any portfolio, whether an investment account or a global industry's range of available technologies, concentration in any area represents risk, and diversification represents resiliency. Unfortunately, the ammonia industry has grown highly concentrated, and its dependency upon one technology and one feedstock represents significant risk in tomorrow's markets. This article features five charts that aim to demonstrate why energy efficiency is insufficient as the only measure of technology improvement, why it is better to optimize instead of maximize, and why market evolution is necessary to support investment decisions in sustainable ammonia synthesis technologies.