The International Energy Agency (IEA) has just published Energy Technology Perspectives 2017, the latest in its long-running annual series, subtitled "Catalysing Energy Technology Transformations."
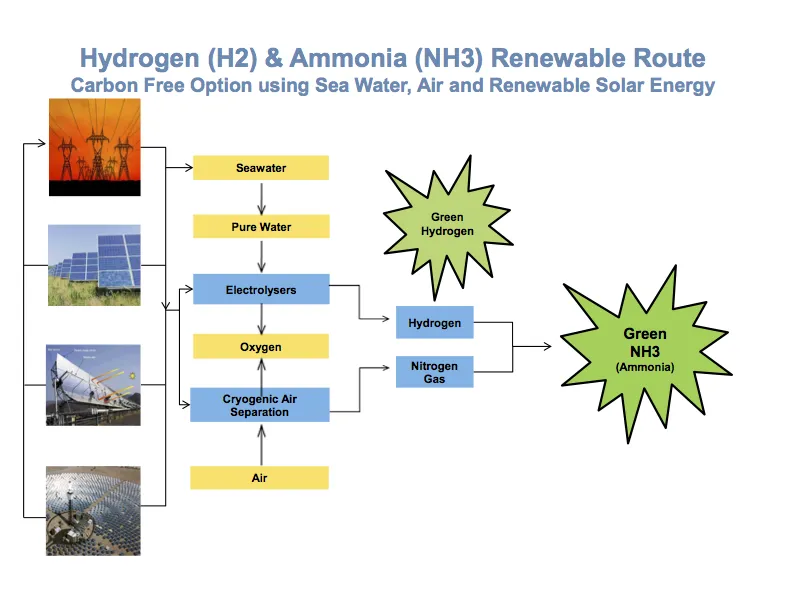
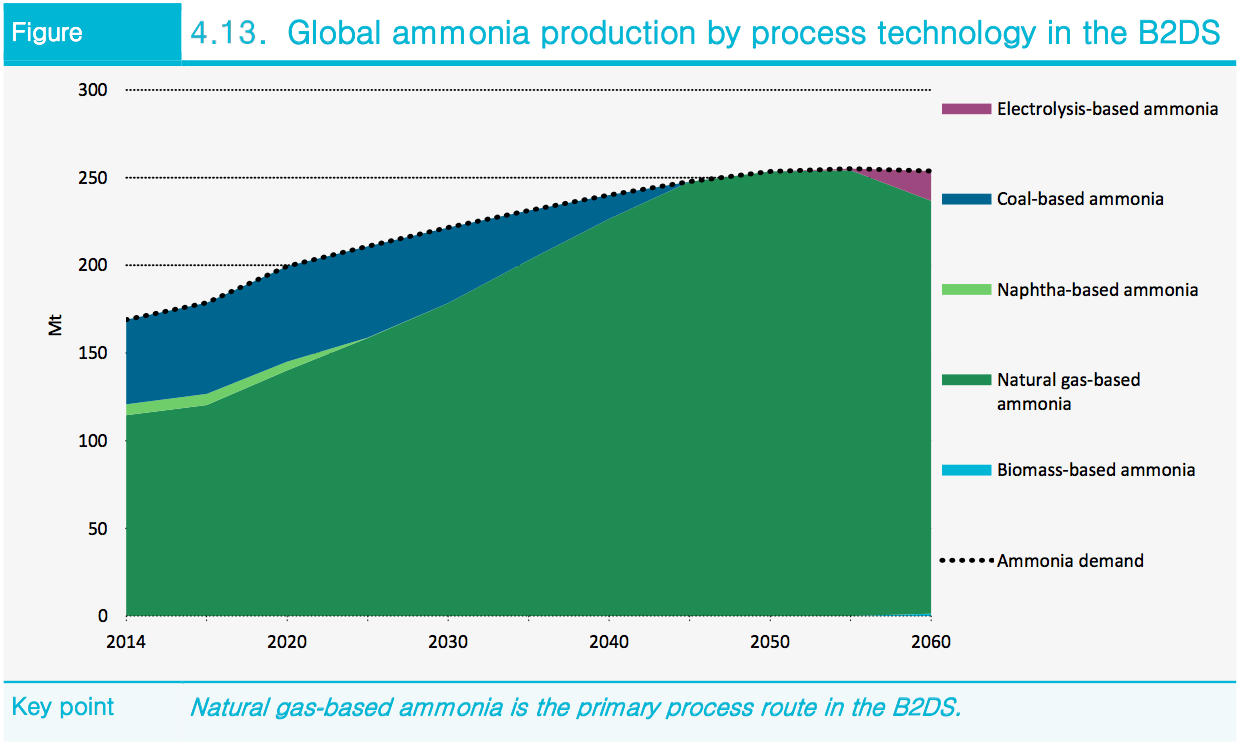
In this year's edition, for the first time, ammonia is featured in two major technology transformations. First, ammonia production is shown making a significant transition away from fossil fuel feedstocks and towards electrification, using hydrogen made with electrolyzers. And, following this assumption that sustainable ammonia will be widely available in the future, the IEA takes the next logical step and also classifies ammonia "as an energy carrier," in the category of future "electricity-based fuels (PtX synthetic fuels)."
The inclusion of this pair of technology transformations represents a major step towards broader acceptance of ammonia as an energy vector, from the perspectives of both technical feasibility and policy imperative.