NH3 Fuel Association President Presents at AIChE Annual Meeting
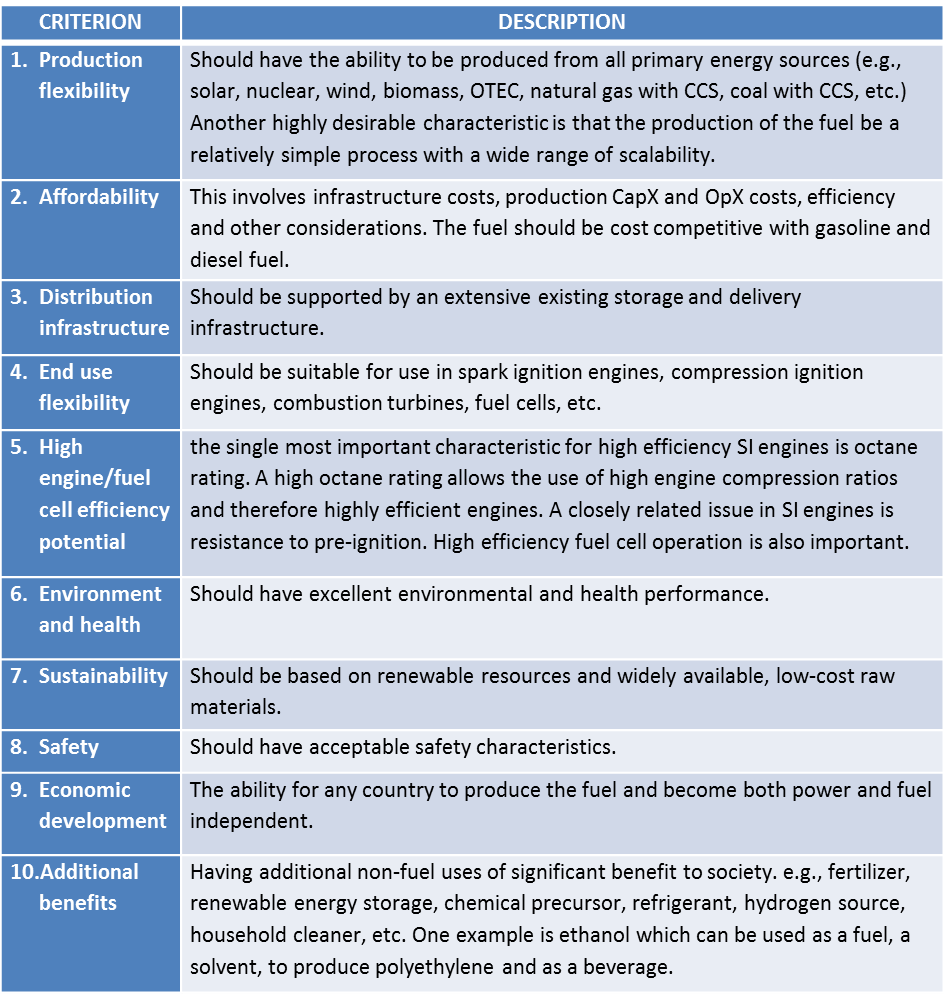
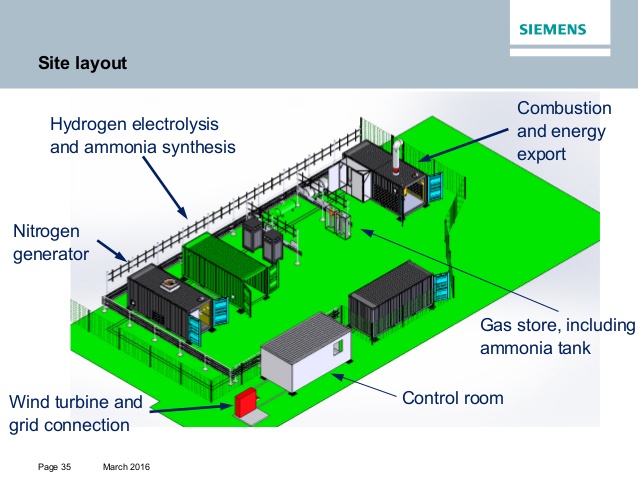
NH3 Fuel Association President Norm Olson presented his paper “NH3 – the Optimal Liquid Transportation Fuel” on November 9 at the annual meeting of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE). The AIChE meeting, held over six days in San Francisco, provided a wide-ranging perspective on the sustainable energy landscape that ammonia energy must compete within.