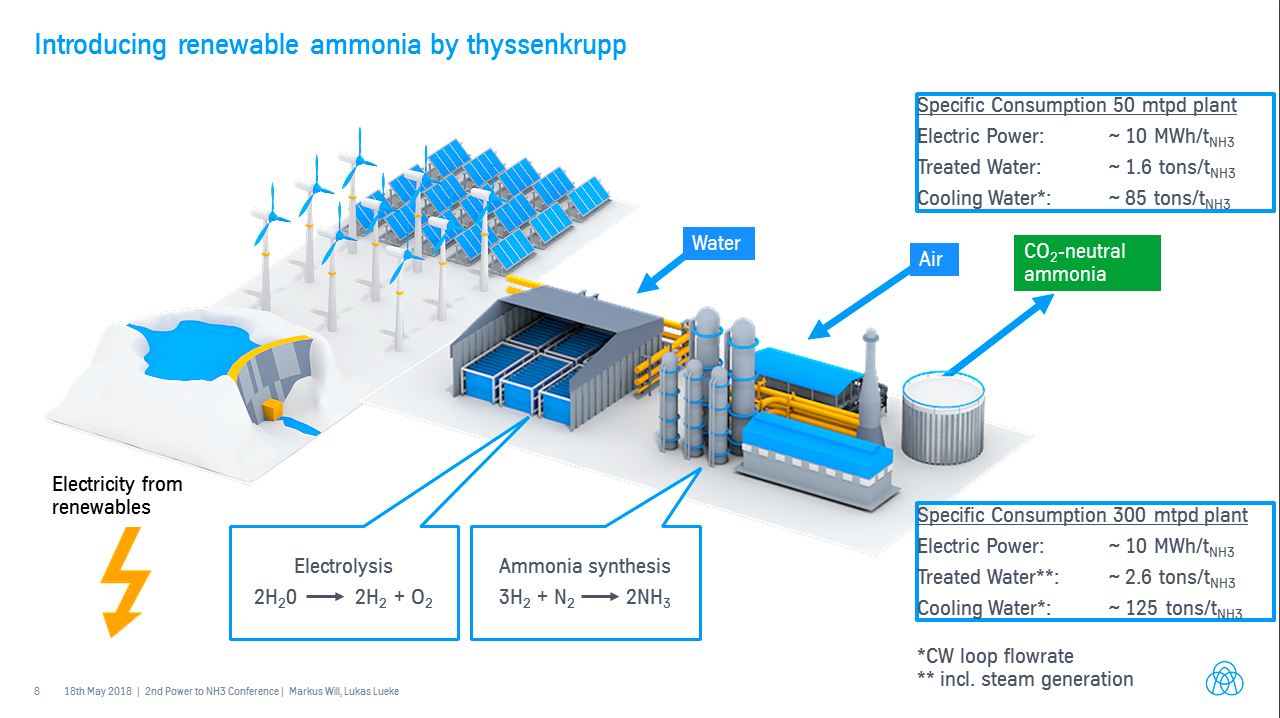
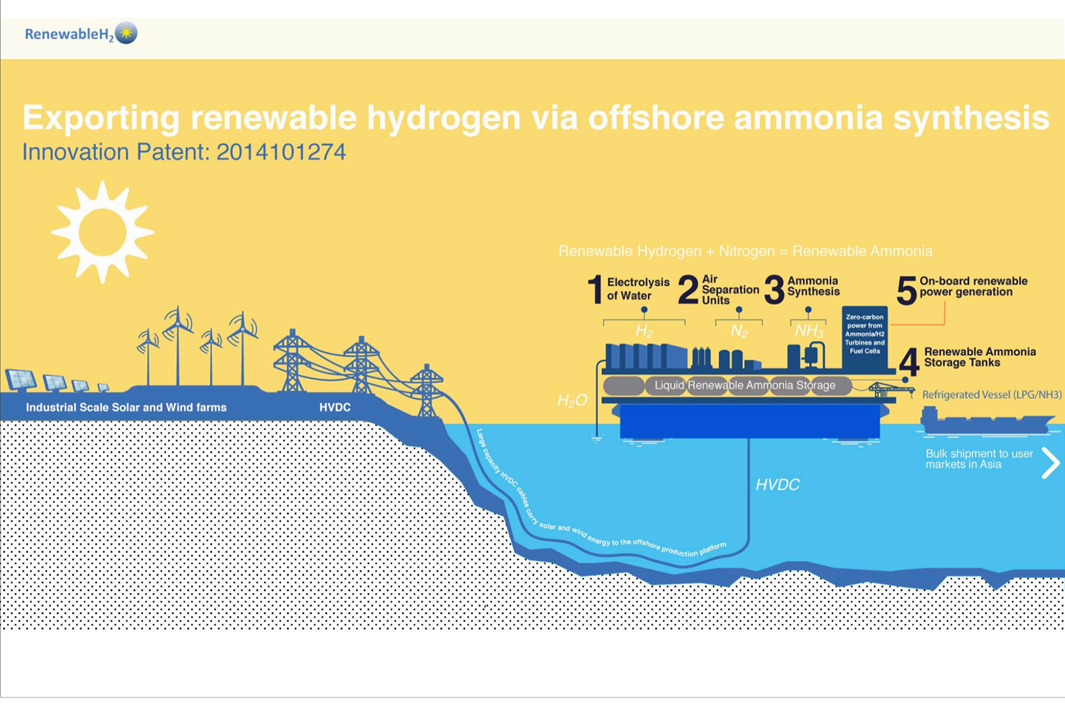
Green ammonia plants are being announced quicker than I can report. Here is a summary of four new projects that propose to use electrolyzers, fed by renewable power, to produce hydrogen for ammonia production. These are big companies, operating in regions with excellent renewable resources, making significant investments in their future. In Chile, it is Enaex, a major ammonium nitrate manufacturer, supplying explosives to the mining industry. In Australia, it is Incitec Pivot, "the second largest supplier of explosives products and services in the world," and Wesfarmers, "the largest Australian company by revenue," according to Wikipedia. In New Zealand, it is Ballance-Agri Nutrients, a big farmers' co-operative and the country's sole fertilizer producer. Each aims to make its business "future-proof." The transition from fossil ammonia to renewable ammonia is underway.