Interim guidelines released for safe ammonia imports in Japan
By Julian Atchison on March 31, 2025
Guidance for existing ports
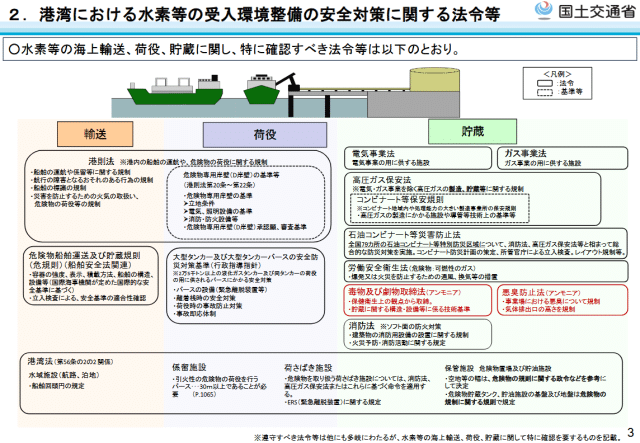
Click to enlarge. The ecosystem of laws and regulations related to the transport, loading/unloading and storage of dangerous cargoes like hydrogen and ammonia, which Japanese ports will have to consider. From Guidelines for Improving the Environment for Receiving Hydrogen and Ammonia at Ports (Interim Summary) (Mar 2025).
Commissioned by the Port Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), an expert review committee is in the process of finalising new guidelines for the safe importation of hydrogen and ammonia into Japan. The guidelines will identify key legislative considerations for port authorities, outline some design, infrastructure, process and safety considerations for current port managers, and is intended to act as a useful starting point for relevant stakeholders to plan for new energy imports.
The guidelines consider an ecosystem of existing laws and regulations that will have to be taken into account for hydrogen and ammonia imports. As well as highlighting some key laws and explaining the implications for port authorities, the guidelines summarize an extensive list of relevant Japanese legislation, including:
Port Regulations Law, Regulations for the Transportation and Storage of Dangerous Goods on Ships (Dangerous Goods Regulations), Port and Harbor Law, Standards for Safety and Disaster Prevention Measures for Large Tankers and Large Tanker Berths (Administrative Guidance Guidelines), High Pressure Gas Safety Law, Electricity Business Law, Gas Business Law, Petroleum Industrial Complex Disaster Prevention Law, Industrial Safety and Health Law, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law (ammonia), Odor Prevention Law (ammonia), Fire Service Law.
Main regulations and provisions related to the consideration of the layout and operation of port facilities for hydrogen and ammonia imports, translated from Guidelines for Improving the Environment for Receiving Hydrogen and Ammonia at Ports (Interim Summary), Mar 2025
The main focus of the new guidelines will be on infrastructure and design considerations: the layout and operation of mooring facilities, cargo handling facilities installed on mooring facilities, pipelines, etc. The final guidelines will suggest that:
- Hydrogen and ammonia ships have mooring points and wharf space that does not overlap with “other wharf uses”, as well as an additional buffer distance to other ships and an exclusion zone for loading arms.
- Pipelines removing hydrogen or ammonia from the mooring point may need to be raised or buried to allow the passage of vehicles and workers, with certain legal requirements in either scenario.
- Infrastructure expansion plans need to be established early, so as to retain mandatory separation distances between structures and outside land. The same is true for plans to receive larger capacity vessels.
- And the continued effects of sea level rise and extreme weather must be considered in facility design, future proofing import bases.
A detailed interim report into the development of the guidelines can be accessed here (Japanese language).