Preparing the Netherlands for large-scale ammonia imports
By Geofrey Njovu on May 25, 2023

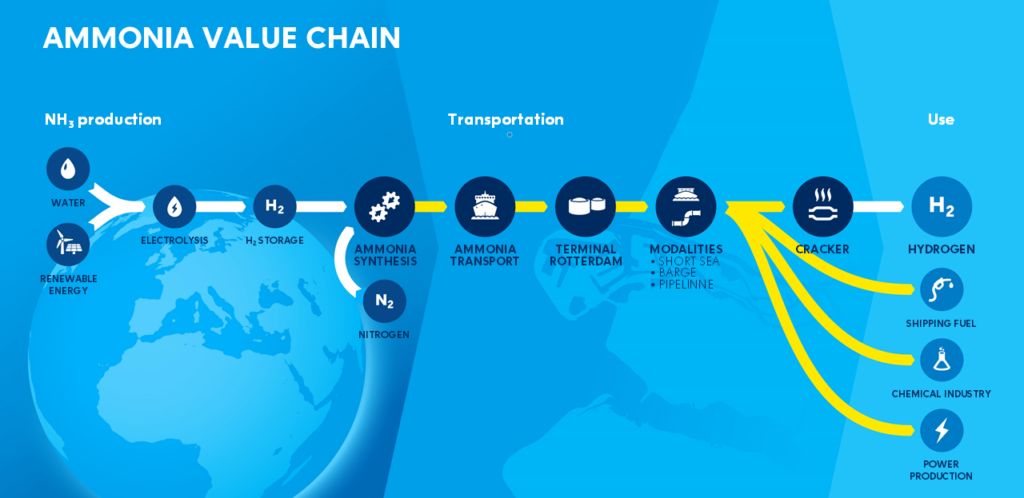
Last December, a pre-feasibility study was commissioned by the Port of Rotterdam Authority and 17 other companies from northwest Europe to explore cracking technologies available to enable hydrogen import as ammonia. Study results have just been released, with the conclusion that it is “technically and economically feasible to safely convert ammonia into 1 million tons of hydrogen per year using a large-scale cracker” at the Port.
Key findings include:
- From a range of suppliers including Haldor, Topsoe, KBR, Thyssenkrupp, Johnson Matthey, Duiker, Casale and H2SITE, ammonia cracking technology is currently commercially available to produce 1 million tons of renewable hydrogen annually.
- Through examining several cracking set up scenarios, the study finds that using a centralized, large-scale ammonia storage and cracker setup might have cost and efficiency benefits compared to using decentralized crackers or storage points.
- Ammonia crackers fit within the safety contours of the port, which has significant experience of safe ammonia storage and transportation for the fertiliser industry.
Cracking technology will be essential for hydrogen import and transportation. The parties involved plan to use this study as a basis for future projects and collaborations.
Dutch authority to “modernise” ammonia storage and loading guidelines
VOTOB, the Dutch Association of Tank Storage Companies, is pulling together a working group to revise PGS-12: the Netherland’s national ammonia storage and loading guideline (Dutch language). It details the risks associated with ammonia handling and standards to be used to ensure employ, environmental safety and fire safety precautions. The working group’s purpose is to “modernise” the guideline to align with “state-of-the-art” best practices.
This is particularly important, as increasing import of large hydrogen quantities in the form of ammonia increases the urgency and demand for safe ammonia terminals and offloading facilities in the Netherlands. The 4-chair workgroup will constitute delegates from Vopak, OCI, Yara and Proton Ventures who will collectively aim to improve the PGS-12. This will lead to a transparent guideline for safe ammonia terminals throughout the country.
The urgency in modernizing PGS-12 to new safety and efficiency levels is evident since ammonia is ever more considered as one of the leading energy carriers by, practically, all major Terminal Operators in The Netherlands…The workgroup constituted by YARA, OCI, VOPAK and Proton shall set up all technical recommendations for the Terminal of the Future addressing safety, energy-efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Willem-Henk Streekstra, Director of VOTOB, in Proton Ventures’ official press release, 1 May 2023