Ammonia fuel for glass production demonstrated in Japan
By Julian Atchison on September 19, 2023
Asahi Glass Corporation

Earlier this June, AGC announced it had successfully used 100% ammonia fuel to produce architectural glass over two days of testing at its Yokohama Technical Center. The project is an ongoing joint effort, with technical contributions from Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology & Tohoku University, and support from government body the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). AGC confirmed that effects on glass quality and furnace materials, control of flame temperature, furnace temperature, and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions were all within acceptable limits.
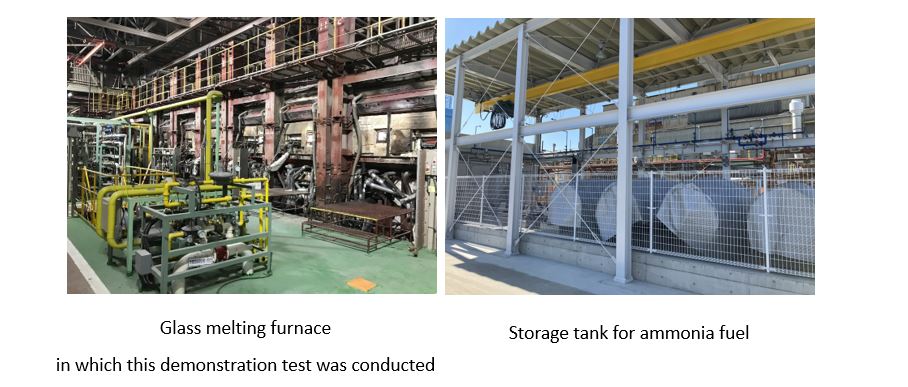
An ammonia-oxygen burner was developed by Taiyo Nippon Sanso, and designed to “prevent a rapid rise in flame temperature through multi-stage combustion”. Compared with conventional fuel combustion (and with tests run under various conditions), the NOx concentration in the exhaust gas was found to be below environmental thresholds, while maintaining the required temperature of the glass melting furnace. From next year, the partners plan to conduct scaled-up tests and demonstrate the technology at other AGC sites. From 2026, AGC’s goal is to fully introduce ammonia combustion technology across its operations. The technology could also be applied to manufacturing other materials such as steel or aluminium.
…and cement!
The news follows an announcement from Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation in April. MUCC revealed it had begun ammonia co-combustion tests to produce cement clinker at its Ube Cement Plant (clinker is an intermediary product leading to Portland cement). To this point, coal has been the primary fuel in this process, with about one tonne of carbon dioxide emitted for every tonne of limestone processed. MUCC reports successful tests, with a goal to increase co-combustion in stages up to 30%. MUCC predecessor Ube Industries participated in the Japanese government’s Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP) from 2014 to 2018.