GE, IHI progress ammonia gas turbine technology roadmap
By Julian Atchison on February 06, 2024
From feasibility to engineering
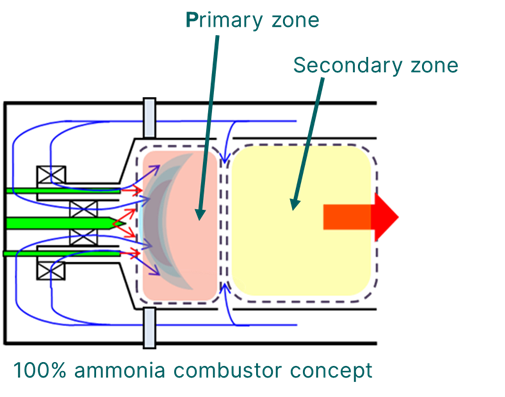
Click to expand. A two-stage combustor for 100% ammonia fuel in gas turbines, under development by IHI and GE Vernova. Source: GE Vernova.
Following two years of exploratory studies into the economic feasibility of deploying 100% ammonia-fired gas turbines across Asia, GE Vernova and IHI Corporation will proceed to an engineering and testing phase. Based on their efforts in 2022 to demonstrate a low-N2O combustor for a 2 MW, 100% ammonia-fired turbine, IHI will lead development of a two-stage combustor for larger-scale gas turbine models. Combustion testing will take place in IHI’s facilities in Japan.
Following two years of joint studies on the economics of the ammonia value chain, we are now thrilled to ink a new chapter in our collaboration with IHI and proceed to the next phase…With GE Vernova’s expertise in engineering and manufacturing of gas turbine combustion systems and balance of plant systems, and IHI’s know-how in ammonia combustion technology, we’ll be focused on the technological development and technical deliverables, aiming for the validation of the combustion technology in the next two years, and to a potential commercially available product by 2030.
Jeffrey Goldmeer, GE Vernova Director of Hydrogen Value Chain in his organisation’s official press release, 24 Jan 2024
IHI and GE Vernova are already working with Sembcorp to retrofit gas turbines at Sembcorp’s Sakra power plant to run on 100% ammonia fuel. The Sakra power plant features two GE 9F gas turbines – one of the three models combustor retrofits are being developed for under the roadmap agreement.
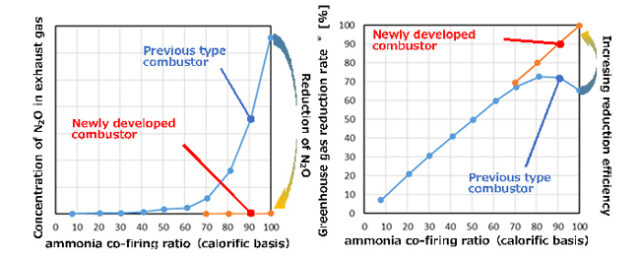
Click to learn more. IHI demonstrated a low-N2O combustor for a 100% ammonia-fired, 2 MW gas turbine in 2022, and will base development of utility-scale combustors on this research. Source: IHI Corp.
In their 2022 demonstration, IHI improved on previous ammonia-capable combustors. To that point, ammonia fuel co-firing above 70% resulted in significant N2O emissions, and an overall drop in the greenhouse emissions reduction capability of the system. Development and subsequent demonstration of the two-stage process almost eliminated N2O emissions.
The joint exploration will focus on crafting the combustion system that will convert GE’s F-class turbines, already deployed worldwide, to burn ammonia at scale. According to Goldmeer, that will require a two-stage combustion system, featuring “both a rich and a lean stage,” because even when you burn ammonia originally made with carbon-free sources, nitrogen oxide emissions are potentially very high. Getting those under control is critical for the IHI and GE Vernova teams, who will share in the fruits of their progress — and in any intellectual property that emerges from their venture.
From Ammonia’s Big Bang: GE Vernova and Japan’s IHI Aim to Unleash Ammonia Value Chain, 24 Jan 2024