Mitsubishi Heavy Industries: successful combustion test of ammonia single-fuel burners
By Geofrey Njovu on January 09, 2024
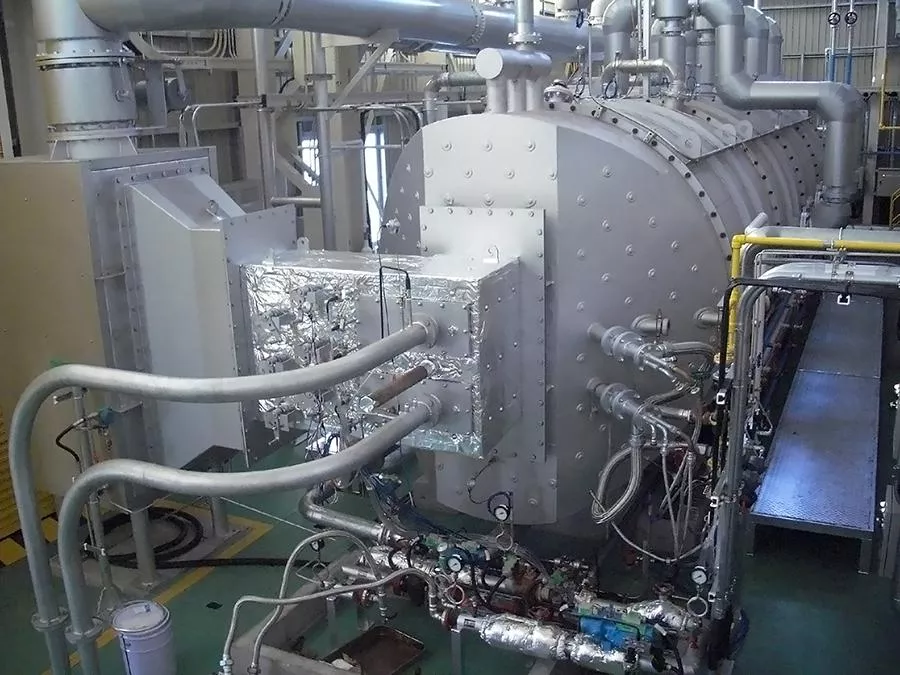
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has completed a combustion test of its ammonia single-fuel burner at the Nagasaki District Research & Innovation Center in Nagasaki. The test revealed stable ammonia combustion and suppressed nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions compared to coal firing, both crucial factors for the use of ammonia fuel in thermal power generation boilers.
A combustion test furnace with a 0.5 tonnes-per-hour fuel consumption rate was used to conduct two tests: a single-fuel burner test using an ammonia burner, and a high-ratio ammonia co-firing test with coal.
MHI initially announced plans to develop both single and mixed ammonia-capable boilers in 2021. By 2024, the group plans to develop ammonia single-fuel firing burners for both circular firing and opposed firing. This test is part of the Fuel Ammonia Supply Chain Establishment project conducted by the Green Innovation Fund Project.
Going forward, MHI plans to scale the test to simulate operations in a large, 4 tonne-per-hour test furnace. Pending successful testing, steps will be taken towards commercial application of the burner in thermal power plants in Japan and beyond. Potential applications include low-ratio to high-ratio co-firing with coal in utility and industrial boilers. Ammonia combustion technology is gaining traction in Japan. In 2023, an ammonia-oxygen burner was tested with success in glass production, and ammonia was co-combusted with gas to power cement clinker production.