NH3 Fuel Conference 2018
October 31, 2018 November 1, 2018 David L. Lawrence Convention Center, Pittsburgh, PA Pittsburgh United States
31 October – 1 November
Schedule
Opening Session: “Ammonia Energy Technology Roadmap”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 8:00 am 9:30 am
Presentation
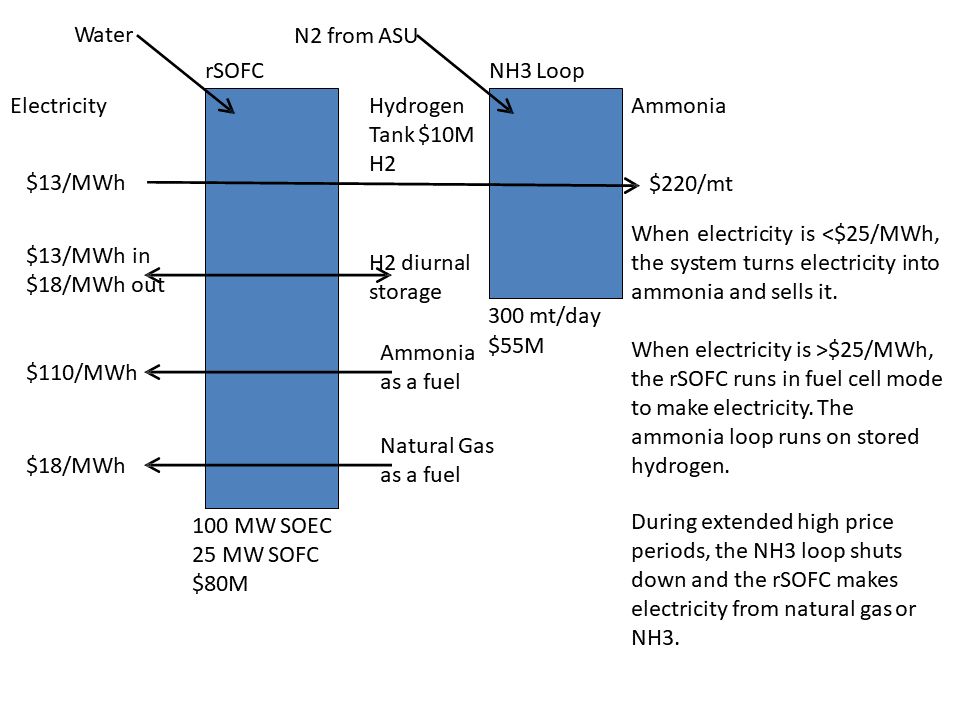
The Battolyser as a tool to overcome production problems by the intermittancy of green energy
The intermittency of sustainable energy sources calls for either flexible production or storage of energy, to keep continuous processes running continuously. The newly developed Battolyser technology has the possibility of both, creating flexible production and storage in one piece of equipment. The Battolyser is therefore a tool to keep production processes of hydrogen and / or ammonia under a continuous mode at lowest CAPEX. The design of this Battolyser can be such that the vulnerable ammonia Haber Bosch synthesis process can be kept in operation during certain periods of outage of (green) power, without installing additional large batteries. The Battolyser…
Presentation
Power-to-Ammonia-to-Power (P2A2P) for Local Electricity Storage in 2025
A carbon-free, circular economy is required to decrease greenhouse gas emissions. A commonly named alternative to the carbon-based economy is the hydrogen economy. However, storing and transporting hydrogen is difficult. Therefore, the ammonia economy is proposed. Ammonia (NH3) is a carbon-free hydrogen carrier, which can mediate the hydrogen economy. Especially for long-term storage (above 1 day), ammonia is more economically stored than hydrogen. Transportation costs are greatly reduced by adopting a decentralized energy economy. Furthermore, political-economic factors influence energy prices less in a decentralized energy economy. With small-scale ammonia production gaining momentum, business models for the decentralized ammonia economy are…
Presentation
Cost Evaluation Study on CO2-Free Ammonia and Coal Co-Fired Power Generation Integrated with Cost of CCS
This study presents a cost estimation for electricity generated by CO2-free ammonia and coal co-firing. Regulation of CO2 emissions seems to be gaining pace due to the global warming issue so the introduction of CO2-free energy in power generation has become desirable. Ammonia is one of the potential energy carriers for power generation and development of ammonia combustion technology with low NOx emissions has been conducted in Japan. In order to investigate the feasibility of the introduction of CO2-free ammonia in Japan from both the technical and economic viewpoints, we estimated the ammonia supply chain cost from ammonia production integrated…
Presentation
Ammonia-Hydrogen Power for Combustion Engines
Ammonia blends can potentially become a breakthrough chemical for power generation, cooling storage and distribution of energy. Gas turbines and internal combustion engines are potential candidates for the use of the resource in an efficient way that will enable commissioning of combined cycles to power communities around Europe and around the world while serving as sources of heat and chemical storage. Therefore, development of these systems will bring to the market a safer, zero carbon fuel that can be used for multiple purposes, thus decentralizing power generation and increasing sustainability in the communities of the future whilst positioning the developing…
Presentation
Ship Operation Using LPG and Ammonia As Fuel on MAN B&W Dual Fuel ME-LGIP Engines
LPG has been used as fuel in the car industry for many years and now, with Exmar and Statoil’s orders for ocean-going ships fitted with the dual fuel ME-LGIP engine, LPG will be used on marine engines as well. The new engine series is currently being developed to match all types of bigger merchant ships. This order was made in consequence of the new 2020 0.5% sulphur fuel cap, but this step forward has not stopped the discussion and interest in lowering CO2, NOx, SOx and particulate emissions even further. On the contrary, it has actually been further fuelled by…
Presentation
Roadmap to All Electric Ammonia Plants
Haldor Topsøe A/S is a world leading supplier of technology and catalyst for the ammonia industry. It is also a developer of Solid Oxide Electrolyzer technology. A road map towards all electrical ammonia plants of the future has been worked out implementing at first steps hybrid natural gas based/classical electrolyzer technology and ultimately SOEC based plants without air separation units.
“Ammonia Fuel and Energy Storage: Cracking & Fuel Cells”: Chaired by Amgad Elgowainy, Argonne National Laboratory
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 9:45 am 11:15 am
Presentation
Ammonia As a Hydrogen Carrier for PEM Fuel Cells
Ammonia (NH3) is easily liquefied by compression at 1 MPa and 25°C, and has highest volumetric hydrogen density of 10.7 kg H2 /100L. It has high gravimetric hydrogen density of 17.8 wt%. The heat of formation of NH3 is about 1/10 of combustion heat of hydrogen. NH3 has advantages as a hydrogen carrier for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). ISO 14687-2:2012 specifies the quality characteristics of hydrogen fuel. The maximum concentration of NH3 and N2 for the FCVs is 0.1ppm and 100 ppm, respectively. The minimum H2 purity is 99.97%. We need component technologies to produce high-purity hydrogen from ammonia, together…
Presentation
Catalytic Membrane Reactors for Efficient Delivery of High Purity Hydrogen from Ammonia Decomposition
The deployment of fuel cell electric vehicles is constrained by the paucity of hydrogen fueling stations and price, which is dominated by the costs of hydrogen storage and transportation. With more hydrogen per volume than liquid H2 and an extensive distribution infrastructure in place, ammonia is a promising vector for efficient hydrogen distribution. In this talk we describe the development of innovative catalytic membrane reactor (CMR) technology for the delivery of high purity H2 from ammonia cracking. The CMR integrates state-of-the art catalysts with thin metal membranes in an innovative design. Conventionally, the catalyst is supplied to CMRs in the…
Presentation
Development of a Highly Efficient COx-Free Ammonia Dehydrogenation System for Fuel Cell Applications
The shortage of fossil fuels and emission of carbon dioxide to the environment have attracted an interest in discovering renewable energy as the next generation energy source. Owing to its intermittent and unpredictable nature, however, excess renewable energy needs to be stored and reused on demand. In the regard, hydrogen, which possesses a high gravimetric energy density and carbon free combustion process, has been extensively researched as a promising renewable energy carrier. However, the distribution and storage of hydrogen still raise important challenges due to the low volumetric energy density of hydrogen for its wide utilization. Currently, gaseous hydrogen transportation…
Presentation
Material Discovery and High Throughput Exploration of Ru Based Catalysts for Low Temperature Ammonia Decomposition
High throughput experimentation gives us the unique ability to generate massive, multidimensional datasets that are not typical for heterogeneous catalysis studies. Here, we show the synthesis and catalytic screening of over 100 different Ru based bimetallic catalyst combinations using 33 different metals that were synthesized via incipient wetness impregnation. The catalysts were analyzed using Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (WAXS) for phase identification. Catalysts were screened for ammonia decomposition activity using a 16-channel parallel plug flow reactor. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) imaging was used to analyze all 16 effluent streams in parallel in under one minute. All results obtained from WAXS…
Presentation
Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous Silica Composites As Potential Ammonia Storage Materials
Ammonia may provide an alternative energy supplier for its strong capability as hydrogen carrier. However, it is a problem that how to storage this kind of chemical at relatively high temperature, for example 300°C in fuel cell. In this work, a composite material based on metal halides and ordered mesoporous silica framework is developed and used to target ammonia at relatively high temperature. The silica framework is fabricated via evaporation induced self-assembly method and has tunable mesoporous structure with addition of hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB). Several metal salts at various concentrations are added to the mesoporous framework via wetness…
Presentation
Development of Catalytic Reactors and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Systems for Utilization of Ammonia
Koichi EguchiYosuke TakahashiTakahiro MatsuoHayahide YamasakiHidehito KuboAkihiro OkabeTakenori Isomura
Hydrogen is the primary fuel source for fuel cells. However, the low volume density and difficulty in storage and transportation are major obstacles for the practical utilization. Among various hydrogen carriers, ammonia is one of the promising candidates because of its high hydrogen density and boiling point and ease in liquefaction and transportation. The reaction temperature of ammonia cracking to nitrogen and hydrogen, being about 600°C or higher, is close to the operating temperature of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). The integration of these two devices is beneficial in terms of heat and energy managements and will lead to the…
“Sustainable Ammonia Synthesis: Better & Beyond Haber-Bosch”: Chaired by Maxim Lyubovsky, US Department of Energy, Fuel Cell Technologies Office
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 9:45 am 11:15 am
Presentation
Importance of Reaction Mechanism Involved in Design of the Catalyst and the Reactor for Future Ammonia Synthesis
The ammonia synthesis reaction is considered to involve several elementary steps [1]: N2 + 2* → 2N(a) (1) H2 + 2* → 2H(a) (2) N(a) + H(a) → NH(a) + * (3) NH(a) + H(a) → NH2 (a) + * (4) NH2 (a) + H(a) → NH3(a) + * (5) NH3(a) → NH3 + * (6) Here, the symbol * indicates empty sites. For most metal catalysts, the dissociative adsorption of dinitrogen (step 1) is the rate-determining step, and all the other steps and its reverse step (from 2 to 6) are fast enough to be almost in equilibrium for…
Presentation
Ammonia Absorption and Desorption in Ammines
While adsorption onto solids is a common separation process, absorption into solids is much less often used. The reason is that absorption is usually assumed ineffective because it includes very slow solute diffusion into the solid. An exception may be the separation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen using ammines, especially at temperatures close to those used in ammonia synthesis. There, ammonia can be selectively absorbed by calcium chloride; nitrogen and hydrogen are not absorbed. The kinetics of ammonia release seem to be diffusion controlled. The kinetics of absorption are consistent with a first order reaction and diffusion in series,…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Better Haber-Bosch”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 10:15 am 10:45 am
Presentation
Scale up and Scale Down Issues of Renewable Ammonia Plants: Towards Modular Design
Renewable sources of energy such as biomass, solar, wind or geothermal just to mention some of the most widely extended are characterized by a highly distributed production across regions (EPA, 2017). Total renewable energy available is more than enough to provide for society needs, but the traditional production paradigm is changing. Economies of scale have featured current industry and its infrastructures based on large production complexes (i.e Dow, Exxonmobil or BASF hubs). The well-known six tenths rule has extensively been used in the chemical industry to scale up or down the cost of technologies. This rule is suitable for large…
Presentation
Advances in Making High Purity Nitrogen for Small Scale Ammonia Generation
The presentation will address recent developments in the Solar Hydrogen Demonstration Project in which hydrogen, nitrogen and ammonia are made from solar power, water, and air; and used to fuel a modified John Deere farm tractor. In industrial applications very pure nitrogen is made by cryogenic distillation of air. Using Pressure Swing Absorption systems alone it is extremely difficult to achieve the required purity. An improved method was developed for making high purity nitrogen, for smaller systems. Will discuss how, when Oxygen contaminates the reactor catalyst, Hydrogen is used to purge the catalyst, and subsequently used as fuel.
Presentation
Vanadium As a Potential Catalytic Membrane Reactor Material for NH3 Production
In solid or liquid states, ammonia salts and solutions are the active components of most synthetic fertilizers used in agriculture, which consume 83% of the world’s ammonia. Today, ammonia for fertilizers is industrially produced via the Haber-Bosch process at 400-500 °C and at pressures up to 30 MPa (300 bar). These harsh operating conditions are necessary due to the high affinity of dissociated nitrogen atoms towards the catalyst surface in addition to the high barrier associated with N2 dissociation. For these reasons, the need for advanced catalytic methods for the reduction of N2 to ammonia remains a requirement for sustainability…
Presentation
Advanced Catalysts Development for Small, Distributed, Clean Haber-Bosch Reactors
The traditional Haber-Bosch (HB) synthesis of anhydrous ammonia will adapt to clean power by sourcing the hydrogen from renewable electrolysis. However, the very large scale of current HB plant designs are not well-matched to smaller and more distributed clean power resources. Plant/reactor designs need to be made at a smaller scale in order to best utilize clean hydrogen. Small, megawatt scale HB reactors have an additional advantage of being better able ramp up and down with variable renewable power. This talk will detail ARPA-e funded work into the design and optimization of these smaller, clean NH3 reactors, which utilize much…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Beyond Haber-Bosch”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 10:45 am 11:15 am
Presentation
Ammonia Synthesis Via Radiofrequency Plasma Catalysis
Introduction: In 1909, a compound named Ammonia was discovered. Through the 20th century, the immense potential of this chemical was exploited by using in almost every product, from process industry for fertilizer and chemical production to every use in cosmetics, household cleaners and medicines. Recently, fuel cells operating on liquid ammonia as working fluid have been developed on research scale. Despite of using 1-2% of total energy production for the synthesis of this compound, no significant changes have been made to the process since the first Haber-Bosch process plant has been setup. Plasma catalysis is the use of plasma and…
Presentation
Terrestrial Energy, National Lab, Southern Company – Partnership Overview Using Integral Molten Salt Reactor Technology with HyS Acid for Hydrogen Production
Demands for safe secure supplies of potable water across the planet are increasing faster than can be provided by natural, ever depleting sources of fresh water. At the same time, world demand for electric power is also accelerating. Making H2 from Natural Gas is not an optimal or efficient process that is also un-economic at higher gas costs. An Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) is uniquely suited to provide the very high temperatures (585 °C+ working temps.) that are needed to both generate significant amounts of Hydrogen, Oxygen (a feed for industrial oxygen uses) and Electricity needed for advanced economies…
Presentation
Creating a Redox Materials Database for Solar-Thermochemical Air Separation and Fuels Production
Josua VietenDorottya GubanMartin RoebChristian SattlerPatrick HuckMatthew HortonKristin PerssonBrendan Bulfin
Converting heat from renewable sources into other forms of energy is considered an essential factor in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, high temperatures can be reached using concentrated solar power (CSP), and the thus-captured energy can be converted into so-called solar fuels via thermochemical processes. These consist of the partial reduction of a redox material, usually a metal oxide, at high temperatures following the exothermic re-oxidation of this material at a lower temperature level using steam or CO2, which are thus converted into hydrogen or carbon monoxide, respectively. These two gases can be combined to generate syngas…
Presentation
Microwave Catalysis for Ammonia Synthesis Under Mild Reaction Conditions
Jianli HuHanjing TianYan LuoXinwei BaiDushyant ShekhawatChristina WildfireVictor AbdelsayedMichael J. SpencerRobert A. DagleStephen DavidsonAlbert E. Stiegman
A scalable, cost-effective catalytic process of ammonia synthesis is developed by using microwave excitation under mild reaction conditions. In this research project funded by DOE ARPA-E, our interdisciplinary team of WVU, NETL, PNNL, FSU and two industrial partners have demonstrated that ammonia synthesis can be carried out at 200-300 °C and ambient pressure. This transformational process integrates system elements of electromagnetic sensitive catalysts and microwave reactor design. Taking advantages of state-of-the art non-equilibrium microwave plasma technology, catalytic ammonia synthesis undergoes a new reaction pathway where the barrier for the initial dissociation of the dinitrogen is decoupled from the bonding energy…
“Ammonia Combustion: Turbines, Furnaces, Engines”: Chaired by Eric Miller, US Department of Energy, Fuel Cell Technologies Office
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 1:15 pm 3:15 pm
Presentation
Basic Co-Firing Characteristics of Ammonia with Pulverized Coal in a Single Burner Test Furnace
Ammonia is expected as a potential fuel to substitute fossil fuels, because it does not discharge carbon dioxide and is easily handled by liquefaction. There are several ways for the direct use of ammonia as a fuel; for example, use in fuel cells and combustion devices. One of the possible application is the combustion use in thermal power plants. In particular, co-firing of ammonia in coal-fired power plants seems to have a relatively great advantage on the suppression of greenhouse gases, because coal is one of the main emission source of carbon dioxide. On the other hand, it is concerned…
Presentation
Development of Low-NOx Combustor of Micro Gas Turbine Firing Ammonia Gas
Osamu KurataNorihiko IkiTakahiro InoueTakayuki MatsunumaTaku TsujimuraHirohide FurutaniMasato KawanoKeisuke AraiEkenechukwu Chijioke OkaforAkihiro HayakawaHideaki Kobayashi
A massive influx of renewable energy is required in order to mitigate global warming. Although hydrogen is a renewable media, its storage and transportation in large quantity is difficult. Ammonia, however, is a hydrogen energy carrier, and its storage and transportation technology is already established. Although ammonia fuel combustion was studied in the 1960s in the USA, the development of an ammonia fuel gas turbine had been abandoned because combustion efficiency was unacceptably low [1]. Recent demand for hydrogen energy carrier revives the usage of ammonia fuel. The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) in Japan, in…
Presentation
Two Stage Ammonia Combustion in a Gas Turbine like Combustor for Simultaneous NO and Unburnt Ammonia Reductions
Ammonia is expected not only as a hydrogen energy carrier but also as a carbon free fuel. Recently, ammonia fueled gas turbine combustor was successfully demonstrated. However, large amount of NOx was produced when ammonia burns because ammonia includes nitrogen atom in the ammonia molecule. In addition, unburnt ammonia concentration in exhaust gas also needs to be reduced. In this study, we proposed a combustion concept in order to reduce NO and unburnt ammonia concentrations in the exhaust gas simultaneously in a gas turbine like model swirl combustor. In this concept, two stage (rich – lean) combustion was employed. Two…
Presentation
Auto-Ignition Kinetics of Ammonia at Intermediate Temperatures and High Pressures
The anxiety over global greenhouse gas emissions has intensified the demand for the development and use of CO2-neutral energy technologies. Ammonia is now attracting attention as a carbon-free energy carrier, because it has good energy density (22.5 MJ/kg) and can be easily liquefied (about 10 bar at 298 K). In addition, ammonia is produced according to the Haber-Bosch process, which makes it one of the most widely-produced inorganic chemical in the world. It could also be produced with renewable energy sources such as wind and solar energy using P2X technology. As a potential fuel for applications in gas turbines and…
Presentation
Experimental and Computational Study for Reduction of NOx Emissions in the Ammonia / Methane Co-Combustion in a 10 KW Furnace
Ryuichi MuraiRyohei OmoriTakahiro KitanoHidetaka HigashinoNoriaki NakatsukaFumiteru AkamatsuYuya YoshizuruJun Hayashi
There are severe issues on increasing amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in the world. Many studies are devoted to alternative fuels. One of promising candidates is the utilization of ammonia which is zero emission of CO2, a hydrogen energy carrier, and also can be burned directly as a fuel. For direct combustion of ammonia in industrial furnaces, there were two issues which were weaker radiative heat flux and a huge amount of NOx emission compared with the combustion of methane. We already have reported [1] the solution of the former issue by using the oxygen enriched combustion. The objective…
Presentation
Exploring ammonia's potential as a marine fuel
International shipping is responsible for approximately 90% of the world trade. Looking to the relative emissions, in gram CO2 per ton km, maritime transport score significantly better compared to others like rail, road and airfreight. However, since most of the transport is done by ships the absolute contribution of greenhouse gases (GHG) by the maritime industry is clearly visible. Of all the global emissions the maritime industry is responsible for 3% CO2, 13% SOx, and 15% NOx. To reduce SOx and NOx several regulations are either upcoming or already in play. Current regulations require the sulphur emissions to be less…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Ammonia Combustion”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 2:00 pm 3:00 pm
Presentation
Simulation Analysis of NH3 Mixed Combustion in Clinker Manufacturing Process
Tatsurou IzumiHiroki KujiraokaYuya YoshizuruTakeshi SuemasuMakoto UedaToyoaki NikiTakayasu ItouMasayuki NishioRyuichi MuraiFumiteru Akamatsu
Recent years, the action for the low-carbon society becomes active all over the world. NH3 has potential to become the free-carbon energy source. In SIP project, that Cabinet Office started, we work on the technology development applying NH3 to the field of industrial furnace (SIP: Strategic Innovation Promotion Program). In this study, we evaluated the effect of NH3 use in the cement clinker manufacturing process. Cement manufacturing is one of the fields of industry to exhaust large amounts of CO2. As past works, we studied for the reduction of heat consumption rate, troubleshooting and so on by using kiln operation…
Presentation
Optimization of the NOx Reduction Condition in the Combustion Furnace for the Combustion of "Heavy-Oil - NH3 System" Using CFD
In late years the discharge of the CO2 became the very big problem. The combustion of the fossil fuel in particular exhausts much CO2. Our project team (SIP) is intended to reduce CO2 by using NH3 (10%~30%) in substitution for heavy oil. The ‘SIP energy carriers’ was launched in 2014 (SIP: Strategic Innovation Promotion Program). Ammonia direct combustion team was formed. We conducted a co-research program with Osaka University in this project. We performed experiment of heavy oil – NH3 mixed combustion in the 10kW furnace. As the results, we obtained much experimental data. When we were combusted NH3 and…
Presentation
Ignition of an Aqueous Ammonia / Ammonium Nitrate Fuel
To achieve a truly renewable energy market, the intermittent power generation of sources such as solar and wind must be overcome. Renewable ammonia can be synthesized using these sources to be used as a long-term energy storage medium. For this reason, the use of ammonia as a synthetic fuel has garnered significant attention in recent years. Aqueous AAN (ammonia/ammonium nitrate) is a carbon-free ammonia based monofuel suitable for energy storage applications. This fuel is safe to store and transport, and its combustion products consist mainly of water and nitrogen. Effective use of this fuel requires an in-depth understanding of the…
Presentation
Improved Method of Using Hydrogen and Ammonia Fuels for an Internal Combustion Engine
A tractor mounted internal combustion engine is fueled by Hydrogen or a combination of Hydrogen and Ammonia. Developments of an improved method of fuel injection and ignition control. Hydrogen is port injected in the intake manifold, and liquid ammonia is injected in the throttle body. A dual fuel ECU, Engine Control Unit, controls the fuel mixtures and the firing of multiple coils for ignition. The paper will address significant engine performance improvements and the resulting fuel consumption and engine emissions levels.
“Sustainable Ammonia Synthesis: Electrochemical Production”: Chaired by Mark Ruth, National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 1:15 pm 3:15 pm
Presentation
A Low Pressure Membrane Based Renewable Ammonia Synthesis
Ammonia is currently mostly produced by the highly energy and carbon-intensive Haber–Bosch process, which requires temperatures of 450–500 °C and pressures of up to 200 bar. The feedstock for this process is hydrogen from natural gas (NG), coal or oil, and nitrogen produced from air by cryogenic route or pressure swing adsorption (PSA). The share of NG, coal and fuel oil feedstock for the global production of ammonia is 72%, 22% and 4% respectively, contributing to approximately 420 million tons of CO2 emissions per annum, representing over 1% of global energy related emissions. The energy consumed for ammonia synthesis by…
Presentation
Analysis of influence of operating pressure on dynamic behavior of ammonia production over ruthenium catalyst under high pressure condition
Process technologies on energy conversion of renewable electricity into hydrogen energy carrier are significant to deploy long-term storage and long-distance transport of much more renewable inside and outside Japan. Ammonia is a potential hydrogen carrier that contains 17.6 wt% of hydrogen. Moreover, as an energy carrier, ammonia is thought to be a clean fuel as only water and nitrogen are produced on direct combustion. Many researchers and engineers consider that ammonia plants using hydrogen produced by solar electricity or wind electricity will be much smaller than those currently used [1]. There is an issue of low pressure condition for feed…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Electrochemical I”
Sunday, October 31, 2021 1:30 pm 2:00 pm
Presentation
Identifying the Prospects of Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis on Mxenes Using First Principles Calculations
Electrochemical synthesis of ammonia is a major challenge aimed at making production of ammonia sustainable. Currently ruthenium is the transition metal of choice for catalyzing the industrial Haber-Bosch process. However, electrochemical ammonia synthesis on ruthenium suffers from high overpotential and the competing hydrogen evolution reaction. Recently layered transition metals carbides and nitrides (MXenes) have been identified as a potential material class for ammonia synthesis. MXenes are particularly interesting owing to the high degree of tunability in surface chemistry due to the transition metal choice, interlayer distance, number of layers in the material, and surface termination. These choices affect the electron…
Presentation
Highly-Selective Electrochemical Reduction of Dinitrogen to Ammonia at Ambient Temperature and Pressure
Catalytic conversion of dinitrogen (N2) into ammonia under ambient conditions represents one of the Holy Grails in catalysis and surface science. As a potential alternative to the Haber-Bosch process, electrochemical reduction of N2 to NH3 is attractive owing to its renewability and flexibility, as well as sustainability for producing and storing value-added chemicals from the abundant feedstock of water and nitrogen on earth. However, owing to the kinetically complex and energetically challenging N2 reduction reaction (NRR) process, NRR electrocatalysts with high catalytic activity and high selectivity are rare. In this contribution, as a proof-of-concept, we demonstrate that both the NH3…
Presentation
Electrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia Using Metal Nitride Catalsyts
With the development of the Haber process and the subsequent work done by Bosch, ammonia production become an industrially and economically viable way to fix nitrogen. This helped increase the global population and estimates put it at about 40% of the global population’s food comes from ammonia made by the Haber-Bosch process[1]. However, the Haber-Bosch process is an energy intensive process requiring high pressure (15-30 MPa) and relatively high temperature (430 °C – 480 °C) and is highly centralized with only about 13 companies and about 29 plants[2,3]. Renewable energy resources offer a possible alternative way to fix nitrogen at…
Presentation
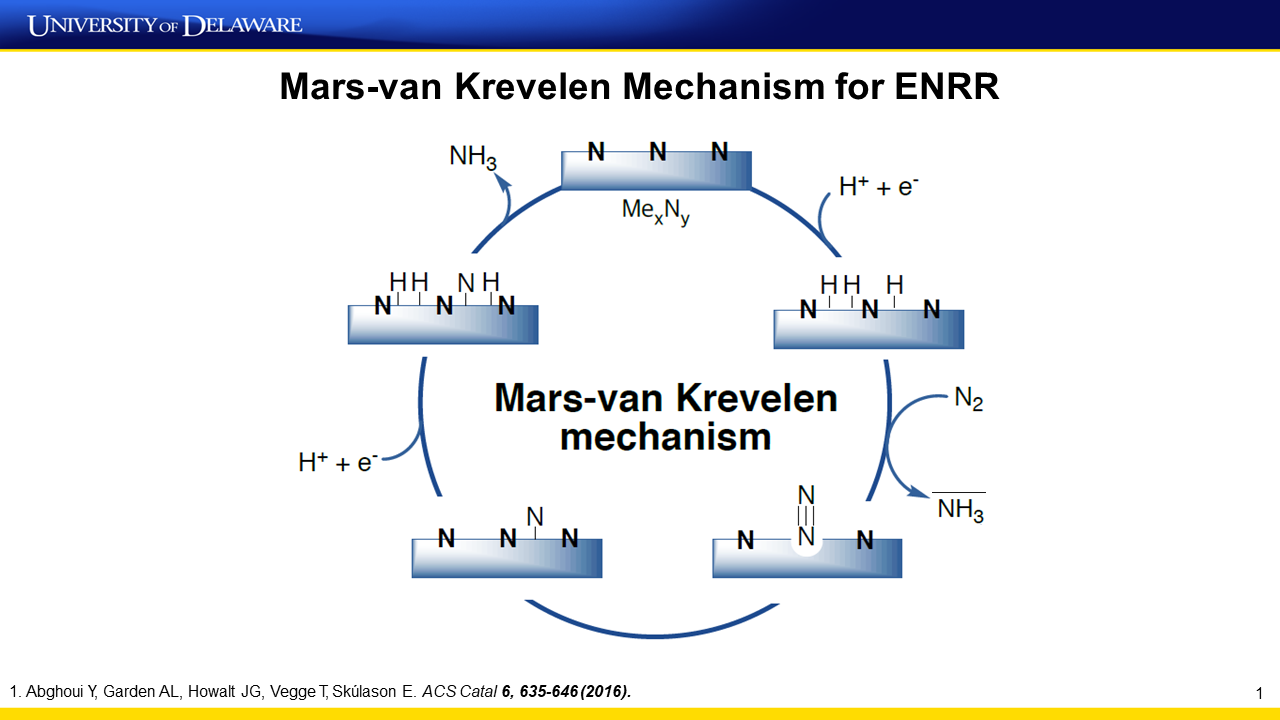
Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Reaction on Transition Metal Nitride Nanoparticles in Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers
Transition metal nitride nanoparticles are synthesized and utilized as catalysts for electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (ENRR) to produce ammonia in a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer (PEMEL). The catalysts show an average ENRR rate and Faradaic efficiency (FE) of 3.3 × 10−10 mol s−1 cm−2 (6.6 × 10−10 mol s−1 mg−1) and 5.95% at −0.1 V within 1 h, respectively. Both the ENRR rate and FE are approximately two orders of magnitude higher than those of noble metal catalysts. Time-dependent results suggest that the catalytic activity of transition metal nitride nanoparticles is stable at −0.1 V, with the catalytic activity decreasing…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Electrochemical II”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 2:00 pm 2:30 pm
Presentation
DFT Analysis of Elementary N2 Electro-Reduction Kinetics on Transition Metal Surfaces
Ammonia is currently produced through the catalytic Haber Bosch process (HB) at temperatures of about 300 to 500 °C and pressure of about 200-300 atm. In a future with plentiful renewable electricity from distributed sources, an electro-chemical system to produce ammonia could efficiently generate ammonia on site and on demand. Possible heterogeneous catalysts for electro-chemical nitrogen reduction are currently marred by the poor rate and selectivity due to difficulty in activating the strong N-N bond and to the competing hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), resulting in infeasible faradaic efficiency. To develop more selective and active catalysts, better understanding of the mechanistic…
Presentation
Enhanced Electrochemical Ammonia Production Via Peptide-Bound Metal
Approximately half of the people on the planet are alive because of synthetically produced ammonia. However, due to the fossil fuels used in the current ammonia synthesis process, its production contributes a significant amount to the world’s greenhouse gas emissions. Haber-Bosch synthesis, which is the most widely used method of producing synthetic ammonia today, requires high temperatures (400-500 °C) and pressures (150-200 atm). This process is also energy intensive, consuming approximately 2% of worldwide energy. By taking an electrochemically-based approach to ammonia synthesis, those harsh conditions and emissions can be eliminated. However, current catalysts are not selective for the desired…
Presentation
New Insights into Electrocatalysis of Nitrogen Reduction to Ammonia
Ammonia was electrochemically produced from nitrogen and water using a ruthenium–platinum (RuPt) alloy catalyst cathode and a nickel anode at ambient pressure and room temperature. The rate of ammonia formation was 5.1 × 10−9 gNH3 s−1 cm−2 with a 13.2% faradaic efficiency at an applied potential of 0.123 V vs. RHE; it reached 1.08 × 10−8 gNH3 s−1 cm−2 at 0.023 V. Ammonia production was investigated under selected potentials and temperatures. Real-time direct electrochemical mass spectrometric (DEMS) analysis of the evolved gases was performed at various applied potentials. In general, the mass-to-charge ratio signals of hydrogen and ammonia were detected,…
Presentation
Electrochemical Reduction of Nitrogen to Ammonia over Transition Metals
The ability to produce ammonia in a sustainable and efficient manner has been a topic of scientific and industrial importance for many years. The Haber-Bosch process has acted as the primary process for transforming nitrogen and hydrogen gas into ammonia. This process has become unsustainable in the foreseeable future and requires a cost-effective alternative. Ammonia is a critical component of fertilizer that is vital to the agriculture industry. The electrochemical reduction of N2 to ammonia would eliminate carbon dioxide emissions that are present in current ammonia production processes and allow for a environmentally favorable process. Although the electrochemical reduction of…
Sub-session - Rapid-fire presentations: “Electrochemical III”
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 2:30 pm 3:00 pm
Presentation
A Study on Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis with Proton-Conducting Solid Oxide Electrolytic Cells
Ammonia has become one of the most important chemicals with its versatility since the Haber-Bosch process was invented. Recently, ammonia has been getting interests because of its possibility as a hydrogen carrier. Since ammonia has high energy density and carbon-free characteristics, using ammonia as a fuel of solid oxide fuel cells is advantageous. However, the Haber-Bosch process spends much electricity because of the high pressure condition, and the process consumes more than 1% of energy consumption worldwide. Therefore, the development of a new method for the ammonia production is necessary. In this study, solid oxide based electrolytic cells were fabricated…
Presentation
Low-Pressure Electrolytic Ammonia Synthesis Via High-Temperature Polymer-Based Proton Exchange Membrane
The University of North Dakota Energy and Environmental Research Center (EERC) and North Dakota State University (NDSU) have developed a low-pressure electrolytic ammonia (LPEA) production process. The LPEA process uses an electrochemical cell based on an innovative polymer–inorganic composite (PIC) high-temperature (300°C) gas-impermeable proton-exchange membrane conceptualized and partially developed by EERC and NDSU. Because of its operability at ambient pressure and quick start-up capability (versus traditional high-pressure Haber Bosch-based plants), the LPEA process offers compatibility with smaller-scale plants and intermittent operation, and a cost-effective means of monetizing (and storing) renewable energy as ammonia. EERC, NDSU, and Proton OnSite are embarking…
Presentation
Atmonia: Sustainable Ammonia Production Using Electrocatalysis at Ambient Temperature and Pressure
Helga Dogg FlosadottirArnar SveinbjörnssonEgill SkúlasonFatemeh HanifpourFriðrik MagnusYounes AbghouiJian Yang
Density functional theory simulations have shed light on reaction mechanisms, rate limiting steps and minimum energy paths for reactions to occur, in vacuum as well as in various media. Using that, we have selected certain criteria and revealed a few metal nitride surfaces that should be efficient and selective catalysts for nitrogen reduction in water. Recently, experimental confirmation was acquired for one of the surfaces. A novel methodology was developed where electrochemical catalysis chamber was directly connected in-line with a flow injection analysis method, providing direct detection of reaction rate and catalyst current efficiency, which is then further confirmed with…
Presentation
Electrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia Using Nitrogen and Water in Alkaline Electrolytes Under Ambient Conditions
Sustainable synthesis of Ammonia (NH3) is gaining great attention not only for its use as an alternative renewable energy fuel but also to substitute production of distributed fertilizers through the conventional Haber Bosch process. The conventional Haber-Bosch process to produce NH3 uses fossil fuels in deriving hydrogen from steam reforming of natural gas, is energy intensive and also leads to significant CO2 emission. Alternatively, electrochemical synthesis of ammonia (ESA) through the nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) in alkaline medium saves the use of hydrogen as a reactant as the aqueous electrolyte forms the source of proton. However, the standard reduction potential…
“Ammonia Energy Global Demonstrations": Chaired by Madhav Acharya, US Department of Energy, ARPA-E
Wednesday, October 31, 2018 3:30 pm 5:30 pm
Presentation
Test Results of the Ammonia Mixed Combustion at Mizushima Power Station Unit No.2 and Related Patent Applications
At the Mizushima Power Station Unit No.2 (Coal-fired, Location: Kurashiki, Okayama Prefecture, rated output: 156,000 kW), the Chugoku Electric Power Company conducted the ammonia mixed-combustion test from July 3 to 9, 2017, in order to reduce the environmental burden of coal-fired power stations. We compile the test results and report it to Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), and we are pleased to inform you today that we applied for patents on the findings obtained in this examination. This test is part of the “ammonia direct burning” as a commissioned research topic on “energy carriers” out of the “Strategic Innovation…
Presentation
Performance of Ammonia-Natural Gas Co-Fired Gas Turbine for Power Generation
Ammonia is paid special attention as renewable energy carrier [1-3], because it offers advantages in generation, transportation and utilization. Haber-Bosch method is already established as ammonia generation method; large amount of ammonia is already used as fertilizer and chemical raw material. Ammonia can be liquefied at room temperature. Its transport and storage system are already established. Ammonia is cheaper to transport than hydrogen. Ammonia can be used as carbon-free fuel in internal combustion engines as alternative to conventional hydrocarbon fuels. However, it has different combustion characteristics. For example, the nitrogen atom contained in the ammonia molecule, causes high NOx emission…
Presentation
Rapid Ramp NH3 Prototype Reactor Update
Starfire Energy has built and operated a low pressure, fast-ramping prototype reactor using its Rapid Ramp NH3 process. It has synthesized, captured, and liquefied NH3 with all system pressures staying below 12.5 bar. The prototype reactor’s performance will be discussed.
Presentation
Demonstration of CO2-Free Ammonia Synthesis Using Renewable Energy-Generated Hydrogen
In Japan, the government funding project SIP, Strategic Innovation Promotion Program, supports the research, development and demonstration of “Energy Carriers”. The concept of the “Energy Carriers” value chain is to produce hydrogen energy carriers overseas from fossil resources using CCS or renewable energy, and transport it to Japan for utilization as clean energy. The purpose of the program is to help realize a low-carbon society in Japan by using hydrogen. Among energy carriers, ammonia is the one of the most promising carriers, because of the ease of transportation as a liquid, higher hydrogen density, and proven technologies for commercial and…
Presentation
Realisation of Large-Scale Green Ammonia Plants
The global ammonia production is nowadays mostly based on fossil energy carriers (natural gas, coal, naphtha, etc.). It consumes approximately 1.4% fossil energy carriers and releases more than 1.4% of global CO2 emissions. In order to continue the global transition from the fossil fuel and nuclear energy age to the renewable energy age, ammonia could play a key role. Beside the continued utilization for fertilizer industry, ammonia could become an energy and/or hydrogen carrier as well. thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions (tkIS) developed a concept to establish Green Ammonia Plants as an alternative to conventional world-scale ammonia plants. As industry leader in…
Presentation
Design Optimization of an Ammonia-Based Distributed Sustainable Agricultural Energy System
Small-scale, distributed production of ammonia better enables the use of renewable energy for its synthesis than the current paradigm of large-scale, centralized production. Pursuant to this idea, a small-scale Haber-Bosch process has been installed at the West Central Research and Outreach Center (WCROC) in Morris, MN [1] and there is ongoing work on an absorbent-enhanced process at the University of Minnesota [2], [3]. Using renewables to make ammonia would greatly improve the sustainability of fertilizer production, which currently accounts for 1% of total global energy consumption [4]. The promise of renewable-powered, distributed ammonia production for sustainability is in fact not…
Presentation
Evaluation of the Cement Clinker Fired in the Combustion Furnace of Heavy-Oil and NH3
Hiroki KujiraokaTatsurou IzumiYuya YoshizuruTakeshi SuemasuMakoto UedaToyoaki NikiTakayasu ItouRyuichi MuraiFumiteru Akamatsu
In recent years, global warming caused by an increase in CO2 emission released by combustion of fossil fuel has become a big problem. To realize a low-carbon society, active use of renewable energy and promotion of hydrogen energy are necessary. We are participating in “SIP (Strategic Innovation Promotion Program) energy carriers”, developing technology to replace 30% fossil fuel with ammonia (NH3) on the calorie basis. Assuming that NH3 is used as a thermal energy for a cement kiln, we conducted the following two basic experiments. First, we fired the clinker in the atmosphere-controlled electric furnace, calculated the reaction rate of…
Presentation
Ammonia-to-Hydrogen System for FCEV Refuelling
Ammonia can play a significant role in fuelling the world’s growing fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) fleet through technologies which allow the decomposition of NH3, and subsequent extraction and purification of H2. CSIRO has recently demonstrated a pilot-scale ammonia-to-hydrogen system, incorporating an ammonia decomposition stage with a subsequent membrane-based hydrogen purification stage, at a rate of several kilograms of H2 per day. Through partnerships with an industrial gas producer and two FCEV manufacturers, the resulting H2 has been compressed and dispensed into FCEVs. System design, materials, performance and strategies for scale-up and demonstration will be discussed.
NH3 Energy Implementation Conference
Thursday, November 1, 2018 8:00 am 5:30 pm
Presentation
Development of Technologies to Utilize Green Ammonia in Energy Market
KEYNOTE ADDRESSS Shigeru Muraki, Director of the Energy Carriers office within Japan’s Strategic Innovation Promotion (SIP) Program and Chairman of the Green Ammonia Consortium
Presentation
Ammonia: Opportunities for Grid Support
Ammonia: Opportunities for Grid Support Mark Ruth, US Department of Energy, NREL.
Presentation
Technologies to use carbon free ammonia in power plant
Technologies to use carbon free ammonia in power plant Toshiyuki Suda, IHI Corporation.
Presentation
Ammonia as an energy sector fuel
Ammonia as an energy sector fuel Jonathan Lewis, Clean Air Task Force
Presentation
Ammonia in electricity generation
Ammonia in electricity generation Shaun Mann, Tri-State Generation and Transmission
Presentation
Ammonia as a Carrier of Hydrogen Fuel
Ammonia as a Carrier of Hydrogen Fuel Bill David, University of Oxford
Presentation
Electrolysis for Renewable Ammonia: How do we get to a relevant scale?
Electrolysis for Renewable Ammonia: How do we get to a relevant scale? Steve Szymanski, Nel Hydrogen
Presentation
Ammonia as a Marine Fuel
Ammonia as a Direct Fuel: fueling the decarbonized maritime industry Moderator: Agustin Valera-Medina, Cardiff University Niels de Vries, C-Job Naval Architects René Sejer Laursen, MAN ES Emile Herben, Yara
Presentation
Moving from Brown to Green Ammonia
Moving from Brown to Green Ammonia Rob Stockwell, Casale
Presentation
International Cooperation for Implementation of Green Ammonia
International Cooperation for Implementation of Green Ammonia Yasushi Fujimura, JGC Corporation
Presentation
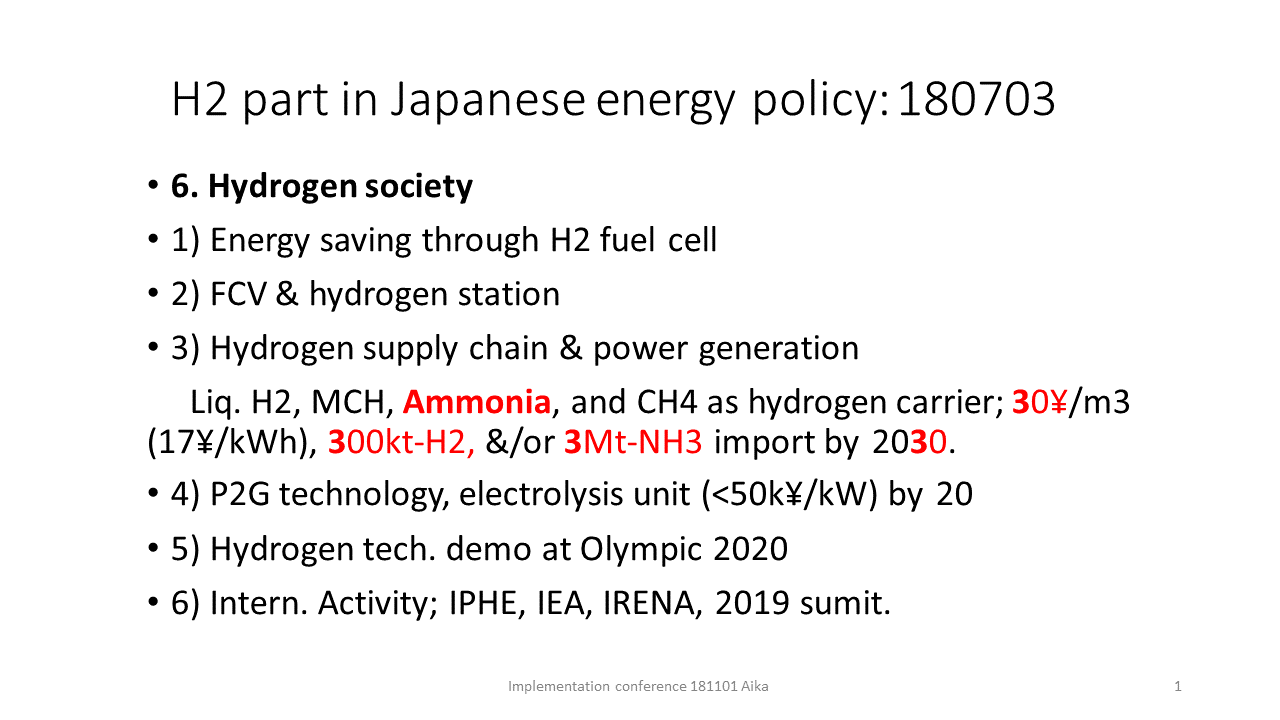
How is the “green” evaluated for NH3?
How is the “green” evaluated for NH3? Ken-ichi Aika, Tokyo Institute of Technology